What Triggered China's Ban on BHP Iron Ore Shipments?
In a move that has shaken global commodity markets, China Mineral Resources Group (CMRG) implemented a temporary ban on new purchases of dollar-denominated seaborne iron ore cargoes from mining giant BHP in early October 2025. The halt represents a significant escalation in ongoing pricing disputes between the world's largest iron ore consumer and one of its primary suppliers.
The ban specifically targets BHP's dollar-denominated shipments and comes at a strategically important time—during China's Golden Week holiday period when markets typically experience a seasonal slowdown. This timing appears deliberate, leveraging the natural lull in trading activity to maximize negotiating pressure.
At the core of this dispute lies China's growing determination to exert greater control over iron ore price trends. Through CMRG, its centralized state purchasing entity established to consolidate buying power, China aims to counter price increases that have persisted despite bearish market sentiment.
The scale of this disruption is substantial—BHP supplies approximately 250 million tons of iron ore annually to China, representing about 20.8% of China's massive 1.2 billion ton annual import volume. With negotiations expected to continue through China's Golden Week holiday period, market participants are closely watching for signs of resolution before trading fully resumes on October 8, 2025.
The Strategic Context Behind the Ban
China's move reflects a calculated approach to resource acquisition that extends beyond simple commercial disagreement. The establishment of CMRG as a centralized buying authority represents Beijing's strategic shift toward greater state control over essential industrial inputs.
