Understanding the Regulatory Architecture Behind America's Critical Minerals Bottleneck
The United States controls vast domestic rare earth deposits yet remains strategically vulnerable to supply chain disruptions from adversarial nations. This paradox reflects deeper structural challenges within America's regulatory framework rather than simple resource scarcity. While policymakers debate industrial strategy and defence spending, the fundamental constraint lies within permitting reform in rare earths that can require nearly a decade to approve critical mineral projects.
The regulatory bottleneck represents more than bureaucratic inefficiency. It embodies a collision between environmental stewardship obligations and national security imperatives, creating a complex policy environment where traditional mining approval processes struggle to accommodate the urgency of strategic mineral security. Understanding this tension requires examining how regulatory frameworks either enable or constrain domestic production capabilities.
What Is Permitting Reform and Why Does It Matter for Rare Earth Security?
Defining Critical Minerals Permitting in the Modern Context
Federal permitting for rare earth projects operates through multiple overlapping jurisdictions, each governed by distinct regulatory authorities and timelines. The National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) requires comprehensive environmental impact assessments, while the Clean Water Act mandates water quality certifications, and the Mine Safety and Health Administration oversees operational safety protocols. Furthermore, state-level requirements add additional layers of complexity, often requiring separate environmental reviews, water rights allocations, and local zoning approvals.
This multi-jurisdictional approach creates sequential dependencies where permits must often be obtained in specific orders, with each approval contingent upon previous authorisations. Unlike conventional manufacturing facilities, rare earth extraction involves complex chemical processing that triggers additional regulatory scrutiny under the Toxic Substances Control Act and Resource Conservation and Recovery Act.
The Strategic Importance of Regulatory Streamlining
The Defense Production Act has authorised significant federal investments in domestic rare earth production, with Pentagon conditional loans targeting companies like MP Materials and ReElement Technologies. However, these investments cannot achieve their strategic objectives if regulatory approval timelines exceed the planning horizons of both private investors and military procurement cycles.
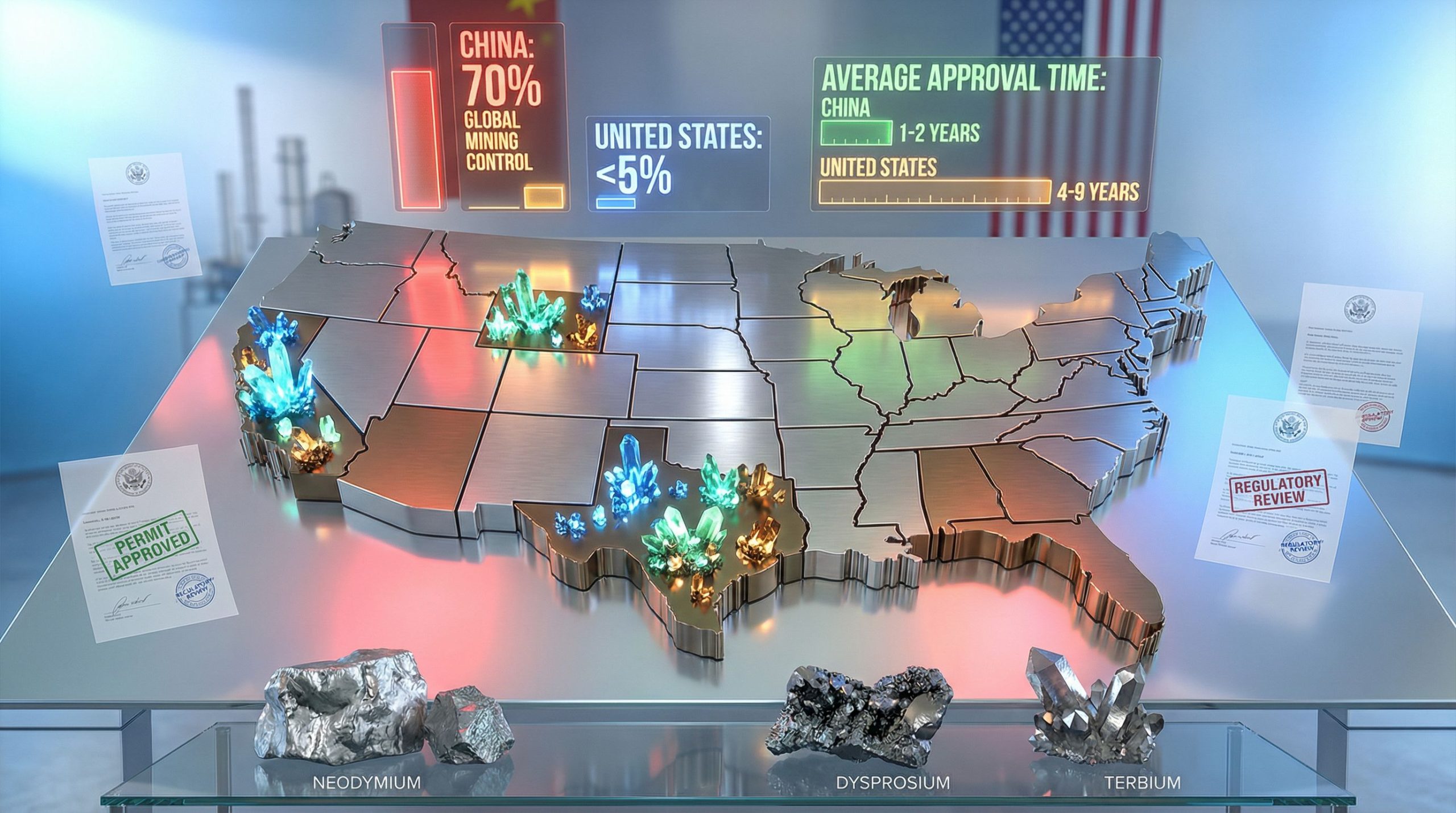
