Autonomous mining technology represents a transformative shift in how mining operations approach safety, productivity, and environmental responsibility. This revolutionary approach combines AI-driven mining technology, sensor systems, and machine learning to create mining operations that can function with minimal human intervention while delivering substantial operational improvements.
What Is Autonomous Mining Technology and Why Does It Matter?
Modern mining operations face unprecedented pressure to improve safety standards, enhance productivity, and reduce environmental impact. These challenges have accelerated the development of sophisticated automated systems that represent a fundamental shift from traditional manual mining practices.
The integration of autonomous mining technology has become essential for companies seeking to remain competitive in an increasingly demanding market environment. Furthermore, the pressure from stakeholders for sustainable mining practices continues to drive innovation in this sector.
Defining Modern Autonomous Mining Systems
Autonomous mining technology encompasses integrated systems that combine artificial intelligence algorithms, advanced sensor networks, and machine learning capabilities to operate mining equipment with minimal human intervention. These systems utilise GPS positioning, LiDAR scanning, radar detection, and computer vision technologies to create comprehensive environmental awareness for mining equipment.
The distinction between semi-autonomous and fully autonomous operations lies in the degree of human oversight required. Semi-autonomous systems require operators to monitor and occasionally intervene in operations, while fully autonomous systems can execute complete mining cycles independently within predefined parameters.
However, the implementation of these systems requires careful consideration of industry innovation trends and technological capabilities. Moreover, successful deployment depends on comprehensive understanding of operational requirements and site-specific conditions.
The Economic Case for Mining Automation
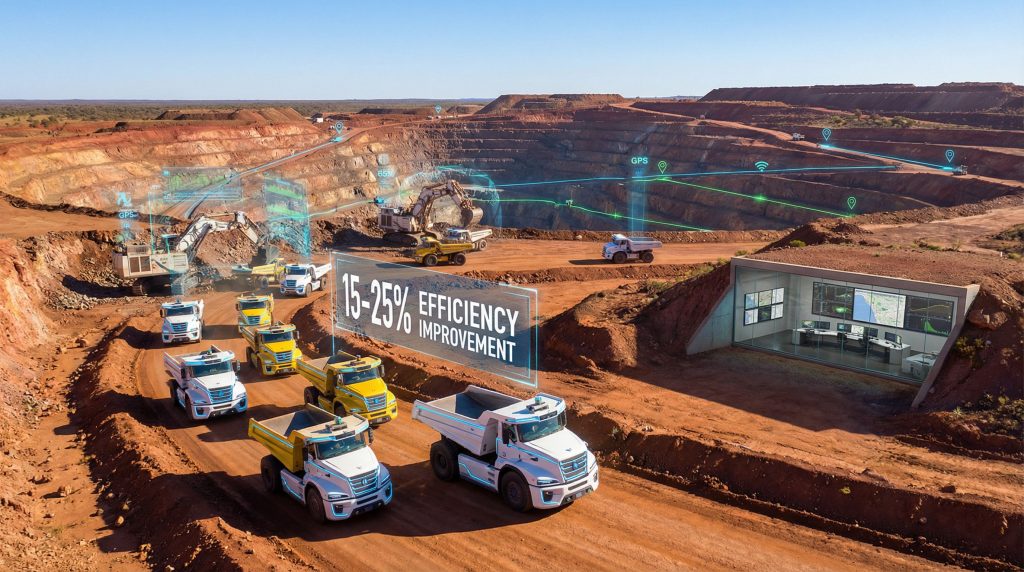
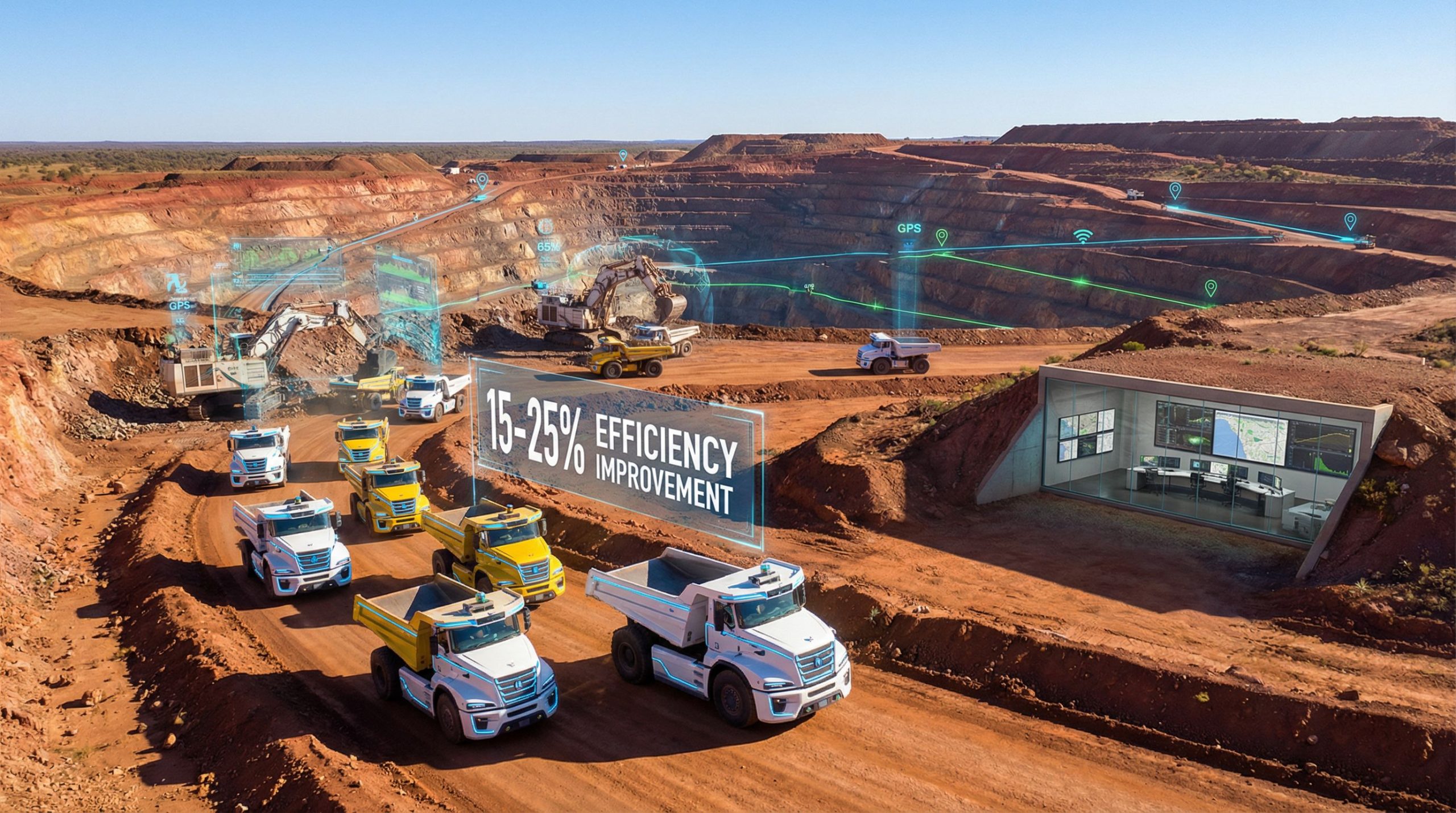
The financial justification for autonomous mining technology centres on substantial productivity improvements and cost reductions across multiple operational categories. Industry analysis suggests potential efficiency gains of 15-25% in autonomous operations compared to traditional methods, though actual results vary significantly based on site conditions and implementation quality.
