The Escalating Crisis in South32 Mozambique Smelter Negotiations
South32 Mozambique smelter negotiations have reached an unprecedented crisis as six years of discussions have failed to secure a viable power agreement beyond March 2026. The facility, which produces 370,000 tons annually, represents one of the most significant industrial operations in Southern Africa, yet negotiations with Mozambique's state-owned utility Hidroeléctrica de Cahora Bassa (HCB) have reached a complete impasse.
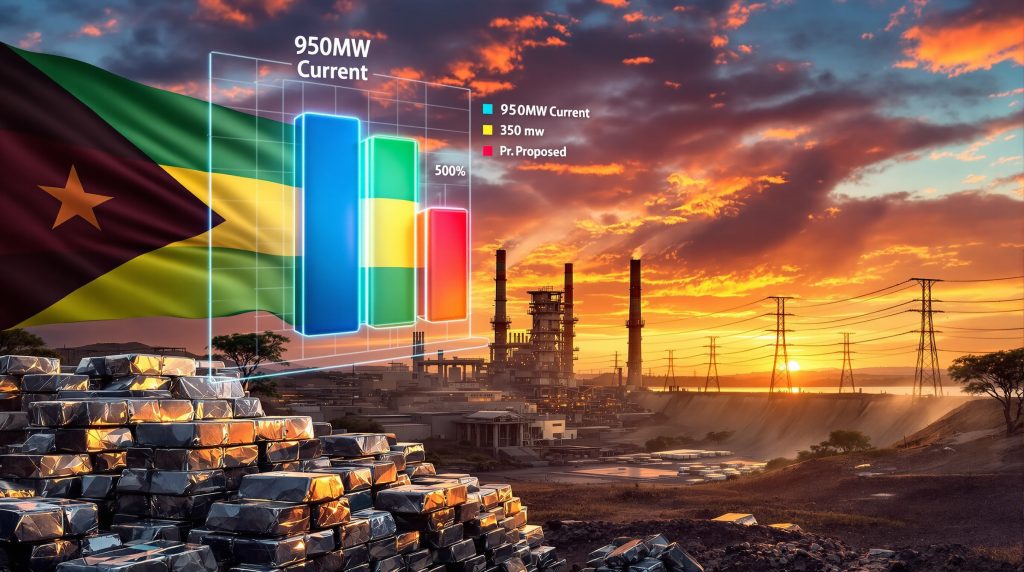
The current electricity arrangement provides 950MW predominantly from the Cahora Bassa hydroelectric facility, with pricing tied to Mozambique's national Producer Price Index. However, the government's latest proposal offers only 350MW at approximately double the current tariff, creating an economically unviable scenario for continued operations. This situation highlights broader energy security challenges facing industrial operations across the region.
Understanding the Fundamental Power Supply Constraints
The negotiation deadlock stems from Mozambique's hydroelectric capacity limitations following two years of severe drought conditions. This climate-related infrastructure stress has created a supply-demand imbalance that extends far beyond typical commercial negotiations.
South32 CEO Graham Kerr explained the economic reality facing the operation, noting that electricity costs represent approximately one-third of smelter operating expenses. The proposed tariff increases would fundamentally alter the facility's cost structure, eliminating profit margins entirely. Furthermore, this regional economic impact demonstrates how energy constraints affect industrial competitiveness across resource-dependent regions.
Technical Capacity Requirements vs. Available Supply
The technical specifications of aluminum smelting create inflexible power requirements. Modern aluminum smelters operate continuous electrolytic processes that cannot easily scale down production. The 63% capacity reduction from 950MW to 350MW would effectively prevent meaningful operations, as aluminum smelting requires consistent, high-volume electricity supply for the electrolytic reduction process.
Industry analysis indicates that aluminum smelters typically require minimum capacity thresholds to maintain economic viability. Operating below these thresholds creates unit cost increases that render production uncompetitive in global markets.
Drought Impact on Regional Power Generation
The Cahora Bassa hydroelectric facility, completed in 1974, represents one of Africa's largest hydroelectric installations with a designed capacity of 2,075MW. However, extended drought conditions have reduced water levels significantly, forcing capacity constraints across the regional power grid.
Mozambique's power sector challenges reflect broader Southern African energy infrastructure vulnerabilities, where hydroelectric generation accounts for significant portions of total capacity. Climate variability increasingly threatens large industrial operations dependent on consistent power supply. However, renewable energy integration offers potential long-term solutions for industrial power supply diversification.
