The global aluminum industry faces unprecedented transformation as EU aluminum scrap export restrictions reshape traditional trading patterns and supply chain dynamics. European policymakers are implementing strategic resource retention policies designed to secure domestic manufacturing competitiveness while supporting circular economy objectives. Furthermore, these regulatory changes intersect with evolving US trade tariffs and broader global trade shifts, creating complex market dynamics that challenge established international commodity flows.
Understanding the Strategic Framework Behind Europe's Resource Retention Policy
European policymakers have developed comprehensive regulatory mechanisms designed to control aluminum scrap flows through sophisticated monitoring and enforcement systems. The European Commission launched export monitoring capabilities in July 2024, establishing baseline data collection protocols that track cross-border scrap movements in real-time. These systems represent the foundation for more restrictive measures planned for implementation by spring 2026.
European Trade Commissioner Maros Sefcovic announced the preparatory work for new EU aluminum scrap export restrictions at the European Aluminium conference in Brussels, emphasizing that proposed measures would balance the interests of producers, recyclers, and downstream manufacturing sectors. The regulatory framework incorporates multi-tiered approaches including potential export licensing requirements, quality certification standards for scrap classification, and digital documentation protocols for enhanced supply chain transparency.
The technical architecture underlying these controls involves harmonizing classification systems across all 27 EU member states, creating standardized quality specifications for different aluminum scrap grades. Export threshold volumes will trigger mandatory pre-approval processes, while penalty structures provide financial consequences for non-compliance violations. Digital tracking capabilities may incorporate blockchain-based documentation to ensure supply chain transparency and prevent circumvention through third-country transshipment routes.