China's dominance in rare earth markets stems partly from its ability to coordinate industrial policy with regulatory approval processes. Chinese mining projects typically receive approvals within 1-2 years, compared to 4-9 years for comparable U.S. projects. This regulatory efficiency advantage compounds over time, allowing Chinese producers to respond rapidly to market opportunities while American competitors remain trapped in approval processes.
Environmental Review vs. National Security Imperatives
Environmental protection and national security objectives need not be mutually exclusive, but current regulatory frameworks struggle to balance these priorities effectively. The challenge lies not in eliminating environmental oversight but in designing review processes that can achieve thorough analysis within timeframes compatible with strategic objectives.
Modern environmental assessment methodologies can incorporate advanced modelling techniques and parallel review processes that maintain analytical rigour whilst reducing overall approval timelines. In addition, the key is restructuring review sequences to eliminate unnecessary delays while preserving substantive environmental protections.
How Long Does Traditional Rare Earth Mine Approval Actually Take?
Federal Review Timelines by Project Type
Federal permitting timelines vary significantly based on project complexity and environmental sensitivity. Traditional metallic mining projects typically require 4-5 years for complete approval, while rare earth extraction projects often extend to 8-9 years due to their chemical processing requirements and waste management solutions considerations.
Average Permitting Duration Comparison
| Project Type | United States | International Benchmark | Key Factors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Mining | 4-5 years | 2-3 years | NEPA review, state coordination |
| Rare Earth Extraction | 8-9 years | 2-4 years | Chemical processing permits, waste management |
| Processing/Refining | 6-7 years | 1-3 years | EPA oversight, community engagement |
The extended timelines for rare earth projects reflect the complex regulatory treatment of chemical separation processes required to produce individual rare earth oxides from mixed ore concentrates. These processes involve acids, solvents, and waste products that trigger additional environmental review requirements beyond those applied to conventional mining operations.
State-Level Complications and Jurisdictional Overlap
State regulatory requirements often operate independently of federal timelines, creating potential for duplicative reviews and conflicting requirements. Water rights allocation, particularly in western states, can add 1-2 years to project timelines as state water engineers evaluate long-term impacts on existing water users and environmental flows.