The Economics Behind the Negotiation Breakdown
South32 has already recorded a $372 million impairment against the Mozal facility in its fiscal 2025 results, demonstrating the financial magnitude of the situation. This write-down reflects management's assessment that current asset values cannot be supported under proposed power arrangements.
The company ceased pot relining programmes in August 2025, a critical maintenance activity for aluminum smelters. Pot relining involves replacing the carbon and refractory lining in electrolytic cells, typically required every 5-8 years. Postponing this maintenance indicates management's expectation that operations will not continue under current arrangements.
Care and Maintenance Transition Costs
Industry experts indicate that aluminum smelters face 3-4 year recovery timelines once placed in care and maintenance. The restart process requires extensive equipment rehabilitation, skilled workforce retraining, and significant capital investment before production can resume.
Graham Kerr emphasised the permanency of shutdown decisions for aluminum smelters, noting that restart costs often exceed original construction expenses. This reality reflects the specialised nature of aluminum smelting technology and the degradation that occurs during extended shutdowns.
Global Aluminum Market Context
The potential Mozal closure occurs as global aluminum markets transition from surplus to potential deficit conditions. Industry forecasts suggest aluminum supply-demand balances could tighten significantly by 2027, making the loss of 370,000 tons annual capacity particularly significant.
Mozambique currently supplies 22% of the European Union's unalloyed aluminum imports, highlighting the geopolitical implications of facility closure. European aluminum supply chain diversification efforts may accelerate as a result of this development.
Regional Economic and Employment Implications
The Mozal facility directly employs 5,200 workers across its operations, representing Mozambique's largest industrial employer. Additionally, hundreds of South African suppliers provide goods and services to the facility, creating extensive cross-border economic linkages.
Regional economic multiplier effects extend throughout Southern Africa's industrial supply chain. The facility's closure would eliminate demand for specialised transportation, maintenance services, and raw materials sourced across the region. This demonstrates how South African mineral beneficiation projects rely on stable regional industrial demand to maintain economic viability.
Cross-Border Supply Chain Disruption
South African companies have developed specialised capabilities serving the Mozambique aluminum sector over more than two decades. These include:
• Technical maintenance services for smelting equipment
• Specialised transportation for aluminum products
• Engineering consulting for process optimisation
• Raw material supply including carbon anodes and flux materials
The loss of this demand would force supplier diversification or downsizing, particularly affecting companies with limited geographic diversification beyond Southern Africa.
Alternative Solutions and Industry Precedents
South32 continues engaging with both HCB and South Africa's Eskom regarding potential power supply arrangements. However, cross-border electricity agreements face additional regulatory complexity and transmission infrastructure limitations. According to reports, the company faces significant challenges in securing viable alternatives.
Renewable Energy Integration Potential
Modern aluminum smelters increasingly explore renewable energy solutions, particularly solar and wind power combined with battery storage systems. However, the scale requirements for aluminum smelting present significant challenges:
• Consistent baseload power requirements of 950MW
• 24/7 operational needs incompatible with intermittent renewable sources
• Grid stability requirements for sensitive electrolytic processes
• Capital investment timelines extending beyond current agreement deadlines
Industry examples of successful renewable integration typically involve hybrid systems combining multiple power sources with substantial grid infrastructure investment.
Regional Power Pool Participation
The Southern African Power Pool (SAPP) facilitates electricity trading among member countries, potentially offering alternative supply arrangements. However, regional power constraints affect multiple members simultaneously, limiting available capacity for large industrial consumers.
Current SAPP trading volumes primarily address residential and small commercial demand rather than industrial consumers requiring consistent high-capacity supply. Institutional reforms may be necessary to accommodate large industrial power agreements across borders.
South32's Portfolio Diversification Strategy
Despite the Mozambique challenges, South32 demonstrated strong operational performance across other assets during the first quarter. The company achieved a 135% increase in quarterly manganese production to 1.4 million wet metric tons, significantly exceeding analyst expectations of 1.23 million tons.
The Australian manganese operations recovered successfully from Tropical Cyclone Megan damage, with domestic production reaching 854,000 tons compared to zero output in the previous year. South32 secured $503 million in insurance settlements related to cyclone damage, providing financial flexibility for portfolio optimisation. This diversification strategy aligns with broader trends in mining industry consolidation where companies seek to balance portfolio risks across multiple commodities.
