Understanding the Iron Ore Pricing Correction: Market Dynamics and Future Outlook
What Factors Are Driving the 2025 Iron Ore Price Correction?
Supply-Demand Imbalance Fundamentals
The current iron ore pricing correction stems from a fundamental supply-demand imbalance that has built up gradually throughout 2024 and into 2025. Production expansion from major miners has significantly outpaced global consumption, creating persistent downward pressure on prices. Recent data indicates Australian and Brazilian production volumes have increased by approximately 7% year-over-year, while demand growth has remained relatively flat.
New projects coming online in Guinea have further exacerbated the supply situation, with initial production volumes exceeding market expectations. These developments have coincided with Chinese steel production constraints, which have limited the growth of the world's largest iron ore consumer, creating a perfect storm for price decline factors.
Port inventories have reached multi-year highs, with stockpiles at major Chinese ports exceeding 145 million tonnes in September 2025, approximately 15% above the five-year average for this period.
Macroeconomic Influences on Price Movement
Beyond pure supply-demand dynamics, broader macroeconomic factors have accelerated the iron ore pricing correction. The construction sector, particularly in China, has shown persistent signs of contraction, with floor space under construction declining for the sixth consecutive quarter. This slowdown has directly impacted steel consumption patterns and consequently iron ore demand.
Manufacturing activity metrics in key markets have also signaled contraction, with PMI readings below the critical 50-point threshold for several months. Currency fluctuations have further complicated the pricing landscape, as the relative strength of the US dollar has effectively increased the local currency cost of dollar-denominated iron ore purchases for many importing nations.
Global economic uncertainty continues to weigh on commodity markets broadly, with iron ore particularly vulnerable due to its heavy reliance on infrastructure and construction activity, which are typically early casualties of economic downturns.
How Significant Is This Iron Ore Price Correction?
Price Movement Analysis and Context
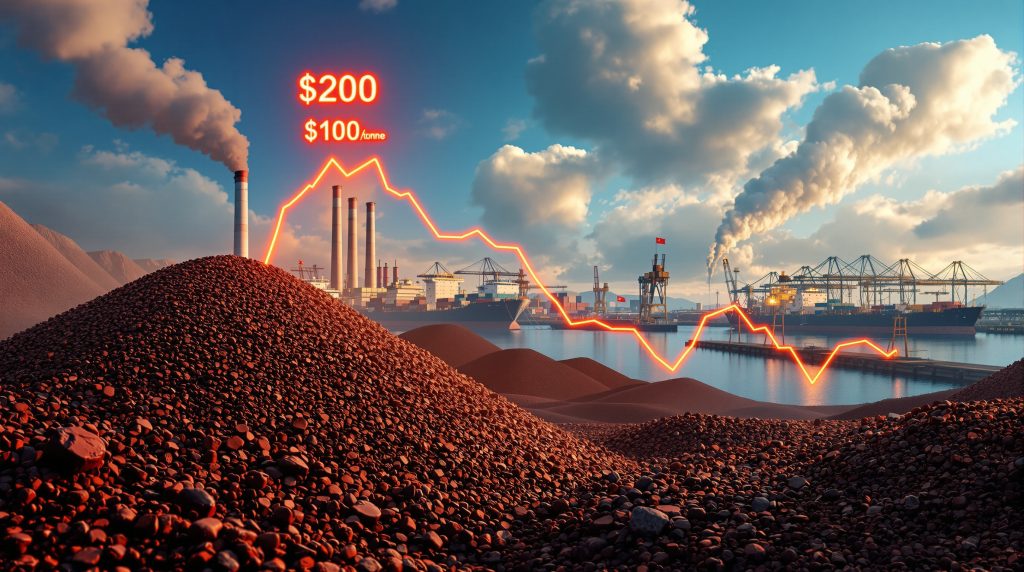
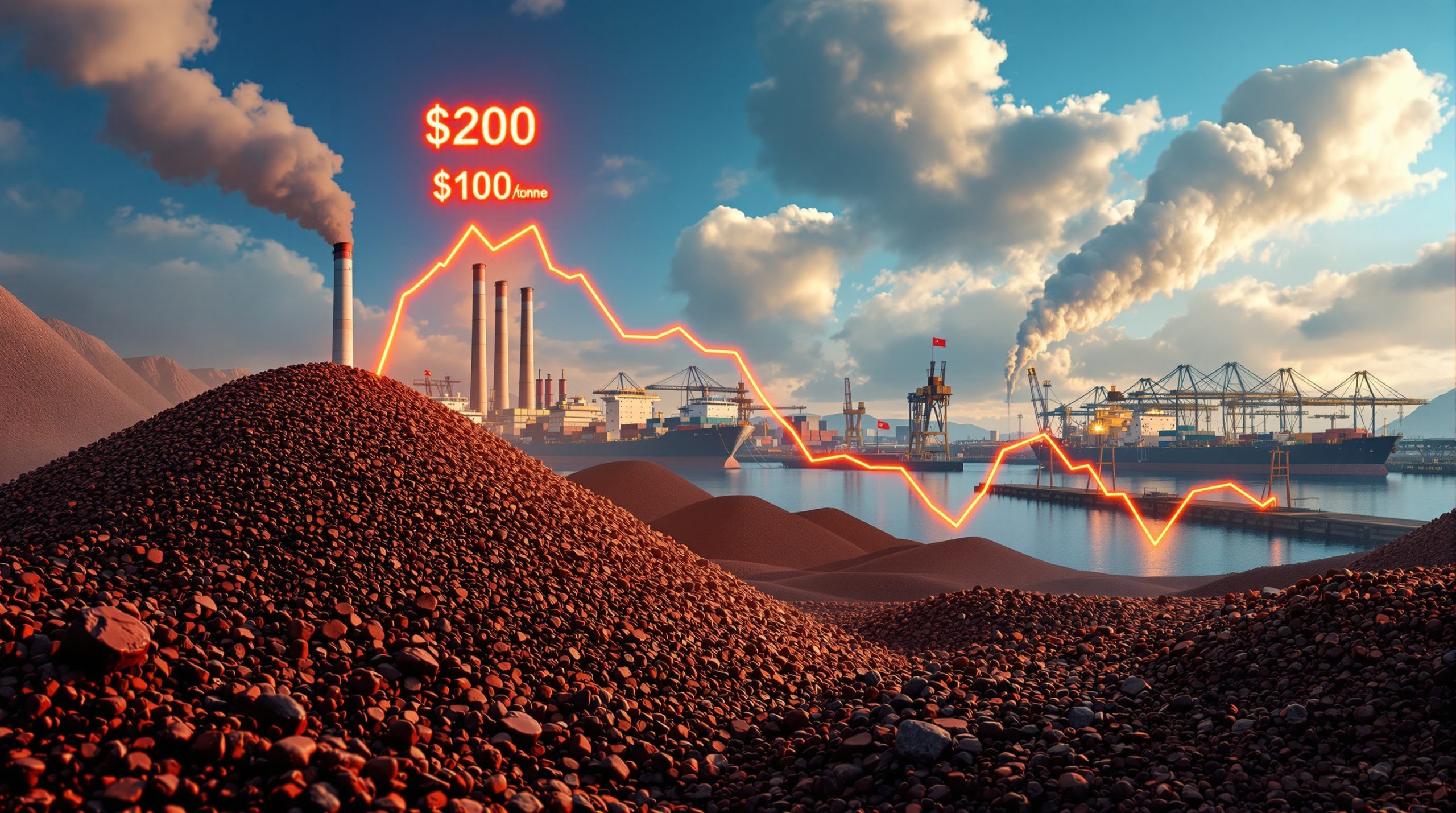
The current iron ore pricing correction has seen values decline from peaks around $219 per tonne in early 2024 to a trading range of $96-110 per tonne by September 2025. This represents a decline of approximately 50-56% from peak to trough, making it one of the more significant corrections of the past decade, though still less severe than the 2014-2015 collapse that saw prices fall below $40.
