Understanding SECL's Paste Fill Technology Implementation at Singhali Coal Mine
South Eastern Coalfields Limited (SECL), a subsidiary of Coal India, is pioneering sustainable mining practices in India through the implementation of paste fill technology at the Singhali underground coal mine. This groundbreaking initiative represents a significant shift in how underground coal mining can be conducted in environmentally sensitive or densely populated areas. The introduction of these sustainable mining innovations marks a turning point for the industry.
What is Paste Fill Technology and How Does it Work?
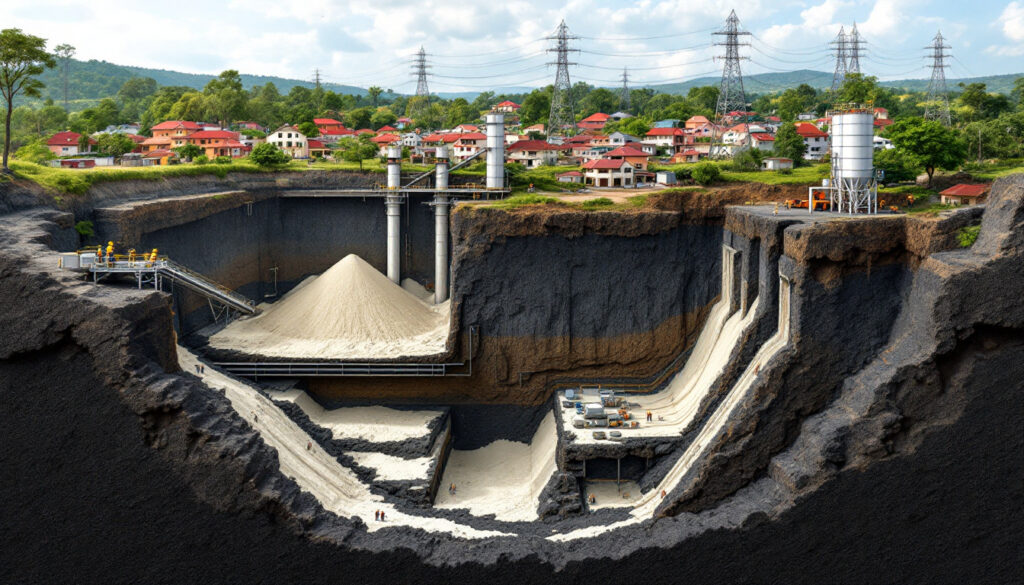
Paste fill technology is an innovative mining approach that fundamentally changes how underground voids are managed after coal extraction. Unlike traditional methods that allow for surface subsidence, paste fill provides structural support while incorporating industrial byproducts.
The Fundamentals of Paste Fill Technology
The process involves creating a specialized mixture using fly ash, crushed overburden material from opencast mines, cement, water, and binding agents. This engineered paste is pumped into the voids created by mining operations, where it hardens to provide structural support.
This technology creates a dual benefit: it maintains the structural integrity of the mine while eliminating the need for traditional surface land acquisition that often accompanies underground mining operations.
The paste mixture's composition can be precisely engineered to achieve specific strength requirements, making it adaptable to various geological conditions and mining depths.
Technical Implementation in Underground Mining
Paste fill technology replaces conventional caving methods with a more sustainable approach that preserves surface integrity. The hardened paste provides sufficient support to prevent surface subsidence, which is crucial when mining beneath populated areas or critical infrastructure.
The implementation requires specialized equipment for mixing and pumping the paste material into mining voids. Continuous monitoring systems track the fill's performance and structural integrity throughout the mine's operational life.
By maintaining the integrity of surface structures above mining operations, this technology enables coal extraction in areas that would otherwise be inaccessible due to surface constraints or environmental concerns, addressing some of the global coal challenges that the industry faces today.
SECL's Landmark Agreement for Singhali Coal Mine
The adoption of paste fill technology at Singhali represents a watershed moment for sustainable mining in India's coal sector.
Details of the $823 Million Partnership
SECL has entered into a significant agreement valued at Rs70.4bn ($823.6m) with TMC Mineral Resources to implement paste fill technology at the Singhali mine. This 25-year contract marks SECL as the first coal Public Sector Undertaking (PSU) in India to adopt this advanced mining technique at scale, according to a recent report from Mining Technology.
The partnership is expected to yield approximately 8.4 million tonnes of coal over its lifetime, revitalizing a mine that has been operational since 1993 but faced constraints due to surface developments.
This contract demonstrates substantial financial commitment to sustainable mining practices, setting a precedent for other PSUs in the coal sector.
Strategic Importance for Indian Coal Mining
This initiative represents a significant shift toward sustainable mining practices in India's coal industry. The successful implementation at Singhali could serve as a blueprint for restarting operations in other underground mines facing similar surface constraints.
The project demonstrates SECL's commitment to innovative mining solutions that balance production needs with environmental responsibility. By adopting paste fill technology, SECL positions itself as a leader in environmentally responsible mining techniques within India's coal sector.
This approach aligns with global trends toward more decarbonisation in mining and could enhance India's reputation in responsible resource extraction methods.
Why is Paste Fill Technology Ideal for Singhali Mine?
The unique challenges at Singhali make paste fill technology particularly appropriate for this site.
Unique Challenges at the Singhali Site
The Singhali mine has been operational since 1993 and contains approximately 8.45mt of G-7 grade non-coking coal reserves. The mine was initially developed using the traditional Bord and Pillar method, which leaves pillars of coal to support the roof.