| Metric | Traditional Operations | Autonomous Operations | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Equipment Utilisation | 65-75% | 85-95% | 20-30% increase |
| Fuel Efficiency | Baseline | 10-15% reduction | Cost savings |
| Maintenance Costs | Reactive approach | Predictive optimisation | 25-40% reduction |
| Safety Incidents | Industry average | 50-70% reduction | Risk mitigation |
Nevertheless, recent studies reveal that 72% of pilot projects in autonomous mining only partially meet their intended value objectives. This gap between potential and realised benefits highlights the importance of comprehensive implementation strategies that address technical, cultural, and organisational factors simultaneously.
Consequently, mining companies must approach autonomous mining technology implementation with realistic expectations and thorough planning. In addition, the integration of data-driven operations becomes crucial for maximising the return on investment.
How Do Autonomous Mining Systems Actually Work?
Fleet Coordination and Communication Infrastructure
Autonomous mining operations depend on robust communication networks that enable real-time coordination between multiple pieces of equipment. Private 5G networks have emerged as the preferred solution for mining sites, providing the low-latency, high-bandwidth connectivity required for continuous equipment monitoring and control.
These networks support Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystems where sensors throughout the mine site collect environmental data, equipment performance metrics, and operational parameters. Central command centres process this information using advanced algorithms to optimise routing, scheduling, and resource allocation across the entire mining operation.
The integration of edge computing capabilities allows critical decisions to be made locally, reducing dependence on constant connectivity and improving system resilience in remote mining locations. Furthermore, this approach enhances the effectiveness of advanced sensor systems throughout the operation.
Navigation and Safety Technologies
"The cornerstone of autonomous mining safety lies in sophisticated proximity detection and collision avoidance systems that create virtual safety zones around equipment and personnel."
Navigation systems combine multiple technologies to create precise positioning and movement capabilities. GPS provides broad location awareness, while LiDAR and radar systems offer detailed environmental mapping and obstacle detection. Computer vision technologies analyse visual information to identify potential hazards, changes in terrain, and operational parameters.
Real-time route optimisation algorithms continuously adjust equipment paths based on changing site conditions, traffic patterns, and operational priorities. These systems can adapt to weather changes, equipment failures, and unexpected obstacles while maintaining safety protocols and productivity targets.
What Are the Major Categories of Autonomous Mining Equipment?
Autonomous Haul Trucks and Transport Systems
Large-scale haul trucks represent the most visible and widely deployed autonomous mining equipment. These vehicles, typically with payload capacities ranging from 100 to 400 tons, operate continuously without human drivers, following predetermined routes while adapting to real-time conditions.
Leading manufacturers including Caterpillar, Komatsu, and Hitachi have developed specialised autonomous truck systems designed for mining environments. These vehicles feature redundant safety systems, advanced collision avoidance technology, and the ability to communicate with other equipment and central control systems.
| Model | Manufacturer | Payload Capacity | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| 794 AC | Caterpillar | 291 tonnes | Cat MineStar Command system |
| 930E-5SE | Komatsu | 327 tonnes | FrontRunner AHS integration |
| EH5000AC-3 | Hitachi | 296 tonnes | Autonomous haulage capability |
Self-Operating Drilling and Extraction Equipment
Autonomous drilling systems utilise AI-guided positioning to achieve precise hole placement and depth control. These systems can operate continuously, eliminating traditional shift-based limitations and improving consistency in blast hole patterns. Advanced sensor technology allows drilling equipment to adapt to varying rock conditions and adjust parameters automatically to maintain optimal performance.
The integration with blast planning software enables drilling systems to execute complex patterns with millimetre precision, improving fragmentation quality and reducing downstream processing costs. For instance, this precision becomes particularly valuable when implementing autonomous mining technology across multiple drilling sites simultaneously.