What distinguishes this correction from previous cycles is its relatively gradual nature. Rather than experiencing a sharp, panic-driven collapse, prices have methodically stepped down over several quarters as market fundamentals progressively deteriorated. This pattern suggests a structural rather than speculative correction, potentially indicating a longer recovery timeline.
Historical recovery patterns following similar corrections typically show limited upside momentum until a clear catalyst emerges, such as significant supply disruptions or unexpected policy stimulus. Technical support levels appear to be establishing new price floors in the $90-95 range, with resistance forming around $110-115.
Market Sentiment Indicators
Trading volume patterns during the correction phase reveal interesting insights into market sentiment. Volume has consistently increased during downside price movements, indicating widespread participation in the sell-off rather than isolated liquidation events. This pattern typically suggests strong conviction behind the price direction.
Futures market positioning data shows persistently bearish sentiment, with commercial hedgers increasing short positions while reducing long exposure. Open interest in iron ore price trends futures has remained robust throughout the correction, indicating active market engagement rather than abandonment.
Analyst consensus forecasts have trended lower throughout 2025, with median price projections for Q4 2025 and Q1 2026 now hovering around $95-100 per tonne, down from previous forecasts of $120-130. Institutional investor positioning in major mining equities reflects similar caution, with reduced exposure to iron ore-focused producers compared to more diversified miners.
Why Are Chinese Policies Central to the Iron Ore Correction?
Production Restriction Impacts
Chinese policy decisions continue to play a pivotal role in the iron ore pricing correction. Production restrictions across key steelmaking hubs have directly impacted consumption patterns, with particular intensity in the Tangshan region ahead of a military parade commemorating the 80th anniversary of World War II victory. These restrictions have forced steel mills to operate at reduced capacity, dampening iron ore demand during what would typically be a seasonal uptick period.
Environmental compliance requirements have further constrained steel output, with stricter emissions standards imposing production caps on mills that fail to meet upgraded pollution control benchmarks. The cumulative effect has been a reduction in China's annualized crude steel production capacity of approximately 50-60 million tonnes during peak restriction periods.
Steel capacity utilization rates across major production centers have averaged 76-80% in recent months, significantly below the 85-90% levels seen during previous price boom periods. This constrained operational environment has allowed steelmakers to be more selective in their raw material purchasing, contributing to price pressure in the iron ore market.
Strategic Import Decisions
China's strategic approach to iron ore imports has evolved during the correction phase. Port inventory management has become increasingly sophisticated, with buying decisions more closely tied to immediate production needs rather than speculative stockpiling. This just-in-time approach has reduced the urgency in purchasing, allowing buyers to be more price-sensitive.
Diversification efforts have accelerated, with increased iron ore imports from non-traditional suppliers including Canada, Ukraine, and South Africa. Though these volumes remain small relative to Australian and Brazilian shipments, they represent an intentional strategy to reduce price vulnerability through supply diversification.
State reserve management policies have also influenced market dynamics, with strategic stockpiles being carefully managed to avoid further price support during the correction phase. The National Development and Reform Commission has reportedly advised against aggressive stockpiling during the correction, preferring to allow market forces to reach equilibrium.
How Are Major Producers Responding to Lower Prices?
Operational Strategy Adjustments
Major iron ore producers have implemented varied responses to the pricing correction, with operational strategies carefully calibrated to balance market share protection with financial discipline. Cost efficiency initiatives have taken center stage, with miners across all tiers working to lower their production expenses to preserve profit margins in a lower price environment.
Production volume decisions have been notably restrained, with top-tier producers maintaining output levels despite price pressure. This contrasts with previous cycles where production cuts were more quickly implemented. The reluctance to reduce volumes suggests producers are prioritizing market share preservation and operational continuity over short-term price support.
Capital expenditure reprioritization has been evident across the industry, with growth projects being subjected to more stringent review processes. Several expansion initiatives have been delayed or scaled back, though core replacement projects continue to advance to maintain production capabilities.