Implementation Timeline and Stakeholder Engagement
Public consultation phases throughout 2025 will gather input from industry stakeholders before final regulatory adoption. Evidence gathering and impact assessment completion will inform member state coordination protocols, ensuring consistent enforcement across European customs jurisdictions. The spring 2026 implementation timeline allows sufficient preparation for both regulatory authorities and affected industries to establish compliance mechanisms.
Recycling Europe, representing EU recycling operations, has called for comprehensive stakeholder involvement in consultation processes, emphasizing the need for fact-based policy development supported by empirical evidence rather than speculative market assessments. However, surveillance measures introduced by the European Commission demonstrate the regulatory commitment to monitoring scrap flows more closely.
Current Export Volume Analysis Justifying Regulatory Intervention
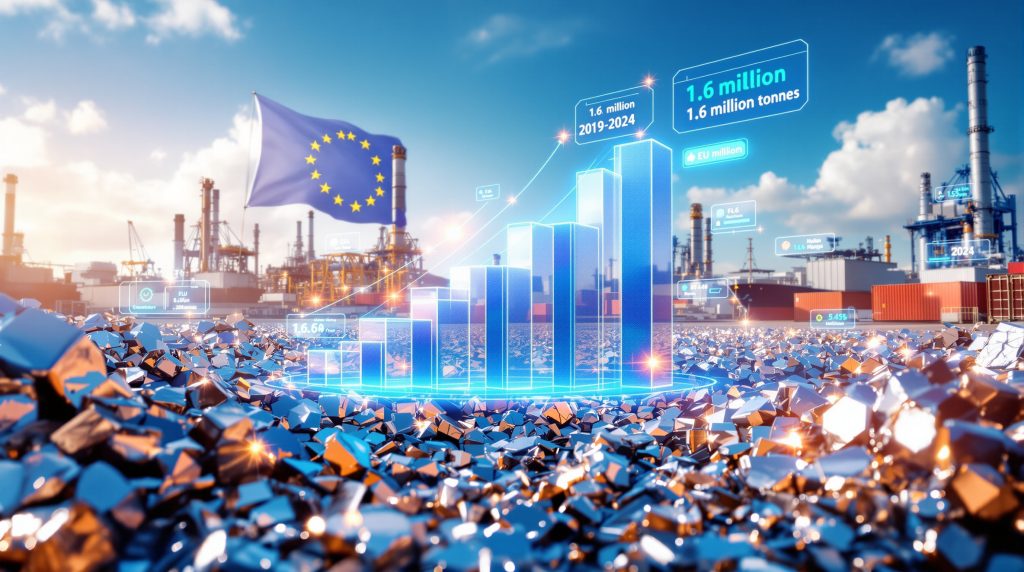
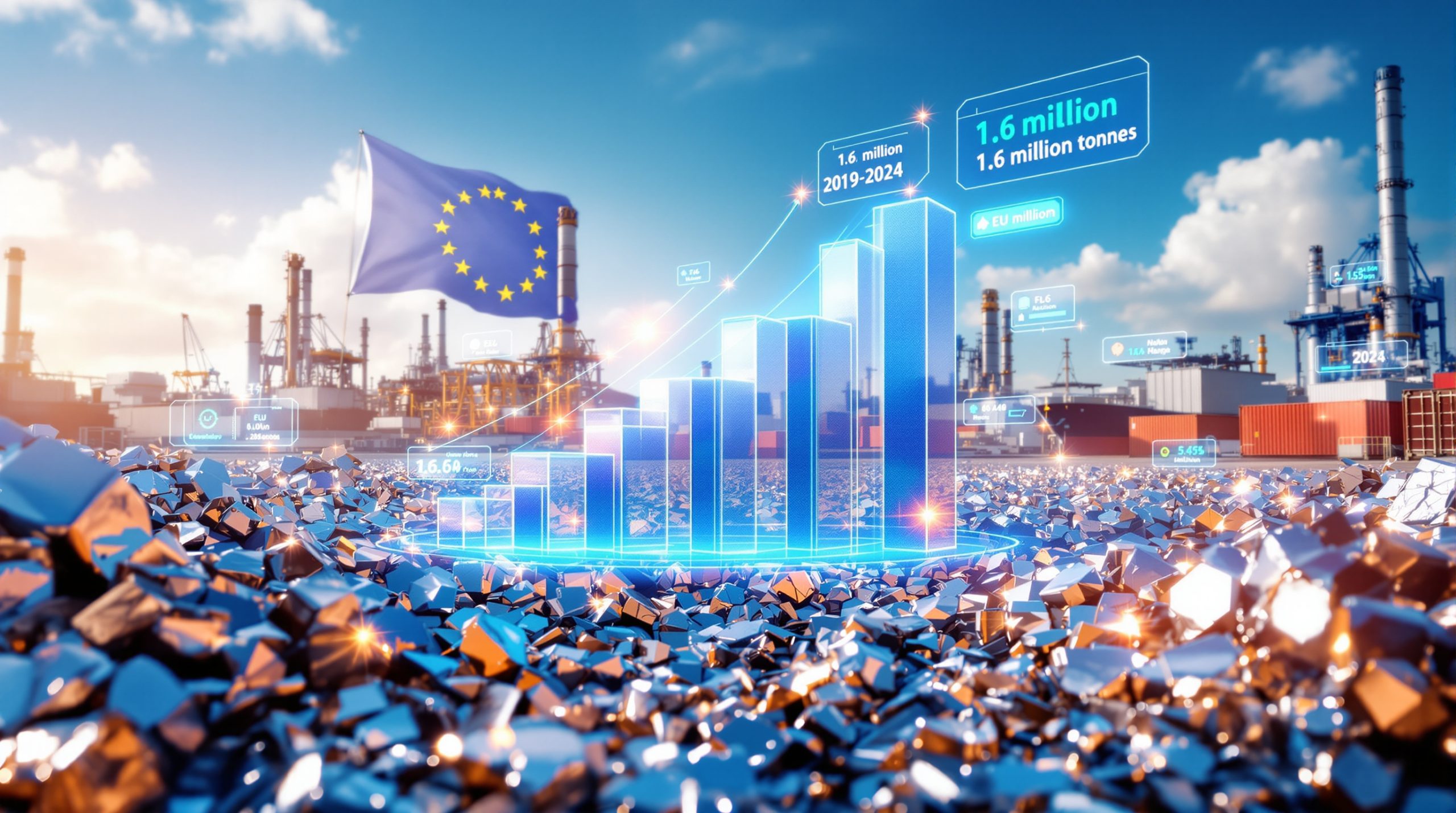
EU Aluminum Scrap Export Growth Trajectory
| Year | Export Volume (Million Tonnes) | Growth Rate | Primary Destinations |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 0.84 | Baseline | Asia-Pacific |
| 2024 | 1.26 | +50% | Asian Markets |
European aluminum scrap exports reached a record 1.26 million metric tons in 2024, representing a 50% increase compared to 2019 baseline levels according to data from the European Aluminium industry group. This dramatic volume escalation has prompted regulatory concerns about domestic supply security for European manufacturing sectors requiring recycled aluminum inputs for decarbonisation benefits.