Mining operations on federal lands face additional complexities through Bureau of Land Management or Forest Service review processes, which can extend environmental analysis timelines significantly. These agencies must coordinate with state environmental departments, creating opportunities for regulatory conflicts and approval delays.
Environmental Impact Assessment Requirements
Environmental Impact Statement (EIS) preparation typically consumes 24-36 months of the total permitting timeline, while Environmental Assessment (EA) processes require 12-18 months. Rare earth projects usually trigger EIS requirements due to their scale and processing complexity, automatically extending approval timelines compared to projects eligible for streamlined EA review.
The EIS process includes mandatory public comment periods, agency consultation requirements, and opportunities for administrative appeals that can add months or years to approval timelines. While these provisions serve important transparency and accountability functions, they also create predictable delay mechanisms that adversaries can exploit through strategic opposition.
What Are the Current Legislative Solutions Being Proposed?
The SPEED Act Framework and Implementation Timeline
The Speeding Progress on Efficient Energy Development (SPEED) Act proposes to establish firm timelines for federal agency review processes, with specific provisions for critical mineral projects. The legislation would require agencies to complete NEPA reviews within 18 months for projects deemed strategically important, compared to current timelines that often exceed 36 months.
Key provisions include mandatory parallel processing of federal permits, elimination of duplicative environmental reviews between agencies, and establishment of dispute resolution mechanisms for inter-agency conflicts. The bill also proposes to limit administrative appeals to 90 days and restrict judicial review to claims filed within 150 days of permit issuance.
PERMIT Act Provisions for Critical Minerals
The Promoting Efficient Restoration and Management of Infrastructure and Teamwork (PERMIT) Act focuses on streamlining coordination between federal and state regulatory authorities. The legislation would establish regional permitting offices with authority to coordinate multiple agency reviews and resolve jurisdictional conflicts.
The bill includes provisions for state acceptance of federal environmental reviews, potentially eliminating duplicative analysis while maintaining environmental protection standards. It also proposes performance metrics for federal agencies, with funding consequences for agencies that consistently exceed established timelines.
FAST-41 List Expansion and Project Prioritisation
The Federal Permitting Council has identified ten domestic mining projects for potential inclusion in the Federal Activities Schedule Template and Information (FAST-41) expedited review process. This expansion represents the first systematic application of FAST-41 procedures to strategic mineral projects, potentially reducing approval timelines from years to months.
"The Federal Permitting Council has added ten domestic mining projects to the FAST-41 expedited review list, potentially reducing approval timelines from years to months."
FAST-41 designation provides projects with dedicated federal coordination, mandatory agency timeline compliance, and senior-level dispute resolution mechanisms. However, the process still requires completion of all standard environmental reviews, meaning timeline reduction comes primarily from improved coordination rather than reduced analytical requirements.
How Does China's Permitting System Enable Market Dominance?
Coordinated Industrial Policy vs. Fragmented U.S. Approach
China's rare earth dominance reflects coordinated policy implementation across multiple levels of government, with environmental approvals integrated into broader industrial planning processes. Regional governments compete to attract strategic industries, creating incentives for rapid permitting of projects aligned with national priorities.
The Chinese system allows environmental trade-offs that would be politically impossible in democratic systems, including acceptance of pollution externalities in exchange for strategic industrial capacity. This approach enables rapid project approvals but at significant environmental and social costs that are often hidden from public scrutiny.
Environmental Externalisation and Cost Advantages
Chinese rare earth producers benefit from regulatory frameworks that permit environmental costs to be externalised to surrounding communities and ecosystems. Waste management requirements are often less stringent than international standards, reducing both capital costs and permitting complexity for domestic producers.
This regulatory arbitrage creates competitive advantages that extend beyond simple labour cost differences, allowing Chinese producers to maintain market dominance even as wage levels increase. American producers operating under stricter environmental standards face inherent cost disadvantages that cannot be overcome through operational efficiency alone.