Strategic Asset Management Focus
South32's diversified portfolio approach reduces dependence on single-asset performance, particularly important given the Mozambique situation. The company maintains production forecasts across all operations for fiscal 2026, indicating confidence in core asset performance.
Jefferies analysts highlighted the strong performance across core assets, noting that additional costs exceeded estimates but overall operational recovery demonstrated management capability. This performance provides strategic options for capital allocation away from problematic assets.
Market Response and Investor Sentiment
South32 shares jumped 6.3% to A$3.315 following the quarterly results announcement, reaching their highest level since late March 2025. This positive market response despite the Mozambique challenges indicates investor confidence in the company's broader strategic direction.
The market reaction suggests investors view South32's diversified portfolio as sufficient to absorb the Mozambique impact while benefiting from strengthening base metals markets. Manganese price recovery and operational improvements across Australian assets offset concerns about aluminum smelter closure.
Analyst Perspectives on Portfolio Resilience
Investment analysts increasingly focus on South32's core asset performance rather than Mozambique exposure, indicating market confidence in management's strategic positioning. The company's status as the world's largest manganese producer provides stability during aluminum sector challenges.
Forward-looking market sentiment benefits from expectations of strengthening base metals conditions, particularly manganese demand from steel production and battery applications. This diversification demonstrates the value of multi-commodity mining strategies in managing individual asset risks.
Long-Term Industry and Regional Implications
The South32 Mozambique smelter negotiations extend beyond individual company concerns to highlight broader challenges facing industrial development in emerging markets. Energy security emerges as a critical factor for sustained industrial investment in sub-Saharan Africa.
Climate resilience becomes increasingly important for industrial planning, as drought conditions affecting hydroelectric generation demonstrate infrastructure vulnerability to environmental changes. Future industrial development may require more diversified energy strategies to ensure operational continuity.
African Industrialisation Strategy Reassessment
Mozambique's industrialisation strategy faces a significant setback with potential Mozal closure. The facility represented successful technology transfer and large-scale manufacturing capability development, serving as a model for other African countries pursuing industrial diversification.
The outcome may influence future foreign direct investment decisions across the region, particularly for energy-intensive industries requiring long-term power supply certainty. Regional cooperation becomes essential for supporting large-scale industrial projects that exceed individual country capabilities.
Global Supply Chain Resilience Considerations
European aluminum supply chain security faces increased scrutiny following potential loss of Mozambique capacity. Strategic stockpiling considerations for critical materials may accelerate as supply source diversification becomes a policy priority.
Industrial policy coordination between trading partners gains importance as supply chain vulnerabilities become apparent. The situation demonstrates interconnections between climate change, energy infrastructure, and global manufacturing networks. Furthermore, detailed reporting suggests that time constraints are intensifying pressure on all parties to reach agreement.
Conclusion: Navigating Uncertain Waters
The South32 Mozambique smelter negotiations represent a critical inflection point for industrial development in Southern Africa. With March 2026 approaching as the definitive deadline, the outcome will significantly impact regional employment, supply chain structures, and future investment decisions.
The situation illustrates complex intersections between climate resilience, energy security, and industrial competitiveness in emerging markets. While South32's diversified portfolio provides financial flexibility, the broader implications for Mozambique's industrial development and regional aluminum supply chains extend far beyond individual company performance.
Success in resolving this situation requires innovative approaches to power supply arrangements, potentially involving renewable energy integration, regional cooperation mechanisms, and creative financing structures. The stakes extend beyond immediate operational concerns to encompass long-term industrial development strategies across Southern Africa.
Disclaimer: This analysis contains forward-looking statements and market assessments that involve inherent risks and uncertainties. Industrial investment decisions depend on multiple factors beyond current negotiations, and outcomes may differ materially from current expectations. Readers should conduct independent research before making investment decisions.
Are You Tracking Major Mining Developments Across Southern Africa?
Situations like the South32 Mozambique smelter crisis demonstrate how quickly industrial developments can impact regional markets and investment opportunities. Discovery Alert's proprietary Discovery IQ model provides real-time notifications on significant ASX mineral discoveries and mining developments, helping subscribers identify actionable opportunities as they emerge across diverse commodity sectors. Begin your 30-day free trial today at Discovery Alert to stay ahead of market-moving mining developments.