The majority of these exports flow to Asian markets, creating what European Trade Commissioner Sefcovic characterises as aluminum scrap leakage that leaves EU industries short of critical inputs required for low-carbon production processes. However, industry opposition groups challenge this assessment, with Recycling Europe noting that European Commission monitoring data has not conclusively demonstrated evidence of problematic scrap leakage requiring regulatory intervention.
Geographic Distribution and Market Dynamics
Asian buyers have increasingly focused procurement efforts on European suppliers, driven by reduced availability from traditional North American sources. This geographic reallocation creates competitive disadvantages for European aluminum producers who require recycled inputs to achieve energy efficiency targets mandated by climate legislation.
The export volume growth trajectory indicates accelerating demand from emerging Asian manufacturing centres, particularly those developing aluminum-intensive industries such as automotive components, construction materials, and packaging applications. European recyclers process substantial volumes annually, but domestic consumption patterns may not absorb total processing capacity, creating structural export dependency for capacity utilisation optimisation.
US Trade Policy Impact on European Scrap Markets
American trade policies under the Trump administration have created significant arbitrage opportunities that distort global aluminum scrap flows. US aluminum import tariffs of 50% compared to scrap import tariffs of only 15% generate a 35 percentage point differential that incentivises scrap-intensive production models over primary aluminum utilisation.
This tariff structure has boosted scrap imports into the United States while simultaneously reducing American scrap exports to Asian markets. Consequently, Asian buyers have redirected procurement strategies toward European suppliers, intensifying demand pressure on EU scrap resources and contributing to the record export volumes observed in 2024. These tariff market impacts create cascading effects throughout global supply chains.
Manufacturing Sector Adaptation Strategies
US manufacturers have pivoted operational models to exploit the tariff differential, implementing scrap-intensive production processes that minimise exposure to higher primary aluminum duties. This strategic adaptation reduces American scrap availability for export markets, creating supply constraints that elevate European scrap valuations and attract increased Asian buyer interest.
European aluminum producers face significant competitive disadvantages when sourcing primary materials, as recycling aluminum uses 95% less energy than producing metal from mined bauxite ore. This energy efficiency advantage becomes critical for meeting EU decarbonisation targets while maintaining manufacturing cost competitiveness against international producers with access to lower-cost primary materials.
Market Distortion Effects
The US tariff policy creates cascading effects throughout global aluminum supply chains, redirecting traditional trade flows and concentrating Asian demand on European scrap sources. Manufacturing sectors including automotive, aerospace, and construction materials experience input cost volatility as domestic scrap prices respond to international demand pressures generated by US trade policy distortions.
Critical material shortages threaten industrial competitiveness across European manufacturing sectors that rely on recycled aluminum for achieving sustainability objectives required by climate legislation and corporate decarbonisation commitments.
Industry Sector Responses to Export Control Proposals
European Aluminum Producers: Strategic Policy Support
The European Aluminium industry group strongly advocates for EU aluminum scrap export restrictions, emphasising multiple strategic benefits for continental manufacturing competitiveness. Domestic supply security improvements would reduce dependency on volatile international markets while ensuring adequate recycled inputs for decarbonisation initiatives across energy-intensive production processes.
Manufacturing associations highlight the energy efficiency advantages of recycled aluminum inputs, noting that domestic retention supports circular economy integration objectives established under EU environmental legislation. Smelter operators particularly emphasise the operational advantages of secured scrap supply chains for meeting climate targets while maintaining cost-competitive production capabilities.
