How Mexico's Energy Giant Creates a Structural Drag on Federal Resources
Mexico's fiscal architecture faces unprecedented strain as the nation's oil revenues contract while support obligations expand exponentially. The petroleum sector, once a cornerstone of federal income, has transformed into a net drain on public resources, forcing difficult choices between essential services and energy sector stability. This transformation reflects broader challenges in commodity-dependent economies where state-owned enterprises require increasing subsidisation despite declining productivity.
Understanding the magnitude of this PEMEX support revenue gap requires examining how traditional oil revenue models have inverted, creating fiscal pressures that cascade through multiple government departments and compromise long-term economic planning capabilities.
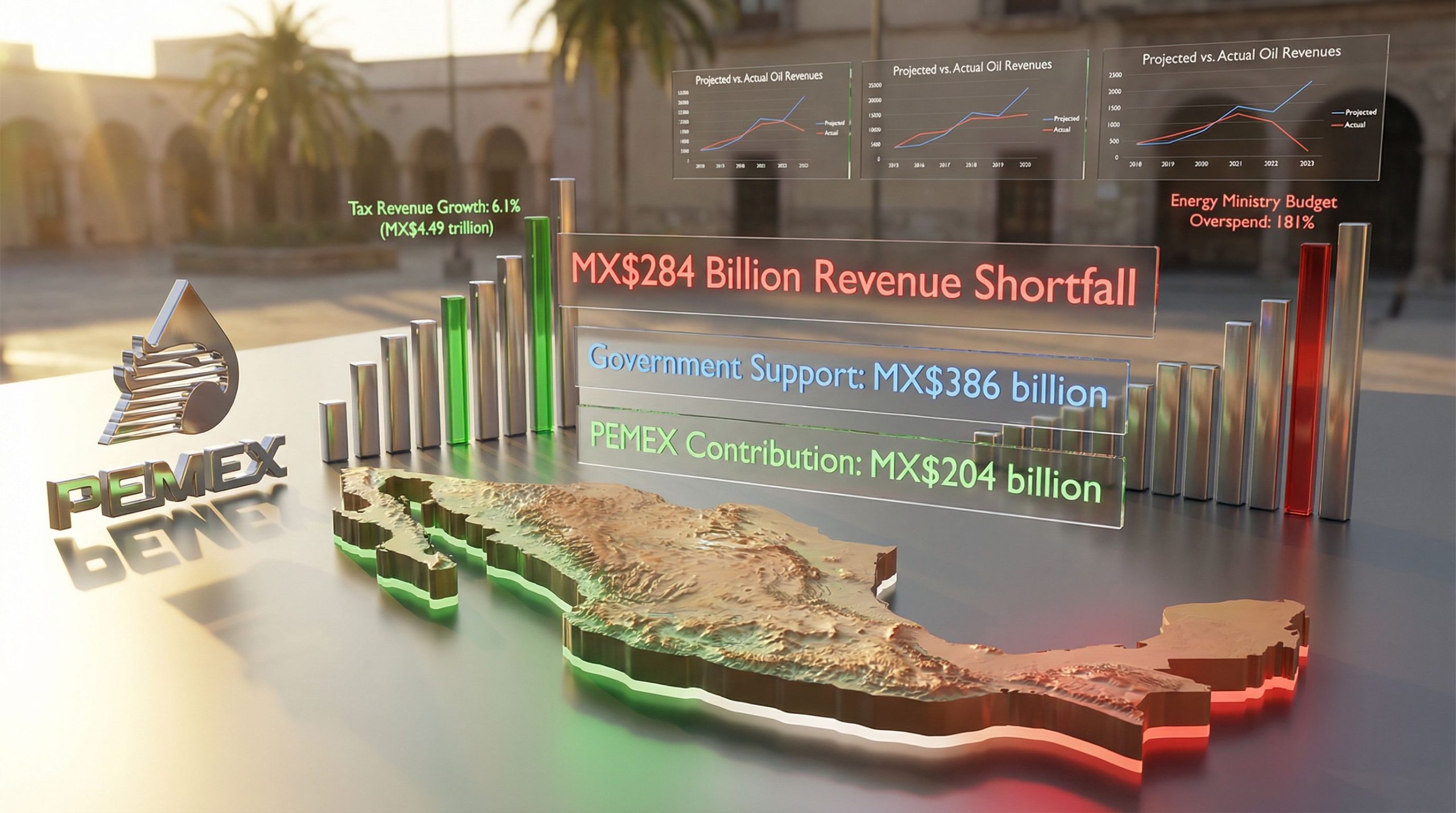
Breaking Down Mexico's MX$284 Billion Revenue Shortfall
Mexico's federal finances reveal a stark contradiction between robust tax collection performance and an expanding fiscal deficit driven primarily by petroleum sector obligations. Through October 2025, the government recorded a MX$284 billion revenue shortfall, despite achieving significant growth in non-oil revenue streams.
