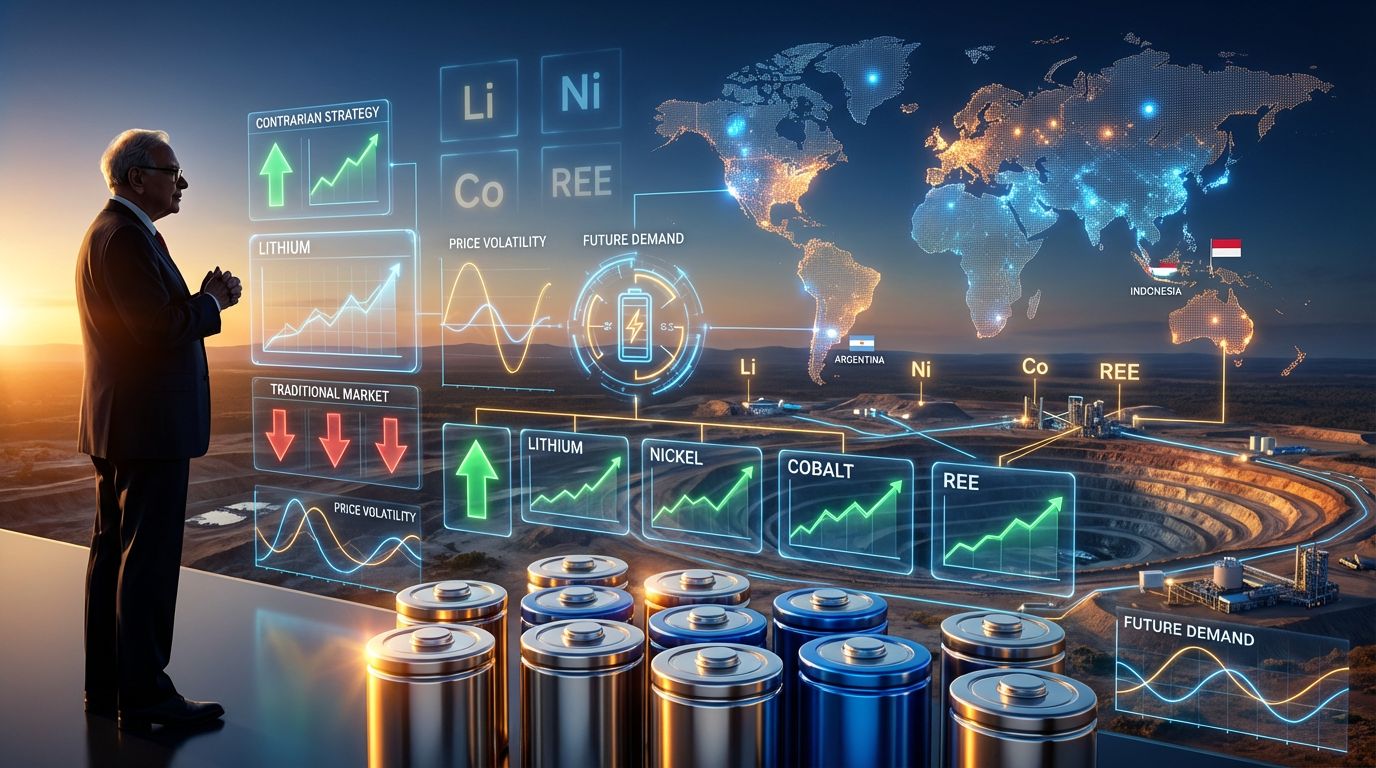
Market sentiment around critical materials often follows predictable patterns of euphoria and despair, yet beneath these surface fluctuations lie structural forces that savvy investors can exploit. When institutional capital flows toward underperforming assets while retail enthusiasm wanes, contrarian opportunities emerge that can generate substantial returns for patient investors willing to challenge conventional wisdom.
The battery metals sector exemplifies this dynamic perfectly, with lithium trading flat year-to-date, graphite experiencing poor performance, and nickel struggling despite long-term demand fundamentals. These temporary dislocations create entry points for investors who understand that commodity cycles operate on different timelines than equity markets, particularly when implementing a contrarian investment in battery metals strategy.
Understanding Contrarian Investment Philosophy in Critical Materials Markets
Defining Contrarian Strategy Beyond Traditional Metrics
Contrarian investing in critical materials requires distinguishing between temporary market pessimism and fundamental value destruction. Warren Buffett's principle of being fearful when others are greedy applies particularly well to commodity cycles, where price volatility can create emotional decision-making among less experienced investors.