Autonomous Loading and Processing Machinery
Modern excavator automation combines hydraulic control systems with computer vision to identify optimal loading positions and bucket trajectories. These systems can distinguish between different material types and adjust loading techniques accordingly, improving efficiency and reducing equipment wear.
Conveyor belt integration allows automated material handling from extraction through processing, with sensor-based mineral identification systems providing real-time quality control. This integration enables continuous optimisation of material flow and processing parameters throughout the operation.
Which Mining Companies Are Leading Autonomous Adoption?
Global Mining Giants and Their Automation Strategies
Rio Tinto has established itself as a pioneer in autonomous mining deployment, particularly through its operations in the Pilbara region of Western Australia. The company operates one of the world's largest autonomous haul truck fleets, with over 130 driverless trucks moving iron ore across multiple mine sites.
BHP has implemented a comprehensive technology integration timeline that includes autonomous trucks, trains, and drilling systems. The company's integrated remote operations centres monitor and control equipment across multiple sites, demonstrating the scalability of autonomous mining technology.
Fortescue Metals Group has focused on autonomous trains and is expanding into truck automation, while Anglo American has piloted autonomous systems across multiple commodities including copper, diamonds, and platinum group metals. Additionally, these companies have recognised the importance of integrating autonomous mining technology with broader operational strategies.
Technology Partnerships and Vendor Relationships
Mining companies typically choose between custom solution development and off-the-shelf systems based on their specific operational requirements and risk tolerance. Strategic alliances between mining operators and technology providers have become essential for successful implementation, with partnerships often involving multi-year development and support agreements.
Regional implementation varies significantly, with Australian operations leading in deployment scale, while Latin American and African mining operations focus on pilot projects and gradual expansion. However, successful implementation requires careful consideration of local conditions and regulatory requirements.
What Challenges Are Slowing Autonomous Mining Adoption?
Technical Infrastructure and Connectivity Barriers
Remote mining locations face significant connectivity limitations that impact autonomous system reliability. Many Latin American mines struggle with limited network infrastructure, while legacy system integration creates complex technical challenges. The convergence of Information Technology (IT) and Operational Technology (OT) systems creates compatibility issues that increase operational risks and implementation costs.
| Challenge Category | Impact Level | Typical Resolution Time | Investment Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| Network Infrastructure | High | 12-24 months | $5-20 million |
| Legacy System Integration | Medium | 6-18 months | $2-10 million |
| Skills Development | High | 24-36 months | $1-5 million |
| Change Management | Very High | 36-48 months | $3-15 million |
Workforce Transition and Cultural Adaptation
Cultural resistance represents the primary challenge in autonomous mining adoption, identified by 27.5% of industry survey participants. This resistance stems from concerns about job security, scepticism regarding new technology reliability, and uncertainty about changing work roles.
Successful workforce transition requires comprehensive change management strategies that demonstrate how autonomous mining technology enhances rather than replaces human capabilities. Organisations must invest in skill retraining programmes that prepare workers for technical roles in equipment monitoring, data analysis, and system maintenance.
Labour relations and union considerations play crucial roles in autonomous adoption, requiring transparent communication about employment impacts and career development opportunities in automated operations. Furthermore, successful implementation depends on addressing these concerns proactively rather than reactively.
Financial Investment and ROI Timeline Concerns
Initial investment requirements for autonomous mining infrastructure often exceed short-term financial expectations, creating barriers for project approval and continued funding. Twenty-three percent of industry participants acknowledge that infrastructure costs for autonomous fleets, sensors, connectivity networks, and integration platforms challenge traditional mining investment models.
"Successful autonomous mining projects require linking investments to strategic key performance indicators and establishing return on investment horizons that align with mining planning cycles rather than quarterly financial reporting."
Risk assessment frameworks must account for technology obsolescence, operational disruptions during implementation, and the potential for partial rather than complete objective achievement in pilot projects. Consequently, companies must develop realistic expectations and comprehensive planning approaches for autonomous mining technology deployment.