Quality optimization strategies have gained prominence, with producers focusing on higher-grade output that commands premium pricing. This selective production approach helps maintain revenue streams even as headline benchmark prices decline.
Financial Performance Implications
The financial impact of the iron ore pricing correction has been significant but manageable for major producers. Revenue declines in the range of 30-40% year-over-year have been reported by leading iron ore exporters, though the effect on bottom-line results has been partially mitigated by operational cost improvements and favorable exchange rate movements for Australia's iron ore leadership.
Profit margin compression has been inevitable, with EBITDA margins for pure-play iron ore miners declining from the 65-70% range during peak pricing to 40-45% in the current environment. While still healthy by broader mining industry standards, this compression has forced careful cash flow management.
Shareholder return policies have shown remarkable resilience during the correction phase, with major producers maintaining dividend payouts at higher levels than historical precedent would suggest. This reflects both stronger balance sheets entering the correction and a strategic emphasis on shareholder loyalty during challenging market conditions.
Balance sheet strength assessments remain largely positive across the tier-one producer landscape, with net debt levels at or near historic lows for most major iron ore miners, providing substantial cushioning against price volatility.
What Quality Differentials Are Emerging During the Correction?
Premium Grade Dynamics
The iron ore pricing correction has catalyzed significant shifts in quality differentials, with premium grade products demonstrating greater price resilience than lower-grade alternatives. The price spread between 65% Fe and 62% Fe products has widened to $15-18 per tonne during the correction phase, compared to $8-12 during the preceding price stability period. This expanding premium reflects both technical efficiency considerations and environmental compliance factors.
As evidenced by specific transaction data from the Fastmarkets pricing notice dated September 24, 2025, even small quality differences command meaningful price variations. The notice documented transactions of 61% Fe Pilbara Blend fines at $103.70-103.95 per tonne, while 62% Fe Pilbara Blend fines traded at approximately $104.97 per tonne CFR China, demonstrating the market's continued quality sensitivity even amid broader price correction.
Environmental factors driving quality preference shifts include tightening emissions standards across Chinese steel mills, which incentivize higher-grade inputs to reduce overall carbon intensity. This regulatory pressure maintains demand for premium grades even as absolute price levels decline.
Production cost differentials across quality segments have also influenced buying patterns, as the energy savings and productivity improvements from using higher-grade ores often justify their premium pricing, especially when overall energy costs are elevated.
Impurity Considerations in Pricing
Impurity-related price adjustments have become increasingly sophisticated during the correction phase, with silica and alumina content penalties being applied with greater precision. Mills operating under stricter environmental regulations have shown particular sensitivity to these elements, which can impact emissions profiles and slag volumes.
Moisture level impacts on effective pricing have gained prominence in negotiations, with buyers demanding discounts for materials exceeding optimal moisture specifications. This reflects both the direct cost of paying for water content and the operational inefficiencies associated with handling and processing high-moisture ores.
Blending strategies have evolved as a key cost-optimization approach, with steelmakers carefully balancing higher and lower-grade materials to achieve desired metallurgical properties while minimizing raw material costs. This strategic blending has allowed for continued utilization of lower-grade ores, albeit at increasingly discounted prices relative to benchmark grades.
Logistics considerations for different ore specifications have further influenced effective pricing, with factors such as handling characteristics, storage requirements, and transportation efficiency affecting the total delivered cost calculation.
How Do Price Index Corrections Impact Market Transparency?
Case Study: September 2025 Pricing Notice
The September 2025 price index correction case provides valuable insights into the mechanisms ensuring market transparency during volatile correction periods. As documented in the Fastmarkets pricing notice dated September 24, 2025, an error was identified and promptly corrected regarding the rationale for iron ore 61% and 62% Fe fines indices (MB-IRO-0008 and MB-IRO-0191).
The specific correction involved trade log entries for Pilbara Blend fines transactions, where details regarding price, laycan dates, and transaction specifications had been incorrectly recorded. The correction clarified that Rio Tinto had conducted transactions through the Beijing Iron Trading Center (COREX) platform involving 170,000 tonnes of 61% Fe Pilbara Blend fines at $103.70 and $103.95 per tonne, with laycan periods in early November.