Tax revenues reached MX$4.49 trillion, representing 6.1% annual growth and exceeding budget projections by MX$90 billion. This outperformance reflected enhanced fiscal oversight mechanisms and improved compliance enforcement across major taxpayer categories.
Simultaneously, non-tax income streams demonstrated remarkable resilience, generating MX$214 billion with 16.4% year-over-year growth, surpassing targets by MX$43 billion. Furthermore, this performance demonstrates the government's ability to diversify revenue sources beyond traditional oil dependency.
Government Revenue vs. PEMEX Support Analysis
| Revenue Source | Amount (MX$ Billions) | Performance vs. Budget |
|---|---|---|
| Tax Revenues | 4,490 | +90 billion above target |
| Non-tax Income | 214 | +43 billion above target |
| PEMEX Contribution | 204 | Below expectations |
| Government Support to PEMEX | 386 | Emergency levels |
| Net PEMEX Impact | -182 | Negative contribution |
The petroleum sector's financial drain becomes apparent when comparing PEMEX's fiscal contribution of MX$204 billion against the MX$386 billion in government support received. This MX$182 billion negative balance represents a fundamental shift from historical patterns where oil revenues supported broader government operations.
Moreover, the oil price rally impact on global markets has not translated into improved fiscal performance for Mexico's state-owned petroleum company.
Budget Execution Constraints Across Federal Ministries
The concentration of resources toward petroleum sector support created severe constraints across other government departments. Multiple ministries operated significantly below planned allocations:
- Ministry of Health: 26% underspent relative to budget authorisation
- Ministry of Infrastructure, Communications and Transport: 29.1% below planned expenditure
- Ministry of Environment: 29.2% shortfall in budget execution
- Ministry of Energy: 181% above original allocation due to emergency PEMEX transfers
This spending pattern demonstrates how petroleum sector obligations crowded out discretionary federal spending across health, infrastructure, and environmental protection programmes. The Ministry of Energy's 181% budget increase operated outside traditional congressional oversight mechanisms, raising questions about fiscal governance and appropriations authority.
Understanding Mexico's Revenue Paradox Beyond Oil Dependencies
Mexico's fiscal performance reveals a complex narrative where strong underlying economic fundamentals clash with structural energy sector challenges. The MX$5 trillion in total government revenues (excluding PEMEX, CFE, IMSS, and ISSSTE) showed 8% annual growth, slightly exceeding budget projections despite petroleum sector headwinds.
Additionally, global US tariff and debt policies create additional pressures on Mexico's trade-dependent economy, potentially affecting future revenue streams.
Tax Collection Excellence Despite Economic Headwinds
The MX$90 billion tax revenue outperformance reflects systematic improvements in fiscal administration and compliance enforcement. Mexico's tax authority (SAT) intensified audit activities focusing on large taxpayers, generating substantial recovery amounts that contributed to the overall revenue surge.
This enforcement strategy proved particularly effective in sectors with traditionally complex compliance requirements. Non-tax revenue streams demonstrated exceptional growth momentum, with fees, duties, and government charges increasing 16.4% year-over-year.
This performance significantly exceeded the 8% aggregate revenue growth rate, suggesting successful diversification of federal income sources beyond traditional taxation.
Historic Debt Service Obligations Constrain Fiscal Flexibility
Mexico allocated a record MX$1 trillion toward debt service payments, representing a historic high that constrains discretionary spending capacity across federal programmes. This autonomous obligation operates independently of policy discretion, creating structural limitations on resource allocation for investment and social programmes.
The debt service burden generates several cascading effects:
- Reduced capacity for countercyclical fiscal policy during economic downturns
- Limited flexibility to increase infrastructure investment without deficit expansion
- Pressure to maintain revenue growth rates to service existing obligations
- Constraints on emergency spending capacity for natural disasters or economic crises
Revenue Composition and Growth Rate Analysis
Mexico's revenue structure reveals interesting differential growth patterns across income sources:
Tax revenues grew 6.1% annually while non-tax revenues expanded 16.4%, suggesting potential for future revenue diversification if regulatory and administrative reforms continue enhancing government fee collection and enforcement capabilities.