The key lies in recognising that contrarian investors use the same information available to everyone else but question whether conventional analysis correctly interprets that data. This sceptical approach becomes crucial when evaluating battery metals investment landscape, where supply-demand narratives can shift rapidly based on geopolitical developments or technological changes.
Risk-adjusted return expectations in volatile commodity markets must account for extended holding periods and significant drawdowns. Successful contrarian positions often require conviction to maintain exposure during periods when the investment thesis appears to be failing.
Market Psychology Patterns in Battery Metal Cycles
Institutional versus retail investor behaviour during commodity downturns reveals important timing signals for contrarian positioning. Smart money typically accumulates positions during periods of maximum pessimism, while retail investors tend to capitulate near market bottoms.
ETF outflow patterns serve as contrarian opportunity indicators, particularly when they occur during fundamental price appreciation. When gold reached new highs in 2024 while experiencing continued ETF outflows, it demonstrated that institutional and central bank buying was driving the move rather than speculative retail interest.
This pattern suggests that precious metals remain contrarian investments despite their strong performance, as retail participation has not reached levels that typically mark market tops. The same principle applies to battery metals, where poor year-to-date performance has created widespread investor apathy.
Furthermore, recognising these behavioural patterns becomes essential when pursuing contrarian junior mining success in the current market environment.
Why Battery Metals Present Exceptional Contrarian Opportunities
Structural Supply-Demand Imbalances Create Long-Term Value
Battery metal demand growth projections vary significantly by material type and timeframe. The International Energy Agency's 2024 Critical Minerals Market Review projects lithium demand growing approximately 3.2 times from 2023 to 2030, while battery nickel demand could increase 10-15 times depending on chemistry evolution.
Cobalt faces projected 5-8 times demand growth through 2030, while graphite markets anticipate 4-6 times expansion based on BloombergNEF analysis. These growth rates, while substantial, require careful evaluation against supply response capabilities and technology substitution risks.
Processing capacity bottlenecks represent a critical constraint often overlooked by investors focused solely on raw material availability. Chinese dominance in cathode manufacturing stems from technological expertise rather than capital availability, creating barriers that cannot be overcome quickly through increased investment alone.
The complexity of chemical engineering in cathode production means that 80% of global scientific papers on metallurgy and material engineering are produced in China, even when translated to English. This knowledge concentration creates competitive advantages that extend beyond simple cost considerations.
Market Timing Advantages in Current Environment
Battery Metal Performance Analysis (2024 YTD)
| Metal Category | Price Performance | Supply Constraints | Technology Risk | Contrarian Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lithium | Flat/Declining | Moderate | Low | High |
| Nickel | Underperforming | High | Moderate | Very High |
| Graphite | Poor | High | Low | High |
| Cobalt | Mixed | Very High | High | Moderate |
| Rare Earths (Heavy) | Variable | Extreme | Low | Very High |
Current market conditions reflect significant disconnects between short-term price performance and long-term fundamentals. Lithium spot prices for battery-grade carbonate trade around $14-16 per kilogram, representing an 80% decline from 2022 highs of $78 per kilogram, despite continued demand growth from electric vehicle adoption.
Nickel's poor performance reflects Indonesian laterite flooding that increased global production over 800% from 2017-2022. However, Indonesian producers now face margin pressure from increased royalty rates and sulphuric acid cost inflation, creating potential supply rebalancing opportunities.
Which Battery Metals Offer the Greatest Contrarian Value?
Nickel – The Most Overlooked Opportunity
Indonesian laterite production transformed global nickel markets through new HPAL (High Pressure Acid Leaching) technology, creating artificial oversupply in Class 1 nickel. This disruption masks underlying value in high-quality sulphide deposits that maintain superior economics and product specifications.
Current Indonesian producers operate near breakeven levels at LME prices around $9,000 per tonne, with processing costs ranging $7-10 per pound for laterite operations compared to $6-8 per pound for sulphide deposits. Increased royalty rates from 5% to 10% in 2023, combined with sulphuric acid cost increases of 400% during certain periods, have compressed margins significantly.
Projects like Sentus Metals in Brazil represent quality sulphide deposits that could benefit from supply rationalisation. Brazilian sulphide operations offer grade advantages and lower processing complexity compared to Indonesian laterites, creating competitive positioning as market conditions normalise.
Technological shifts in battery chemistry also favour specific nickel qualities. While Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) batteries can tolerate lower purity nickel, Nickel Cobalt Aluminium (NCA) chemistry requires premium sulphide nickel, maintaining differentiated demand for high-quality deposits.