Downstream processors in automotive, aerospace, and construction sectors support circular economy integration measures that stabilise input costs and reduce supply chain vulnerabilities to international market disruptions.
Recycling Industry: Organised Opposition Campaign
European recycling industries, represented by EuRIC and Recycling Europe, have mounted organised opposition to proposed export restrictions, challenging both the regulatory necessity and potential economic impacts on sector viability. Industry representatives argue that European Commission monitoring data has not demonstrated conclusive evidence of problematic scrap leakage requiring intervention.
Economic impact studies conducted by recycling associations highlight potential sector disruption effects, including investment deterrence concerns for green transition technologies and capacity utilisation challenges if export markets become inaccessible. The recycling industry emphasises that current processing capabilities may exceed domestic absorption capacity, creating structural export dependency for operational sustainability.
The recycling sector processes substantial aluminum volumes annually, with the majority consumed domestically, but remaining capacity requires export market access for operational viability and continued investment in advanced sorting technologies.
Opposition groups call for fact-based policy development supported by comprehensive impact assessments rather than speculative market intervention based on theoretical scrap leakage concerns. Furthermore, industry analysis from S&P Global suggests these restrictions could slow investments in green aluminum initiatives.
EU Policy Integration and Strategic Autonomy Objectives
Circular Economy and Green Deal Alignment
EU aluminum scrap export restrictions integrate directly with European Green Deal circular economy objectives, reinforcing domestic resource utilisation for decarbonisation targets across industrial sectors. The policy framework complements Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) implementation by reducing reliance on carbon-intensive primary aluminum imports while retaining low-carbon recycled materials within European supply chains.
Critical Raw Materials Act implementation creates synergies through enhanced domestic resource security, reducing strategic vulnerability to international supply disruptions while supporting manufacturing sector competitiveness. Waste Framework Directive revisions coordinate classification standards for scrap materials, ensuring consistent regulatory treatment across circular economy applications.
Strategic Autonomy and Supply Chain Resilience
Resource retention policies support broader EU strategic autonomy objectives by reducing dependency on energy-intensive primary aluminum production while stabilising input costs for domestic manufacturing operations. Enhanced supply chain resilience protects critical materials access for defence and aerospace applications, mitigating geopolitical risks associated with international commodity market dependencies.
Manufacturing sector competitiveness improvements through input cost stabilisation enable European producers to compete effectively against international competitors while achieving climate policy compliance. Critical materials security for high-technology applications supports industrial policy objectives for maintaining technological leadership in strategic sectors.
Geopolitical Risk Mitigation Framework
Domestic resource retention reduces exposure to international market volatility and potential supply disruptions arising from geopolitical tensions or trade policy changes. Strategic materials control supports broader economic security objectives by ensuring adequate inputs for critical industries regardless of international market conditions or trading relationship stability.
Technical and Market Implementation Challenges
Quality Standardisation Complexity
Harmonising aluminum scrap classification systems across 27 EU member states presents significant technical challenges requiring coordination of existing national standards with proposed European frameworks. Mixed scrap processing from automotive shredding operations requires specialised sorting technologies to achieve quality specifications necessary for regulatory compliance.
Contamination levels vary substantially across different scrap sources, necessitating sophisticated quality assessment protocols to ensure consistent classification standards. Cross-border enforcement coordination requires harmonised customs procedures and documentation requirements to prevent regulatory circumvention through jurisdictional arbitrage.
Market Transition Management
Preventing supply chain disruption during policy rollout requires careful coordination between regulatory implementation and industry adaptation capabilities. Existing contractual obligations and established trading relationships may require transition periods to accommodate new regulatory requirements without creating market instability.
Market participants require adequate preparation time to establish compliance systems, modify operational procedures, and adapt business models to regulatory constraints on export activities. Additionally, aluminium scrap assessments in Southeast Asia markets will likely be affected by these changes.