State-Directed Capital Allocation Models
Chinese state-owned enterprises benefit from patient capital that can sustain operations through extended permitting processes when necessary, but more importantly, they operate within a system designed to minimise regulatory delays for strategically important projects. This combination of financial resources and regulatory efficiency creates formidable competitive advantages.
U.S. vs. China Rare Earth Control Metrics
| Metric | China | United States |
|---|---|---|
| Global Mining Control | 70% | <5% |
| Refining Capacity | 90% | <10% |
| Average Approval Time | 1-2 years | 4-9 years |
| State Investment Level | High | Moderate |
Which Federal Investments Are at Risk Without Reform?
Pentagon Conditional Loans and Equity Positions
The Department of Defense has authorised conditional loans and equity investments in domestic rare earth producers, representing hundreds of millions in federal commitments. These investments assume projects will achieve commercial production within specified timeframes, creating financial risks if permitting delays extend project timelines beyond loan covenant requirements.
MP Materials has received significant federal support for expansion of its California operations, while ReElement Technologies has secured funding for advanced separation technology development. Furthermore, these investments remain vulnerable to regulatory delays that could trigger loan acceleration clauses or equity dilution provisions.
MP Materials, ReElement Technologies, and Strategic Partnerships
Companies receiving federal investment commitments face dual pressures from private investors seeking returns and government agencies expecting strategic production capacity. Extended permitting timelines create financial stress that can force companies to seek additional capital at unfavourable terms or abandon projects altogether.
The success of federal industrial policy depends critically on regulatory frameworks that can deliver approvals within investment timeframes. Without permitting reform in rare earths, federal investments may fail to achieve their strategic objectives regardless of their financial generosity.
Defense Production Act Funding Bottlenecks
Defense Production Act authorities provide federal agencies with broad powers to support strategic industries, but these powers cannot overcome regulatory bottlenecks that prevent project completion. Funding alone cannot substitute for regulatory reform when permitting delays make projects financially unviable.
The mismatch between federal investment timelines and regulatory approval processes creates a fundamental strategic vulnerability that adversaries can exploit by maintaining price pressure on international markets while American alternatives remain trapped in approval processes. For instance, the recent strategic antimony loan highlights how critical mineral financing depends on efficient permitting processes.
What Are the Economic Implications for Investors?
Supply Chain Vulnerability and Pricing Volatility
Investors in rare earth projects face unique risks stemming from regulatory uncertainty and extended approval timelines. Unlike conventional commodity investments, rare earth projects cannot respond rapidly to price signals due to permitting constraints, creating persistent supply-demand imbalances and price volatility.
Extended permitting timelines increase project capital requirements due to carrying costs and financing expenses, making domestic projects less competitive against international alternatives. This creates a vicious cycle where regulatory delays increase project costs, making domestic production less economically viable and increasing dependence on foreign sources.
Domestic Production Scalability Challenges
Current regulatory frameworks make it virtually impossible to scale domestic rare earth production rapidly in response to supply disruptions or strategic needs. The 4-9 year approval timelines mean that even urgent national security requirements cannot be addressed through domestic production expansion within policy-relevant timeframes.
This scalability constraint limits the strategic value of domestic rare earth resources and creates persistent vulnerability to supply manipulation by adversarial nations. Investors must factor these strategic risks into valuation models, potentially making domestic projects appear less attractive than their resource quality would suggest.
Export Control Dependencies and Geopolitical Risk
American dependence on Chinese rare earth supplies creates exposure to export control manipulation and geopolitical coercion. Recent Chinese export restrictions demonstrate how regulatory vulnerabilities in one country can be exploited by another nation's industrial policy.
Investors seeking exposure to strategic materials must evaluate not only geological and economic factors but also regulatory and geopolitical risks that can dramatically affect project viability and market dynamics. However, the Trump Executive Order on Permits may signal potential regulatory changes that could improve investment conditions.
How Would Streamlined Permitting Change Market Dynamics?