Lithium Brine Projects – Geographic Arbitrage Opportunities
Argentine brine assets trade at significant discounts to Australian spodumene projects, with valuations ranging 0.3-0.8 times project NPV compared to 1.2-1.8 times for hard rock alternatives. This discount reflects longer development timelines and regulatory uncertainties but creates value opportunities for patient investors.
Processing technology advantages in Argentine brines include:
- Natural lithium chloride concentrations reaching 5-7% versus 1-2% in most other brines
- Recovery efficiency of 60-80% for quality Argentine deposits
- Established evaporation pond infrastructure reducing capital requirements
- Proven hydrogeochemistry in the Atacama basin
Partnership structures with major industrial players reduce development risk significantly. Companies like Lithium Argentina benefit from venture partnerships that provide technical expertise and potential offtake agreements, creating strategic value beyond pure asset quality.
Water availability concerns in the Atacama region create both risks and opportunities, as drought cycles may constrain some operations while benefiting projects with superior water rights or alternative processing technologies. However, understanding these dynamics requires comprehensive innovative lithium strategies in today's market.
Heavy Rare Earth Elements – True Scarcity Value
Heavy rare earth elements face genuine supply constraints that justify contrarian positioning despite recent price strength. Terbium, dysprosium, and samarium concentrate at only five parts per million in most rare earth deposits, creating inherent scarcity that cannot be easily resolved through increased mining activity.
China and Myanmar control approximately 95% of global dysprosium supply and 98% of terbium production, according to U.S. Geological Survey data. This concentration creates pricing disparities where Western markets pay 3-4 times Chinese prices for the same materials.
Current market spreads demonstrate the premium for non-Chinese supply:
- Dysprosium: Western pricing $400-600/kg versus Chinese pricing $100-150/kg
- Terbium: Similar 3-4x premium structure
- Processing complexity requiring over 200 individual chemical separation steps
Brazilian yttrium clays represent potential alternative sources, though commercial production remains theoretical rather than operational. The country possesses significant monazite deposits but currently lacks commercial rare earth separation facilities, limiting near-term supply diversification.
In addition, conducting comprehensive rare earth reserves analysis helps investors understand global supply dynamics and potential opportunities.
Strategic Investment Framework for Battery Metal Contrarians
Due Diligence Criteria for Contrarian Positions
Asset quality assessment requires evaluation across multiple dimensions that extend beyond traditional mining metrics. Grade and scale matter, but jurisdiction quality, infrastructure access, and regulatory stability often determine project success more than resource characteristics alone.
Management track record becomes particularly important in commodity cycle navigation. Teams that have successfully operated through previous downturns understand working capital management, cost optimisation, and strategic timing that separate surviving companies from those that fail during extended market weakness.
Balance sheet strength for surviving extended development timelines cannot be overstated in critical materials investing. Projects that appeared financially robust at commodity peaks often face funding challenges when markets decline, creating opportunities for well-capitalised competitors or distressed acquisition scenarios.
Strategic partnerships with end-users or government backing provide validation signals and reduced market risk. U.S. Department of Defense involvement in projects like Thacker Pass demonstrates governmental recognition of strategic value, though investors should distinguish between loan guarantees and direct equity participation.
Risk Management in Volatile Commodity Markets
Position sizing strategies for high-volatility assets must account for correlation risks across the critical materials sector. Battery metals often move together during broad commodity cycles, reducing diversification benefits compared to traditional sector allocation approaches.
Hedging approaches using commodity derivatives face limitations in smaller metals markets where liquidity constraints make effective hedging expensive or impractical. Natural hedging through diversification across development stages and geographic regions often provides better risk management than financial derivatives.
Portfolio diversification across metal types requires understanding end-use applications and substitution risks. Metals serving defence applications may demonstrate different demand patterns than those primarily used in consumer electronics or automotive applications.
Geopolitical Factors Reshaping Battery Metal Investment Logic
Western Supply Chain Security Premium
Government equity participation in strategic projects creates validation signals but requires careful analysis of terms and conditions. The U.S. Department of Energy's conditional commitment of approximately $2.5 billion for Thacker Pass represents significant federal support, though the structure involves loan guarantees rather than direct equity stakes.
Defence Department funding creates validation signals through strategic stockpile requirements and munitions applications. Antimony's classification as critical for fuses, primers, and tracers has driven government purchase agreements that establish demand floors for domestic production capabilities.
Trade policy impacts on Chinese-dominated supply chains create both opportunities and risks for Western projects. Recent export restrictions on critical materials demonstrate how quickly geopolitical developments can reshape market dynamics and pricing structures.