This ban doesn't exist in isolation but forms part of a broader pattern of China seeking to reshape global commodity markets to better serve its economic interests. By targeting BHP specifically, China signals its willingness to leverage its position as the dominant buyer in the market to extract more favorable terms from even the largest suppliers.
Industry analyst perspectives suggest this confrontation was brewing for some time, with CMRG gradually expanding its influence beyond BHP to other major suppliers including Brazil's Vale. The timing coincides with iron ore demand insights showing prices had rallied approximately 15% from June lows despite broader bearish sentiment in the market.
How Has the Ban Affected Global Shipping Markets?
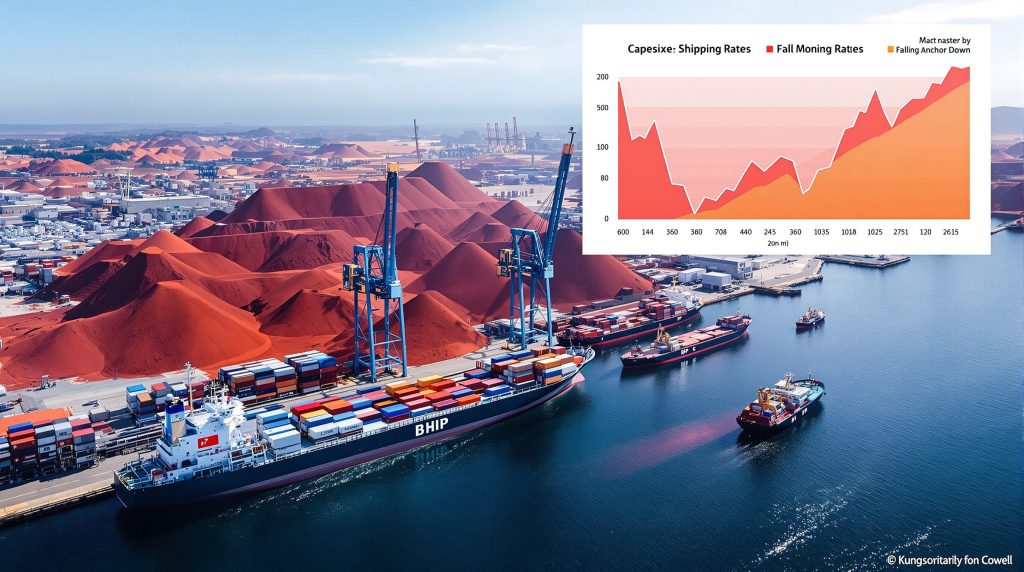
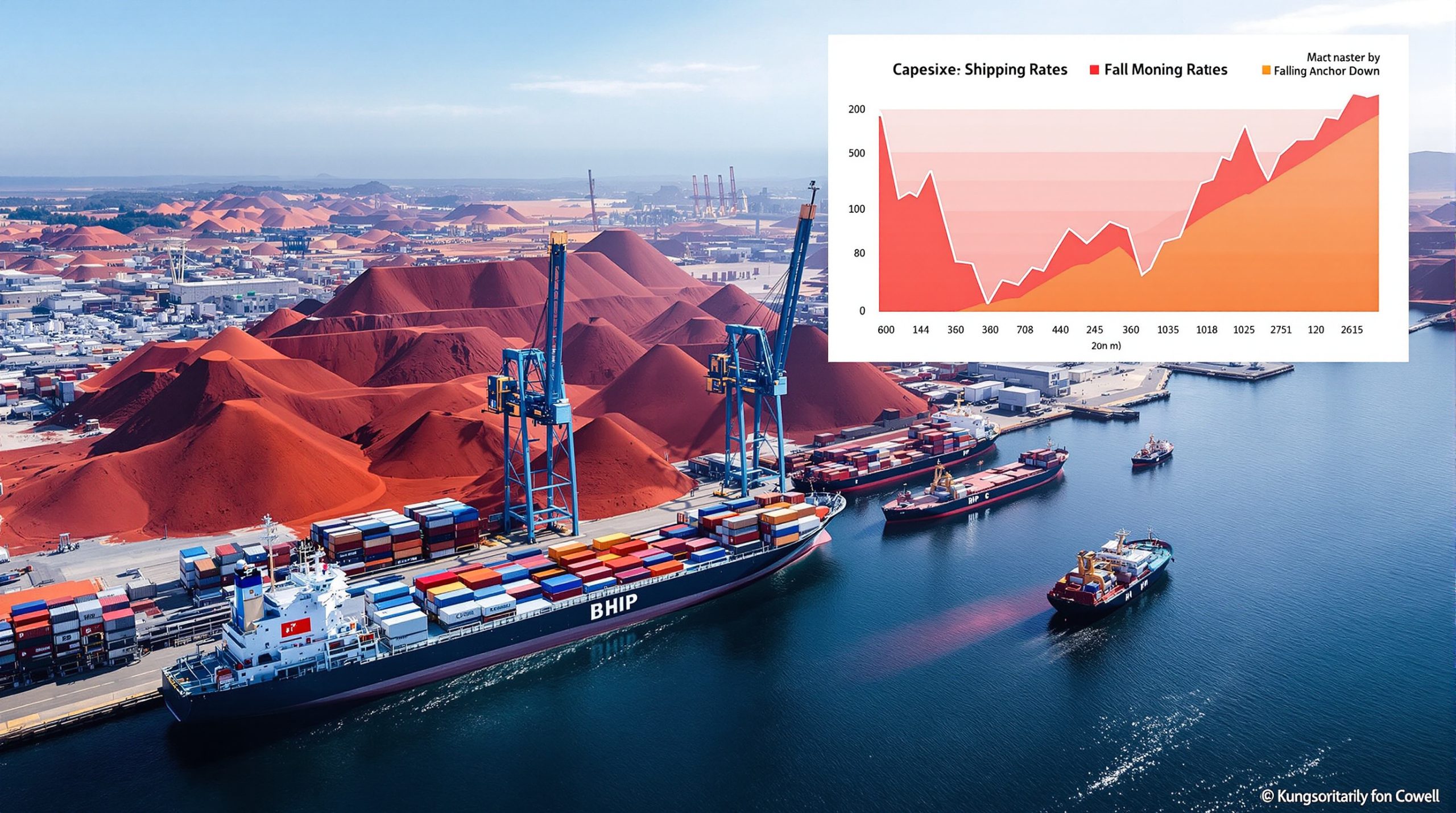
The immediate impact on shipping markets has been dramatic. Capesize bulk carrier rates collapsed by approximately 25% within a single week of the announcement, with a staggering 12.5% single-day drop following the initial news—the largest one-day decline since June 26, 2025.
The Baltic Exchange's 5TC index, a key indicator for global dry-bulk shipping, tumbled to levels not seen since late August 2025. Industry insiders didn't mince words about the severity of the downturn, with Singapore-based freight analyst Lennon Lim from Thurlestone Shipping describing the market reaction as "carnage".
Forward freight rates ended a six-day losing streak on Thursday (October 3, 2025) after BHP appeared to have requested two Capesize bulk carriers for delivery of iron ore to China in two weeks' time. However, uncertainty remains about whether these orders were placed before or after the implementation of the ban.
Why Shipping Markets Reacted So Severely
The extreme sensitivity of Capesize markets to iron ore trading disruptions stems from the vessel category's heavy dependence on this specific cargo. Capesize vessels—massive bulk carriers typically exceeding 150,000 deadweight tonnes—are primarily employed in the iron ore trade, particularly on the Australia-China route.