What makes Singhali particularly challenging is its surface area, which is densely populated with villages, traversed by high-tension electricity lines, and includes a PWD road. These surface constraints make traditional caving methods impractical due to the risk of surface subsidence.
Without paste fill technology, extracting the remaining coal reserves would likely require extensive surface land acquisition, relocation of communities, and rerouting of infrastructure—all of which present significant social, logistical, and financial challenges.
Environmental and Safety Benefits
The implementation of paste fill technology at Singhali offers multiple environmental advantages. It prevents disruption to surface structures and communities, allowing mining to proceed without displacing residents or damaging infrastructure.
The technology promotes waste recycling by incorporating industrial waste materials like fly ash into the paste mixture, contributing to circular economy principles. This productive use of waste materials reduces the need for disposal sites and their associated environmental impacts.
Compared to conventional mining methods, paste fill technology significantly reduces the environmental footprint of coal extraction. The stabilized voids also enhance overall mine safety by maintaining structural integrity, reducing the risk of collapse and improving working conditions for miners.
The Future Impact of Paste Fill Technology in Coal Mining
The successful implementation at Singhali could catalyze broader adoption of this technology across India's coal mining sector.
Setting New Standards for Underground Mining
Paste fill technology has the potential to revitalize operations in mines facing land constraints or surface development, breathing new life into assets that might otherwise be abandoned. The Singhali project creates a blueprint for sustainable coal extraction in populated areas, demonstrating how mining and community needs can coexist.
This approach demonstrates the viability of advanced mining techniques in challenging environments, potentially inspiring innovation throughout India's mining sector. By supporting continuation of mining without surface disruption, paste fill technology can extend the productive life of existing mines while protecting communities and infrastructure.
The utilization of advanced technologies like paste fill aligns with broader industry trends toward implementing digital twins in mining to enhance operational efficiency and sustainability.
Long-term Environmental and Economic Benefits
The adoption of paste fill technology promotes circular economy principles through the utilization of waste materials that would otherwise require disposal. This supports India's broader waste management goals while creating value from byproducts.
By reducing the need for new land acquisition for mining operations, this technology minimizes one of the most contentious aspects of resource development. The ability to extend the productive life of existing mining assets improves the return on investment for mining infrastructure while maintaining employment opportunities in mining communities.
Perhaps most importantly, paste fill technology helps balance resource extraction with environmental protection, supporting India's dual goals of energy security and ecological responsibility, which is increasingly important for the future of underground mining.
Expert Perspectives on Paste Fill Implementation
Industry leaders and technical experts view paste fill technology as transformative for underground coal mining.
Industry Leadership Insights
SECL Chairman and Managing Director Harish Duhan has expressed strong support for the technology, stating: "Paste fill technology will not only secure the future of underground mining but also offer an innovative, eco-friendly solution." This leadership endorsement positions the technology as "a landmark step toward green mining."
Industry experts believe this approach will "shape the future of the coal industry in the years to come" by demonstrating how technological innovation can address long-standing challenges in underground mining while supporting environmental goals.
The adoption of paste fill technology represents a commitment to sustainable development within an industry often criticized for its environmental impacts. As Coal India's stock rose following the announcement, investors appear to recognize the value of this sustainable approach.
Technical Considerations for Implementation
Implementing paste fill technology requires specialized engineering expertise and equipment to ensure proper mixture formulation and placement. The precise mixture composition must be carefully calculated to provide optimal structural support while maintaining cost-effectiveness.
Ongoing monitoring of filled areas for stability is essential to ensure long-term safety and performance. This requires sophisticated instrumentation and data analysis capabilities.
The successful implementation demands close coordination between mining operations and paste production to ensure timely filling of voids and uninterrupted mining progression. This level of coordination represents a technological and logistical advancement in Indian mining operations.
FAQ: SECL and Paste Fill Technology
What makes paste fill technology environmentally friendly?
Paste fill technology utilizes industrial waste materials like fly ash that would otherwise require disposal, supporting waste reduction goals. The method prevents surface subsidence, protecting surface ecosystems, agricultural lands, and water resources.
The technology reduces the overall environmental footprint of mining operations by minimizing surface disturbance and supports sustainable resource extraction practices by enabling mining beneath sensitive areas without compromise.
How does paste fill technology compare to traditional mining methods?
Unlike conventional methods, paste fill technology eliminates the need for surface land acquisition, reducing conflicts with communities and decreasing project delays. The technology provides superior structural support compared to traditional backfilling methods, enhancing both safety and resource recovery.
Paste fill enables mining in areas with surface constraints that would otherwise be inaccessible, expanding the viable resource base. Additionally, the approach incorporates waste recycling principles not present in conventional mining approaches, supporting circular economy objectives.
What other SECL projects are advancing sustainable mining?
Beyond Singhali, SECL's Gevra mine in the Korba area received environmental clearance in March 2024, incorporating advanced environmental management systems. The company is exploring additional applications of paste fill technology at other underground mines facing similar constraints.
SECL maintains a focus on balancing production needs with environmental responsibility across its operations, demonstrated by investments in mine rehabilitation and ecological restoration. The company continues to invest in innovative mining solutions that minimize environmental impacts while maintaining productivity and resource recovery.
Ready to Invest in More Sustainable Mining Technologies?
Discover how innovative mining approaches like SECL's paste fill technology are transforming the industry by visiting Discovery Alert's dedicated discoveries page, where our proprietary Discovery IQ model identifies high-potential mining innovations and investment opportunities before the broader market recognises their value.