Technology Transfer and Processing Capability Gaps
Rare earth separation facility learning curves require 3-5 years to achieve commercial-grade purities, based on industry experience at facilities like Molycorp's Mountain Pass and Lynas Rare Earths' Malaysian operations. This timeline represents a fundamental constraint on supply response that creates sustained opportunities for existing producers.
Chemical engineering expertise concentration in Asia reflects decades of knowledge development that cannot be quickly replicated through capital investment alone. The complexity of cathode manufacturing involves proprietary processes that represent genuine competitive moats for companies possessing this expertise.
Research and development investment requirements for competitive positioning often exceed initial capital cost estimates. Companies must budget not only for facility construction but also for the extended learning period required to achieve consistent product quality and competitive unit costs.
Sector-Specific Contrarian Opportunities and Risks
Uranium – Nuclear Renaissance Driving Demand
Small modular reactor deployment creates additional uranium demand beyond traditional large reactor requirements. These facilities require fuel loading at higher frequencies than conventional plants, creating sustained consumption patterns that may exceed current supply planning assumptions.
Geopolitical supply disruptions from traditional sources have highlighted Western dependence on Russian and Kazakh uranium supplies. Strategic stockpile rebuilding requirements create additional demand that operates independently of electricity generation needs.
Nuclear fuel inventory rebuilding cycles provide sustained price support as utilities rebuild working inventories depleted during the extended uranium bear market. This process typically requires multi-year procurement programs that create predictable demand patterns.
Consequently, understanding uranium market volatility becomes crucial for investors positioning themselves in the nuclear fuel sector.
Tungsten and Specialty Metals – Industrial Demand Resilience
Chinese export restrictions create Western supply premiums that have driven tungsten prices from approximately $300 per metric ton unit to over $500 per metric ton unit. The Shandong mine in South Korea represents the primary non-Chinese supply addition, making its operational performance critical for global market balance.
Defence and aerospace applications provide demand floors that operate independently of general industrial cycles. Tungsten carbide tools and armour applications maintain strategic importance that supports pricing during economic downturns.
Limited global production capacity outside China creates structural supply constraints that cannot be quickly resolved through increased investment. Processing complexity and environmental considerations limit potential supply response even when prices reach economically attractive levels.
Vanadium – Energy Storage Applications Emerging
Vanadium redox flow batteries represent growing applications beyond traditional steel industry demand. This energy storage technology grows over 20% annually in grid-scale applications, though it remains approximately 10% of total vanadium consumption.
Steel industry demand provides baseline consumption that supports vanadium pricing during periods when energy storage applications remain limited. Construction-dependent rebar applications create cyclical volatility but maintain underlying demand floors.
Supply concentration in China creates price volatility opportunities similar to other critical materials. Western vanadium production remains limited, creating potential arbitrage opportunities for projects capable of achieving commercial production.
Investment Vehicle Selection and Implementation Strategies
Direct Equity vs. ETF Approaches
Individual mining company selection requires detailed technical analysis of resource quality, management capability, and development timelines. This approach offers superior upside potential but demands significant due diligence capabilities and ongoing monitoring resources.
Diversified battery metals ETFs provide broader exposure but may include companies with questionable asset quality or excessive development risk. Performance analysis of existing ETFs reveals significant tracking error relative to underlying commodity prices due to corporate-specific risks.
For instance, battery metals investment analysis offers valuable insights into sector dynamics and individual company evaluations that can inform investment decisions.
Private placement and pre-IPO opportunities in development projects offer potential value creation but require sophisticated investor capabilities and extended liquidity timelines. These investments often provide better pricing than public markets but demand comprehensive technical and legal due diligence.
Timing and Entry Point Optimization
Technical analysis applications in commodity investing focus on long-term trend identification rather than short-term trading opportunities. Multi-year chart patterns often provide better timing signals than daily price movements in volatile metals markets.
Fundamental catalyst identification for position initiation includes permitting approvals, financing completions, and strategic partnership announcements. These events often create sustainable price movements that support contrarian positioning strategies.
Dollar-cost averaging strategies work particularly well in volatile critical materials markets where precise timing proves difficult even for experienced investors. Systematic accumulation during periods of negative sentiment often produces superior results compared to attempts at perfect market timing.
Furthermore, lessons from the battery metals bust provide valuable guidance on timing and risk management strategies.
Common Pitfalls in Contrarian Battery Metal Investing
Avoiding Value Traps and Failed Projects
Management quality assessment frameworks must evaluate previous experience in similar commodity cycles and project development contexts. Teams lacking operational experience during market downturns often struggle with working capital management and strategic decision-making under pressure.