How Does Cybersecurity Impact Autonomous Mining Operations?
IT/OT Convergence Security Risks
The increasing convergence of Information Technology and Operational Technology systems in autonomous mining creates new cybersecurity vulnerabilities. Industrial control systems that previously operated in isolation now connect to broader networks, creating potential attack vectors that could paralyse critical operations and compromise worker safety.
Cybersecurity incidents targeting mining operations can result in production shutdowns, equipment damage, and safety hazards. The remote nature of many mining operations compounds these risks by limiting immediate response capabilities and increasing dependence on automated systems for critical functions.
Moreover, the sophistication of automated mining systems creates additional complexity in securing these operations against cyber threats.
Secure Architecture Design Principles
Effective cybersecurity for autonomous mining requires preventive approaches implemented during system design phases rather than reactive security measures added after deployment. Secure architecture principles include implementation of redundancy systems, robust recovery plans, and continuous monitoring of data and system integrity.
Multi-layered security frameworks incorporate network segmentation, encryption protocols, authentication systems, and behavioural analysis to detect and respond to potential threats. These systems must operate reliably in harsh mining environments while maintaining the performance requirements of autonomous operations.
What Does the Future Hold for Autonomous Mining Technology?
Emerging Technologies and Next-Generation Systems
Machine learning advancement in predictive maintenance represents a significant opportunity for autonomous mining optimisation. These systems can analyse equipment performance data to predict failures before they occur, enabling proactive maintenance scheduling that minimises operational disruptions.
Integration with renewable energy systems offers potential for sustainable autonomous operations, particularly in remote locations where traditional power infrastructure is limited or expensive. Solar and wind power systems combined with battery storage can provide reliable energy for autonomous equipment while reducing operational costs and environmental impact.
| Technology Area | Current Status | 5-Year Outlook | 10-Year Projection |
|---|---|---|---|
| AI/Machine Learning | Pilot deployment | Widespread adoption | Standard practice |
| Renewable Integration | Limited trials | Common implementation | Universal standard |
| 5G/6G Networks | Early deployment | Full coverage | Next-gen capabilities |
| Edge Computing | Emerging adoption | Standard feature | Advanced optimisation |
Market Growth Projections and Investment Trends
Global market forecasts for autonomous mining equipment suggest significant growth driven by safety regulations, productivity pressures, and technological maturation. However, the gap between pilot project expectations and realised benefits indicates that growth may be more gradual than initial projections suggested.
Investment trends show increasing focus on integrated solutions rather than individual equipment automation. Investors and mining companies recognise that successful autonomous operations require comprehensive systems thinking rather than piecemeal technology adoption.
Furthermore, the evolution of autonomous mining technology will likely accelerate as companies gain more experience with implementation and optimisation strategies.
Regulatory Evolution and Industry Standards
Safety certification requirements for autonomous equipment continue evolving as regulators gain experience with deployed systems. International standards development organisations are working to establish consistent frameworks for autonomous mining equipment certification and operation.
Environmental compliance considerations increasingly favour autonomous operations due to their potential for optimised resource utilisation and reduced environmental impact. Regulatory frameworks may eventually provide preferential treatment for autonomous operations that demonstrate superior environmental performance.
How Can Mining Companies Successfully Implement Autonomous Technology?
Strategic Planning and Phased Implementation
Successful autonomous mining implementation requires comprehensive strategic planning that extends beyond technology acquisition to encompass organisational culture, governance structures, and capability development. Companies must define clear roadmaps that consider scaling requirements from initial pilot phases through full operational deployment.
- Feasibility Assessment: Evaluate site conditions, infrastructure requirements, and operational compatibility
- Pilot Project Design: Develop limited-scope implementations with clear success metrics and scaling pathways
- Infrastructure Development: Establish communication networks, power systems, and support facilities
- System Integration: Connect autonomous equipment with existing operational systems and processes
- Performance Monitoring: Implement continuous measurement systems to track progress against objectives
- Scaling Execution: Expand successful pilot implementations to broader operational areas
Performance metrics must quantify generated value rather than simply measuring technical functionality. Organisations need indicators that demonstrate business impact, safety improvements, and operational efficiency gains.