Additionally, the correction documented a bilateral trade of 170,000 tonnes of 62% Fe Pilbara Blend fines priced using an index-based formula (November average with a $0.39 discount), with a fixed-price equivalent of $104.97 per tonne CFR China.
Importantly, the notice emphasized that while the rationale required correction, the published price forecast insights themselves remained unaffected, maintaining market confidence in the headline benchmarks while enhancing transparency regarding the supporting transaction data.
Methodology Enhancement Measures
The correction episode highlights the ongoing methodology refinements implemented by price reporting agencies to ensure accuracy during volatile market periods. Data submission verification protocols have become increasingly robust, with cross-checking mechanisms designed to identify potential discrepancies before publication.
Volume weighting methodologies in index calculations provide another layer of market accuracy, ensuring that larger, more representative transactions receive appropriate influence in the final price determination. This approach helps prevent smaller or outlier transactions from disproportionately affecting benchmark levels.
Outlier identification and treatment procedures have been refined over time, with statistical approaches complemented by market expertise to distinguish between genuine market moves and potential data anomalies. This balanced approach helps maintain index integrity during correction phases when price movements may be more pronounced.
Market participant feedback integration has become increasingly formalized, with structured channels for stakeholders to provide input on methodological questions or specific price assessments. The September 2025 correction notice explicitly invited feedback from market participants, demonstrating the interactive nature of modern price reporting.
What Trading Mechanisms Are Evolving During the Correction?
Spot Market Transaction Patterns
The iron ore pricing correction has catalyzed notable shifts in spot market transaction patterns, with platform-based trading gaining increased prominence. As evidenced by the September 2025 pricing notice transactions, the Beijing Iron Trading Center (COREX) platform facilitated multiple significant trades involving 170,000-tonne cargoes of Pilbara Blend fines, demonstrating the market's embrace of transparent electronic trading venues even during price volatility.
Price discovery efficiency during the correction phase has improved through these platform-based mechanisms, allowing for more immediate visibility of transaction levels and reducing information asymmetry between market participants. This enhanced transparency helps prevent panic-driven pricing disconnects that characterized previous correction cycles.
Liquidity metrics across different trading venues have shown interesting divergence, with electronic platforms maintaining relatively stable transaction volumes while traditional bilateral negotiations have become more protracted during the correction. This suggests that standardized, platform-based trading provides greater execution certainty during volatile price periods.
Buyer-seller negotiation leverage has shifted notably during the correction, with purchasing teams exercising greater patience and discipline in negotiations. The September pricing notice transactions demonstrate this dynamic, with index-linked pricing mechanisms incorporating specific discounts ($0.39 per tonne below the monthly average), reflecting buyers' stronger negotiating position.
Contract Structure Adaptations
Contract structures have evolved significantly during the correction phase, with index-linked pricing mechanisms gaining further prominence over fixed-price arrangements. The transaction documented in the September pricing notice exemplifies this trend, using the November average of a 62% Fe index with a specified discount rather than a fixed dollar value.
Term length preferences have shifted toward shorter durations during price uncertainty, with quarter-by-quarter arrangements becoming more common than annual commitments. This allows both parties to reassess terms more frequently as market conditions evolve, reducing the risk of long-term disconnection from market reality.
Volume flexibility provisions have become increasingly sophisticated, with contracts incorporating tolerance ranges rather than fixed tonnage requirements. This approach provides operational flexibility for both producers and consumers while maintaining the core supply relationship.
Quality specification tolerances have similarly evolved, with more detailed parameters around not only Fe content but also impurity levels, physical characteristics, and moisture content. These comprehensive specifications help prevent disputes during a market where quality differentials have become increasingly important price determinants.
How Are Logistics Factors Influencing the Correction?
Freight Rate Correlations
Shipping costs have demonstrated complex correlations with iron ore prices during the correction phase, creating additional layers of market dynamics. Cape-size vessel rates have declined approximately 30-35% from their 2024 peaks, partly tracking the iron ore price correction but showing less dramatic percentage moves.