Permitting and regulatory risk evaluation requires understanding local political dynamics and environmental considerations that extend beyond technical project feasibility. Projects that appear economically attractive may face insurmountable regulatory obstacles that are not immediately apparent.
Capital requirements versus financing availability analysis becomes critical during periods when capital markets restrict access for development-stage companies. Projects requiring additional funding during market downturns often face significant dilution or development delays.
Technology Disruption Risks
Battery chemistry evolution impacts specific metal demand patterns in ways that may not be immediately apparent. The shift toward LFP batteries in Chinese markets reduces nickel intensity while increasing lithium and phosphate requirements, creating winners and losers within the battery metals complex.
Recycling technology advancement potentially reduces primary demand for certain metals, though current recycling rates remain low for most battery materials. End-of-life battery processing capabilities lag behind production growth, creating near-term opportunities even if long-term recycling improves.
Alternative material substitution possibilities require ongoing monitoring of research and development activities in battery chemistry, permanent magnets, and other critical applications. Technological breakthroughs can quickly reshape demand patterns for specific materials.
Future Outlook and Long-Term Contrarian Positioning
Electrification Megatrend Sustainability
Transportation sector transformation timelines extend beyond current political cycles, creating sustained demand growth regardless of short-term policy changes. Electric vehicle adoption continues growing globally even as specific regional policies evolve.
Grid storage deployment acceleration creates additional battery metal demand that operates independently of transportation applications. Renewable energy integration requires energy storage solutions that support continued critical materials consumption growth.
Industrial electrification expands metal requirements beyond traditional automotive and consumer electronics applications. Manufacturing processes increasingly adopt electric systems that require critical materials for motors, controls, and energy storage systems.
Supply Response Lag Creating Opportunity Windows
Mine development timelines versus demand growth rates create structural imbalances that persistent investors can exploit. New mining projects typically require 7-10 years from discovery to production, while demand growth accelerates over much shorter timeframes.
Processing capacity expansion requirements often receive insufficient attention from investors focused on raw material availability. Chemical processing facilities require specialised expertise and extended commissioning periods that create additional supply constraints.
Infrastructure development needs in emerging production regions add complexity and timeline risk to new supply additions. Projects in remote locations require substantial infrastructure investment that may not be justified without sustained high commodity prices.
Building Conviction in Contrarian Battery Metal Strategies
Portfolio Construction Principles
Risk-adjusted return optimisation across metal types requires understanding correlation patterns and end-use application diversity. Metals serving multiple industries typically demonstrate better risk-adjusted returns than those dependent on single applications.
Geographic and political risk diversification becomes increasingly important as geopolitical tensions affect critical materials supply chains. Projects in stable jurisdictions command valuation premiums that may justify lower resource grades or higher operating costs.
Development stage allocation strategies balance risk and return potential through systematic exposure to exploration, development, and production-stage companies. Early-stage investments offer higher upside potential but require longer timeframes and higher risk tolerance.
Monitoring Framework for Position Management
Key performance indicators for contrarian thesis validation include supply-demand balance evolution, pricing trends relative to production costs, and regulatory developments affecting supply chain security. Regular assessment prevents emotional decision-making during periods of price volatility.
Exit strategy development for successful positions requires predetermined criteria for profit-taking and position reduction. Contrarian investments often generate substantial returns over extended periods, making systematic profit-taking important for portfolio management.
Rebalancing triggers based on market cycle evolution help maintain appropriate risk exposure as contrarian positions mature. Successful contrarian investments eventually become consensus positions, requiring portfolio adjustments to maintain optimal risk-return characteristics.
The contrarian investment in battery metals reflects temporary market dislocations that obscure compelling long-term fundamentals. Patient investors willing to withstand volatility and maintain conviction through negative sentiment periods are positioned to benefit from structural supply-demand imbalances that cannot be quickly resolved through increased investment alone.
However, implementing a successful contrarian investment in battery metals strategy requires careful consideration of asset quality, management capabilities, and market timing factors that distinguish genuine value opportunities from permanent capital impairment risks.
Disclaimer: This analysis represents educational content and does not constitute investment advice. Critical materials investments involve substantial risks including commodity price volatility, regulatory changes, and technical development challenges. Investors should conduct thorough due diligence and consider their risk tolerance before making investment decisions in this sector.
Are You Positioned for the Next Battery Metals Discovery?
Discovery Alert's proprietary Discovery IQ model delivers real-time notifications on significant ASX mineral discoveries, including critical battery metals breakthroughs that could benefit from current market pessimism. Explore how major discoveries can generate substantial market returns or begin your 30-day free trial today to identify actionable contrarian opportunities ahead of the broader market.