Potential Trade Retaliation Scenarios
Asian trading partners may implement counter-measures targeting EU exports in response to scrap export restrictions, potentially escalating trade tensions and reducing market access for European manufactured goods. World Trade Organisation dispute resolution procedures could challenge the regulatory framework's compatibility with international trade agreements and multilateral trading system principles.
Bilateral trade agreement renegotiation pressures may arise as affected countries seek compensation for reduced scrap access through alternative trade concessions or market access arrangements. Third-country transshipment route development could undermine policy effectiveness through circumvention mechanisms that redirect scrap flows through non-EU jurisdictions.
Global Market Restructuring and Investment Implications
Regional Supply Chain Reconfiguration
Increased investment in European recycling infrastructure capacity represents the primary market adaptation to export restrictions, with enhanced domestic processing capabilities required to absorb previously exported materials. Asian scrap procurement strategies will diversify toward alternative suppliers in North America, Latin America, and other regions to compensate for reduced European availability.
North American scrap market price volatility amplification may result from increased Asian demand redirected from European sources, creating arbitrage opportunities for suppliers capable of meeting quality specifications and delivery requirements. Middle Eastern and African scrap export opportunities may expand as Asian buyers develop alternative supply chains less dependent on European sources.
Long-Term Market Equilibrium Projections
EU domestic scrap prices are expected to decline due to export restrictions, improving input cost competitiveness for European aluminum manufacturers while potentially reducing recycling sector profitability from reduced international price premiums. Enhanced European manufacturing competitiveness through lower input costs may offset some economic impacts on recycling operations through increased domestic demand volumes.
Global scrap trade route optimisation around regulatory constraints will drive logistics innovation and supply chain adaptation, potentially creating efficiency improvements in international commodity flows. Technology transfer acceleration for advanced recycling processes may result from increased domestic processing requirements and investment in sorting capabilities.
Investment and Business Strategy Considerations
Opportunities for European Industrial Players
Recycling technology companies are positioned for capacity expansion opportunities as domestic processing requirements increase following export restrictions. Enhanced demand for specialised sorting equipment, quality assessment systems, and contamination reduction technologies creates market opportunities for technology providers serving the aluminum recycling sector.
Aluminum manufacturers benefit from improved input cost stability and reduced supply chain vulnerability to international market disruptions, enabling more predictable operational planning and capital investment decisions. Infrastructure development contractors may experience increased demand for compliance system implementation and regulatory monitoring technology deployment.
Environmental services providers facilitating circular economy transitions gain market opportunities from increased domestic recycling activity and regulatory compliance requirements across manufacturing sectors.
Risk Mitigation Strategies for Global Traders
Supply chain diversification beyond European scrap sources becomes critical for maintaining operational flexibility and market access in Asian destinations. Investment in alternative material processing technologies may provide competitive advantages for traders capable of handling diverse scrap sources with varying quality characteristics.
Regulatory compliance system development ensures continued EU market access for international traders while demonstrating commitment to sustainable trading practices aligned with European policy objectives. Strategic partnerships with domestic European recycling operations may provide alternative market access mechanisms through joint venture arrangements or long-term supply agreements.
Market Psychology and Investor Sentiment
Investor confidence in European circular economy initiatives may strengthen as regulatory frameworks demonstrate commitment to domestic resource retention and manufacturing sector support. Uncertainty regarding implementation details and enforcement mechanisms creates near-term volatility in aluminum sector valuations as market participants assess competitive implications.
Long-term investment flows toward European recycling infrastructure and advanced materials processing capabilities reflect structural market adaptation to regulatory frameworks prioritising domestic resource utilisation over international trade optimisation.
Disclaimer: This analysis contains forward-looking assessments based on proposed regulatory frameworks that remain subject to modification through consultation processes and final legislative approval. Market projections involve inherent uncertainties and should not be considered as investment advice or guaranteed outcomes.
Are You Tracking Strategic Metal Market Shifts?
European aluminum scrap restrictions and US trade policy changes are reshaping global commodity flows, creating both opportunities and risks across international markets. Discovery Alert's proprietary Discovery IQ model delivers instant notifications on significant ASX mineral discoveries, helping investors capitalise on market-moving developments as supply chain dynamics evolve across critical materials sectors.