This relative stability in freight rates compared to underlying commodity prices has actually increased shipping costs as a percentage of delivered iron ore value. Where freight previously represented 8-10% of the delivered CFR China value during peak pricing, it now constitutes 12-15% of the total landed cost, elevating its importance in sourcing decisions.
Port congestion metrics have improved considerably during the correction, with waiting times at major Chinese ports declining from 7-9 days to 2-3 days at present. This operational improvement has partially offset the percentage increase in freight costs, improving supply chain efficiency.
Regional freight differentials have emerged as significant factors affecting netback calculations for producers. Brazilian shipments face a higher proportional freight burden than Australian cargoes, widening the effective cost gap between these major supply regions during the correction phase.
Supply Chain Optimization Strategies
Inventory management approaches have adapted throughout the distribution channel, with just-in-time strategies gaining favor over large-scale stockpiling. End users have become increasingly sophisticated in matching inventory levels to actual production requirements, reducing carrying costs during price uncertainty.
The traditional stockpiling approach has given way to more frequent, smaller purchases as buyers seek to minimize price risk exposure. This shift in purchasing patterns has contributed to the correction by reducing the urgency behind large block purchases that previously supported price levels.
Alternative shipping routes have gained consideration as part of comprehensive cost optimization efforts. While the Australia-China and Brazil-China routes remain dominant, diversification through Canadian, South African, and other origin points has increased, partly motivated by delivered cost considerations.
Logistics contract renegotiations have become more frequent during the correction, with terms being adjusted to reflect the changing market environment. Volume commitments, rate structures, and flexibility provisions are all being revisited to align with the new market reality.
What Regional Economic Impacts Is the Correction Creating?
Australian Export Sector Analysis
The iron ore pricing correction has created significant ripple effects throughout Australia's export sector. Revenue implications for major Australian producers have been substantial, with the approximately 50% price decline from peak levels translating to reduced export earnings of roughly AUD 50-60 billion on an annualized basis.
Royalty and tax collection effects have directly impacted government budgets, particularly in Western Australia where iron ore royalties have historically contributed 15-20% of state revenue. Budget projections for fiscal year 2025-2026 have been revised downward, though the impact has been partially mitigated by production volume increases.
Employment impacts in iron ore producing regions have been relatively limited thus far, with major producers maintaining workforce levels despite price pressures. This contrasts with previous correction cycles where layoffs occurred more rapidly, reflecting both stronger corporate balance sheets and the recognition of talent retention importance.
Infrastructure investment adjustments have been more noticeable, with several port expansion and rail upgrade projects placed under review. While maintenance capital expenditure continues, growth-oriented investments are being subjected to more rigorous economic assessment under revised price assumptions.
Brazilian Recovery Dynamics
Brazil's iron ore sector has demonstrated notable resilience during the pricing correction, building on its recovery from earlier operational challenges. Production restoration following previous disruptions has continued despite lower price levels, with output now approaching pre-disruption volumes.
Quality advantage leveraging has emerged as a key strategy for Brazilian producers during the correction. The naturally higher Fe content of Brazilian ores has allowed them to command stronger premiums in a market increasingly sensitive to quality differentials, partially offsetting the headline price decline.
Logistics improvements have enhanced market competitiveness, with rail and port infrastructure upgrades reducing the historical delivery uncertainty that previously disadvantaged Brazilian shipments. These operational enhancements have come at a critical time, providing competitive advantages during challenging market conditions.
Investment outlook remains cautiously positive despite the correction, with major producers proceeding with key replacement projects while carefully evaluating expansion initiatives. This balanced approach reflects confidence in long-term fundamentals while acknowledging near-term pricing challenges.
What Is the Future Outlook for Iron Ore Prices?
Short-Term Price Projection Factors
Analysis of the supply pipeline for the next 6-12 months suggests continued production growth, albeit at a more moderate pace than seen in 2023-2024. Major expansion projects already in commissioning phases will add approximately 30-40 million tonnes of new supply through mid-2026, maintaining pressure on prices absent demand growth acceleration.