This concentration of vessel utility creates a multiplier effect when disruptions occur. When a buyer as dominant as China alters purchasing patterns from a supplier as significant as BHP, the ripple effects through shipping markets are immediate and pronounced.
The situation illustrates the vulnerability of specialized shipping segments to geopolitical and commercial disputes. With limited cargo versatility, Capesize vessel owners have few immediate alternatives when major trade flows are disrupted.
The Strategic Importance of This Dispute
This confrontation highlights the growing strategic dimension of resource security for China and the vulnerability of concentrated supply chains in critical commodities. Beyond immediate price negotiations, the dispute reveals deeper tensions in the global resources landscape.
China's iron ore strategy reflects a broader push toward resource security through centralized purchasing and diversified sourcing. CMRG's establishment represents Beijing's determination to counter what it perceives as excessive pricing power among the major mining companies that dominate global iron ore supply.
For Australia, iron ore represents a critical export commodity, with China purchasing approximately two-thirds of all Australian iron ore exports. This creates an asymmetric dependency that has complicated diplomatic relations between the two countries during previous trade disputes.
The Market Context Behind the Dispute
Iron ore prices have shown remarkable resilience in 2025 despite bearish long-term sentiment, rallying almost 15% from their June lows. This price strength occurred despite China's ongoing efforts to curb overcapacity in its steel sector—efforts that would typically suggest weaker demand.
The pricing dynamics reveal a fundamental tension: China's need to secure reliable raw material supplies for its massive steel industry while simultaneously trying to control input costs. The CMRG ban represents an attempt to leverage China's market position to influence these dynamics.
For BHP and other major miners, the dispute highlights the risks of customer concentration and the growing complexity of navigating China's evolving purchasing strategies. It also demonstrates how quickly commercial disagreements can escalate into disruptions with global market implications.
Alternative Supply Chains and Market Adaptations
As this dispute unfolds, market participants are exploring alternative supply chain arrangements. Traders and shipowners have begun considering cargo rerouting options, with some vessels observed halting in the South China Sea or reducing speed while awaiting resolution.
The potential rerouting of shipments to alternative buyers would result in a boost in ton-miles—a key freight metric that measures both cargo volume and distance traveled. This could partially offset the negative impact on shipping rates if substantial volumes are diverted to more distant markets.
Kpler analyst Alexis Ellender noted observing "at least one vessel that appears to have halted in the South China Sea while en route to Tianjin and others running slow," though cautioned that these observations couldn't be definitively linked to the BHP-CMRG dispute.
Incentives for Resolution
Despite the current standoff, strong incentives exist for both parties to reach a resolution quickly. China's massive steel industry requires reliable iron ore supplies, while BHP depends on Chinese demand for a substantial portion of its production.
The timing of the dispute, coinciding with China's Golden Week holiday, creates a natural deadline for negotiations. As Kpler's Ellender observed: "There is a strong incentive for both parties to wrap up talks before public holidays in China end on 8 October."
Most industry analysts expect "a return to regular trading over the medium term" once the dispute is resolved, though the episode may accelerate China's efforts to diversify its iron ore sourcing and strengthen CMRG's role in centralized purchasing.
The Broader Market Implications
The confrontation between China and BHP illustrates several important trends reshaping global commodity markets. First, it demonstrates China's evolving approach to resource security, with greater state coordination of purchasing strategy across key industrial inputs.
Second, it highlights the ongoing vulnerability of concentrated supply chains to disruption. When a single buyer accounts for over 70% of seaborne iron ore demand and a handful of suppliers control the majority of production, disputes between major players inevitably create market-wide impacts.
Third, the episode underscores how commercial disagreements in commodity markets increasingly overlap with strategic considerations about resource security, market influence, and long-term supply relationships.
Iron Ore Price Resilience
A notable aspect of this dispute is that iron ore prices have remained relatively stable despite the significant disruption in trading patterns. This resilience suggests underlying strength in market fundamentals, with limited immediate alternatives to Australian iron ore for Chinese steel producers.
The 15% rally in iron ore prices from June lows to September 2025 occurred despite China's ongoing efforts to curb overcapacity in its steel sector. This price strength during a period of supposedly weakening demand highlights the complex interplay between short-term supply disruptions and longer-term market trends.
For investors and market participants, the episode demonstrates the importance of monitoring not just traditional supply-demand fundamentals but also the evolving purchasing strategies of dominant market players like CMRG.