Feedstock Gap Reduction Scenarios
Streamlined permitting could enable domestic rare earth oxide production to increase significantly within 3-5 years rather than the current 8-10 year timeline. This acceleration could help address the feedstock gap between domestic mining capacity and downstream processing requirements.
Reduced regulatory uncertainty would likely attract additional private investment to domestic projects, creating competitive dynamics that could drive innovation in extraction and processing technologies. Market participants would benefit from increased supply security and reduced exposure to foreign export controls.
Magnet Manufacturing Supply Security
Domestic magnet manufacturers currently face strategic vulnerability due to dependence on Chinese rare earth feedstocks. Streamlined permitting could enable vertical integration strategies where magnet producers secure upstream rare earth supplies through domestic sources.
This supply chain integration would reduce exposure to Chinese export licensing regimes and provide more predictable input costs for American manufacturers. The strategic value extends beyond cost considerations to include supply security and production flexibility during geopolitical tensions.
NdPr Oxide and Dy/Tb Production Potential
Neodymium-Praseodymium (NdPr) and Dysprosium-Terbium (Dy/Tb) represent the highest-value rare earth products essential for permanent magnet production. Streamlined permitting could enable domestic production of these critical materials, reducing strategic dependence on Chinese suppliers.
The technical complexity of producing separated rare earth oxides requires sophisticated chemical processing facilities that currently face extended regulatory approval timelines. Consequently, permitting reform could enable these facilities to achieve commercial operation within investment-compatible timeframes.
What Environmental Safeguards Remain Under Reform Proposals?
Balancing Speed with Responsible Development
Permitting reform proposals generally maintain substantive environmental review requirements whilst streamlining procedural aspects and eliminating duplicative processes. The goal is achieving thorough environmental analysis within compressed timeframes rather than reducing analytical rigour.
Modern environmental assessment methodologies can support accelerated review timelines through advanced modelling, parallel processing, and focused impact analysis. These approaches can maintain environmental protection standards while reducing unnecessary delays in the approval process.
Waste Management and Tailings Oversight
Rare earth extraction generates significant waste products that require careful management to prevent environmental contamination. Reform proposals maintain oversight of waste management systems whilst streamlining the permitting process for facilities that meet established safety standards.
Advanced waste treatment technologies can reduce environmental impacts compared to historical rare earth operations, but these technologies require regulatory frameworks that can evaluate and approve innovative approaches within reasonable timeframes.
Community Engagement Requirements
Meaningful community engagement remains essential for project success and social licence to operate. Reform proposals generally maintain public participation requirements whilst establishing clearer timelines and procedures for community input processes.
Effective community engagement can actually accelerate project approvals by identifying and addressing concerns early in the development process, reducing the likelihood of litigation and appeals that can extend timelines significantly.
Which Companies Stand to Benefit Most from Reform?
Established Players with Permitted Assets
MP Materials, as the sole operating rare earth mine in the United States, stands to benefit from regulatory changes that enable expansion of existing operations and development of downstream processing capabilities. The company's established regulatory relationships and operational experience provide advantages in navigating reformed permitting processes.
Companies with existing environmental permits may be able to expand operations through modifications to existing approvals rather than completely new permitting processes, potentially enabling faster capacity increases under reformed regulatory frameworks.
Exploration Companies with Advanced Projects
Junior mining companies with advanced exploration projects could see dramatic improvements in project economics if permitting timelines are reduced from 8-9 years to 3-4 years. This timeline compression could make previously marginal projects economically viable and attract additional development capital.
Companies with projects in permitting phases would benefit immediately from reformed timelines, potentially accelerating development schedules and reducing carrying costs significantly. This could create substantial value for shareholders and enable faster deployment of strategic production capacity.
Downstream Processing and Refining Operations
Rare earth processing and refining facilities face some of the most complex regulatory approval requirements due to their chemical separation processes and waste management systems. Streamlined permitting could enable these critical middle-stream operations to develop more rapidly.