Vendor Selection and Technology Integration
Technology vendor evaluation must consider long-term partnership potential rather than simply initial system capabilities. Successful autonomous mining operations depend on ongoing technical support, system updates, and collaborative problem-solving between mining companies and technology providers.
Integration planning with existing operational systems requires careful consideration of compatibility, data flow, and process optimisation. Legacy system modification or replacement may be necessary to achieve full autonomous operation benefits.
"The most critical factor in autonomous mining success is selecting partners who understand mining operations rather than simply technology deployment."
Change Management and Workforce Development
Cultural transformation strategies must address workforce concerns while demonstrating the benefits of autonomous operations for employee safety, job satisfaction, and career development. Training programmes should focus on developing technical skills for equipment monitoring, data analysis, and system troubleshooting.
Communication frameworks for stakeholder engagement must provide transparent information about implementation timelines, employment impacts, and operational changes. Regular feedback mechanisms allow organisations to address concerns and adjust implementation strategies based on workforce input.
In addition, successful change management requires demonstrating how autonomous mining technology enhances rather than replaces human capabilities in modern mining operations.
Frequently Asked Questions About Autonomous Mining Technology
What are the safety benefits of autonomous mining?
Autonomous mining technology significantly reduces safety risks by removing human operators from dangerous environments and eliminating human error factors in equipment operation. Advanced sensor systems and collision avoidance technology create comprehensive safety zones around equipment, while predictive maintenance capabilities prevent equipment failures that could create safety hazards.
How much does it cost to implement autonomous mining systems?
Implementation costs vary significantly based on operation size, site conditions, and automation scope. Initial investments typically range from $5 million for pilot projects to over $100 million for comprehensive fleet automation. However, 23% of industry participants report that infrastructure costs often exceed initial expectations, making careful financial planning essential for project success.
Can autonomous mining work in all types of mining operations?
Autonomous mining technology adapts to different mining methods, but implementation complexity varies considerably. Open-pit operations with predictable conditions and established traffic patterns are most suitable for autonomous deployment. Underground mining, alluvial operations, and sites with complex geology present greater technical challenges that may require specialised solutions or extended development timelines.
What happens to mining jobs when operations become autonomous?
Autonomous mining transforms rather than eliminates employment opportunities. While traditional operator positions may decrease, new roles emerge in system monitoring, data analysis, equipment maintenance, and technical support. Successful implementations include comprehensive retraining programmes that help existing employees develop skills for these evolved positions.
How reliable are autonomous mining systems in extreme weather?
Modern autonomous mining systems include environmental adaptation capabilities that allow continued operation in challenging weather conditions. However, extreme weather events may require temporary suspension of autonomous operations for safety reasons. System design includes weather monitoring capabilities and automated protocols for safe equipment shutdown when conditions exceed operational parameters.
Disclaimer: The autonomous mining technology industry continues evolving rapidly, and implementation success varies significantly based on site-specific conditions, organisational readiness, and technology selection. Companies considering autonomous mining adoption should conduct thorough feasibility assessments and engage with experienced technology partners to develop appropriate implementation strategies. Investment decisions should consider both potential benefits and inherent risks associated with emerging technology deployment in industrial operations.
Ready to Invest in the Next Major Mineral Discovery?
Discovery Alert instantly alerts investors to significant ASX mineral discoveries using its proprietary Discovery IQ model, turning complex mineral data into actionable insights. Understand why historic discoveries can generate substantial returns by visiting Discovery Alert's dedicated discoveries page, showcasing historic examples of exceptional outcomes, and begin your 30-day free trial today to position yourself ahead of the market.