Key Indicators to Watch Going Forward
As this situation develops, several key indicators will signal how the dispute might resolve and what longer-term implications may emerge. Most immediate will be any resumption of BHP shipment bookings after October 8, 2025, when China's Golden Week holiday period ends.
Market participants should also monitor public statements from both CMRG and BHP regarding negotiations, as well as any unusual vessel movements or speed adjustments in the key shipping lanes between Australia and China.
On a longer time horizon, changes to contract structures between major miners and Chinese buyers could signal more fundamental shifts in market dynamics. Similarly, investment decisions in alternative iron ore sources, particularly high-grade deposits in Brazil and Guinea, may accelerate as China seeks to diversify its supply base.
Potential Resolution Scenarios
Three primary resolution scenarios appear most likely. In the first, BHP makes pricing concessions to CMRG, potentially establishing new precedents for other suppliers. In the second, a face-saving compromise emerges that allows both parties to claim success while making minimal substantive changes to existing arrangements.
In the third and perhaps most consequential scenario, the dispute accelerates structural changes in iron ore purchasing patterns, with CMRG expanding its centralized buying role across more suppliers and potentially reshaping traditional pricing mechanisms.
The outcome will have significant implications not just for iron ore markets but potentially for other bulk commodities where commodity market volatility is influenced by China as the dominant global buyer.
Global Resource Market Perspectives
This dispute between China and BHP reflects broader tensions in global resource markets and strategic competition. Iron ore has joined other critical minerals in geopolitical importance, demonstrating how resource leverage can be deployed in commercial negotiations.
The episode highlights the vulnerability of concentrated supply chains and may accelerate resource nationalism trends globally. As countries increasingly view key industrial inputs through a strategic lens, commercial disputes are more likely to intersect with national security considerations.
For the shipping market, the dispute demonstrates how disruptions in a single commodity trade can create ripple effects across global maritime transportation. The Capesize vessel market is particularly exposed to iron ore trade disruptions, creating volatility that impacts freight rates across multiple shipping segments.
Table: Key Players in the Global Iron Ore Market
| Entity | Role | Market Position | Annual Volume |
|---|---|---|---|
| China | Primary importer | ~75% of seaborne market | 1.2 billion tons |
| BHP | Major producer | ~20% of China's imports | 250 million tons |
| China Mineral Resources Group | State buyer | Centralizing China's purchasing | Expanding influence |
| Capesize vessel operators | Primary carriers | Highly dependent on iron ore trade | 180+ million deadweight tons |
| Alternative producers (Vale, etc.) | Competing suppliers | Potential beneficiaries of diversification | Varies by company |
FAQ: Understanding China's Ban on BHP Iron Ore
How long is China's ban on BHP iron ore likely to last?
Most industry analysts expect the ban to be temporary, with strong incentives for both parties to resolve the dispute before trading fully resumes after China's Golden Week holiday on October 8, 2025. However, the episode may lead to longer-term changes in purchasing strategies and contract structures.
Could this dispute spread to other Australian iron ore producers?
While the current ban specifically targets BHP's dollar-denominated cargoes, it demonstrates China's willingness to use its market position for leverage. Other Australian producers could potentially face similar pressure as China seeks to strengthen its negotiating position across the market.
What alternatives does China have for iron ore supply?
China has been actively diversifying its iron ore sources, including increased purchases from Brazil's Vale and developing projects in Guinea's Simandou region. However, Australia remains its most significant supplier in terms of volume, proximity, and reliability, limiting China's immediate alternatives.
How might this dispute impact global steel production?
In the short term, the dispute is unlikely to significantly impact steel production as China maintains substantial iron ore inventories and continues to receive shipments from other suppliers. However, prolonged disruption could potentially create localized supply tightness and contribute to price volatility.
What does this mean for shipping companies?
Shipping companies, particularly those operating Capesize vessels, face significant short-term volatility and rate pressure. However, potential cargo diversions could increase ton-miles and benefit certain shipping routes if the dispute continues, creating both risks and opportunities across different market segments.
Furthermore, the onslow haulage update provides additional context on how domestic iron ore logistics operations are adapting during this period of international trade tension. Meanwhile, analysts are carefully reviewing the 2025 iron ore forecast to determine how this dispute may impact longer-term market projections.
Ready to Spot the Next Major Mineral Discovery?
Take your ASX investing to new heights with Discovery Alert's proprietary Discovery IQ model, providing real-time notifications on significant mineral discoveries before the broader market reacts. Visit Discovery Alert's discoveries page to see how early identification of major findings can deliver exceptional returns to well-positioned investors.