Companies developing advanced separation technologies could benefit from regulatory frameworks that can evaluate and approve innovative processes more efficiently, enabling faster deployment of next-generation rare earth processing capabilities. This aligns with the broader critical minerals strategy being developed at the federal level.
What Are the Risks of Incomplete Reform Implementation?
Continued Import Dependence Scenarios
Failure to implement comprehensive permitting reform in rare earths could perpetuate American dependence on Chinese rare earth supplies, maintaining strategic vulnerability to export controls and price manipulation. This dependence creates persistent national security risks that cannot be addressed through stockpiling or alternative sourcing alone.
Partial reforms that reduce some regulatory delays without addressing fundamental coordination issues may provide limited benefits whilst creating false confidence in domestic production capabilities. Comprehensive reform requires addressing both federal and state regulatory processes.
Strategic Mineral Stockpile Limitations
Government stockpiles can provide temporary buffer against supply disruptions but cannot substitute for domestic production capacity over extended periods. Stockpile management also faces budgetary constraints and technical challenges related to material degradation and technology evolution.
Reliance on stockpiles without developing domestic production capacity leaves the United States vulnerable to extended supply disruptions that exceed stockpile duration or target materials not included in government reserves. The critical minerals cooperation between allies becomes increasingly important in this context.
Technology Sector Supply Chain Vulnerabilities
American technology companies face increasing pressure to secure supply chains against geopolitical risks, but current regulatory constraints limit their options for domestic sourcing. This creates competitive disadvantages relative to companies with access to integrated supply chains in other countries.
The technology sector's rapid growth increases rare earth demand faster than domestic production capacity can expand under current regulatory constraints, potentially increasing import dependence despite federal investments in domestic capacity.
How Should Investors Track Reform Progress?
Key Legislative Milestones to Monitor
Investors should monitor progress of the SPEED Act and PERMIT Act through committee proceedings, floor votes, and implementation guidance development. These legislative vehicles represent the primary mechanisms for achieving comprehensive permitting reform at the federal level.
The timeline for legislative action affects investment decisions significantly, as companies may delay project commitments pending regulatory clarity. Tracking legislative progress enables investors to anticipate market timing and competitive positioning changes.
Federal Agency Implementation Metrics
The Federal Permitting Council publishes quarterly reports on project timelines and agency performance that provide insights into implementation effectiveness. These metrics can indicate whether reforms are achieving intended timeline reductions and coordination improvements.
Agency-specific performance data helps identify bottlenecks and successful practices that could be expanded to additional projects or regulatory contexts. This information supports investment decision-making and policy advocacy efforts.
Industry Partnership Announcements and Funding Decisions
Federal funding announcements, private investment commitments, and strategic partnerships provide market signals about investor confidence in regulatory reform prospects. These announcements often precede formal policy changes and can indicate shifting market dynamics.
Tracking defence contractor investments, international partnership developments, and supply agreement negotiations helps investors understand how market participants are positioning for potential regulatory changes and supply chain restructuring. Furthermore, understanding Grade King Permitting processes can provide insights into regulatory complexities.
The success of permitting reform in rare earths will ultimately depend on sustained political commitment across multiple administrative cycles and effective coordination between federal and state regulatory authorities. The development of rare earth processing hubs represents one potential pathway forward for addressing supply chain vulnerabilities through strategic infrastructure investment.
Disclaimer: This analysis contains forward-looking statements regarding regulatory reform prospects and market implications. Actual outcomes may differ materially from projections due to political, economic, and technical factors. Investors should conduct independent research and consider professional advice before making investment decisions.
Looking for Investment Opportunities in America's Critical Minerals Revolution?
Discovery Alert's proprietary Discovery IQ model delivers real-time alerts on significant ASX mineral discoveries, offering investors immediate insights into actionable opportunities ahead of the broader market. With America's regulatory bottlenecks creating extended development timelines, savvy investors are increasingly turning to Australia's streamlined mining sector, where major discoveries can generate substantial returns within compressed timeframes compared to the 4-9 year U.S. permitting cycles discussed above.