Seasonal demand patterns may provide temporary price support, particularly ahead of the traditional construction season in China beginning March 2026. However, these seasonal effects are likely to create price oscillations within the established range rather than triggering a sustained upward trend.
Technical price support levels appear well-established in the $90-95 range, with multiple rebounds from this zone suggesting strong buying interest when prices approach these levels. Resistance has formed around $110-115, creating a trading range that may persist until a fundamental catalyst emerges.
Potential policy intervention scenarios remain a wild card, particularly regarding Chinese stimulus measures targeting infrastructure and construction. While no major initiatives have been announced, historical patterns suggest that persistent economic weakness could eventually trigger supportive policies, potentially creating a more favorable demand environment.
Long-Term Structural Trends
Decarbonization impacts on traditional iron ore demand represent perhaps the most significant long-term structural consideration. Steel industry transformation efforts are accelerating, with increasing investment in electric arc furnace capacity that relies primarily on scrap rather than iron ore. This gradual shift suggests a flattening demand curve rather than continued growth over the coming decade.
High-grade ore premium evolution in the green steelmaking context presents a potential bright spot, as transitional technologies like hydrogen reduction typically require higher-quality iron ore inputs. Producers of premium products may find stronger demand resilience even as overall market growth moderates.
New production capacity coming online in the next 3-5 years will maintain competitive pressure on the supply side. Major projects in Australia, Brazil, and West Africa are in various stages of development, collectively representing potential additions of 100+ million tonnes by 2030 if all proceed as planned.
Technological disruptions affecting traditional demand patterns bear careful monitoring, particularly advancements in construction techniques that could reduce steel intensity in building projects. Prefabrication, 3D printing, and alternative building materials all present potential headwinds to traditional steel demand growth rates.
FAQs About the Iron Ore Pricing Correction
What triggered the initial iron ore price decline in 2025?
The decline originated from expanding supply from major miners coinciding with weakening Chinese steel demand due to construction sector contraction and production restrictions. This fundamental imbalance was exacerbated by high port inventory levels and broader economic uncertainty, creating persistent downward pressure on prices.
How have price reporting agencies ensured accuracy during the correction?
Price reporting agencies have implemented enhanced verification protocols for transaction data and promptly addressed any reporting discrepancies. The September 2025 correction notice from Fastmarkets illustrates this commitment to accuracy, documenting specific trade log corrections while maintaining overall index integrity through robust methodology.
Are all iron ore grades equally affected by the correction?
No, higher-grade products have demonstrated significantly greater price resilience during the correction. The premium for 65% Fe products over 62% Fe benchmark material has actually expanded during this period, reflecting both operational efficiency benefits and environmental compliance advantages of higher-grade inputs in steelmaking.
What strategies are buyers employing during this correction phase?
Buyers have shifted toward more frequent, smaller volume purchases to minimize price risk exposure. There's increased emphasis on index-linked pricing with negotiated discounts, as evidenced by the September 2025 transaction data. Quality optimization through sophisticated blending approaches has also gained prominence as a cost management strategy.
When might iron ore prices stabilize or recover?
Most market analysts project continued price moderation through 2025-2026, with potential stabilization in the $90-100 range as the market reaches a new supply-demand equilibrium. Significant recovery would likely require either unexpected supply disruptions or substantial Chinese stimulus targeting steel-intensive sectors, neither of which appears imminent.
Further Exploration:
Readers interested in deeper understanding of miners' demand insights can explore educational content available through commodity market resources and price reporting methodologies that provide additional context on assessment processes and market fundamentals shaping the current correction phase.
Ready to Stay Ahead of Major Mineral Discoveries?
Experience instant notifications when significant mineral discoveries are announced on the ASX with Discovery Alert's proprietary Discovery IQ model, turning complex data into actionable investment insights. Understand why major discoveries can lead to substantial market returns by exploring Discovery Alert's dedicated discoveries page showcasing historic examples of exceptional outcomes.