This growth differential indicates that non-tax revenue streams may offer greater expansion potential than traditional income and corporate taxation, particularly as digital economy activities generate new fee and licensing opportunities.
Analysing PEMEX's Extraordinary Support Requirements
PEMEX's financial trajectory through 2025 demonstrates the challenges facing state-owned enterprises operating in competitive international markets while maintaining social and political obligations. By the third quarter, the company had already consumed 179% of its authorised annual support, highlighting structural mismatches between operational performance and financial requirements.
According to S&P Global's analysis, Mexico will continue supporting PEMEX to address its ongoing financial strains, reflecting the government's commitment to maintaining energy sector stability.
Production Decline vs. Operational Improvements
PEMEX faces a fundamental paradox where crude oil production continues declining despite improvements in export volumes and refining capacity utilisation. This creates a structural mismatch between the company's revenue-generating capacity and its fixed cost obligations, including debt service, labour commitments, and infrastructure maintenance.
The production decline generates several compounding financial pressures:
- Fixed cost absorption challenges: Operating expenses remain largely constant regardless of production volumes
- Revenue compression: Lower production reduces oil sales revenue even at stable international prices
- Debt servicing burden: Financial obligations remain fixed while cash generation capacity deteriorates
- Capital investment requirements: Ageing infrastructure requires continuous investment to maintain production capacity
However, recent oil price stagnation insights suggest that global market conditions may further complicate PEMEX's revenue recovery prospects.
Emergency Support Mechanisms and Governance Implications
The 179% support authorisation ratio reveals how PEMEX's financial requirements exceeded standard budgetary planning processes. Emergency transfers operated through the Ministry of Energy, which received budget increases outside traditional congressional appropriations review.
This mechanism raises several governance considerations:
- Appropriations authority: Whether emergency transfers violated congressional budget controls
- Fiscal transparency: How extraordinary support measures are reported and audited
- Future budget planning: Integration of realistic support requirements into annual appropriations
- Political oversight: Legislative review of state enterprise support mechanisms
Debt and Finance Cost Escalation Drivers
The explicit identification of finance and debt-service needs as primary drivers of extraordinary support indicates that PEMEX's obligations have reached levels where servicing costs create autonomous spending requirements. This represents fiscal dominance where debt payments drive budget requirements rather than operational discretion.
Key financial pressure points include:
- Principal payments on existing debt obligations
- Interest rate exposure on variable-rate debt instruments
- Foreign exchange risk on dollar-denominated obligations
- Refinancing requirements for maturing debt instruments
- Working capital needs for ongoing operations
Broader Economic Implications of Sustained Petroleum Support
The PEMEX support revenue gap creates ripple effects throughout Mexico's fiscal architecture, influencing everything from infrastructure investment capacity to social programme funding. The 29% decline in physical investment outside PEMEX represents a significant opportunity cost that may impact long-term economic competitiveness.
Furthermore, Bloomberg's reporting indicates that PEMEX continues to report losses despite receiving $41 billion in government support, highlighting the severity of the company's financial challenges.
Infrastructure Investment Displacement
The concentration of federal resources toward petroleum sector support necessarily reduces available funding for other infrastructure priorities. This creates potential long-term consequences:
- Transportation infrastructure: Delayed maintenance and expansion of road, rail, and port facilities
- Digital connectivity: Reduced investment in telecommunications and broadband infrastructure
- Water and sanitation: Postponed upgrades to municipal water treatment and distribution systems
- Energy transition: Limited funding for renewable energy infrastructure development
This displacement effect is particularly concerning given Mexico's energy transition challenges and the need for substantial infrastructure investment to support economic modernisation.
Regional Development Impact Assessment
The fiscal constraints generated by PEMEX support requirements may disproportionately affect regional development programmes that rely on federal transfers. States with limited local revenue capacity depend heavily on federal infrastructure investment to maintain economic growth momentum.
Potential regional implications include:
- Delayed infrastructure projects in economically disadvantaged regions
- Reduced federal support for state and municipal development initiatives
- Limited capacity for regional economic diversification programmes
- Constrained ability to respond to regional economic shocks
Mexico's Path Toward Energy Sector Financial Independence
Mexican government officials project that PEMEX will achieve financial self-sufficiency by 2027, potentially eliminating the need for annual budgetary transfers. This timeline depends on successful implementation of debt refinancing strategies, simplified tax regimes, and integrated refinery operations that enhance cash flow generation.
Consequently, understanding tariffs and investment impact becomes crucial as Mexico navigates potential trade policy changes that could affect PEMEX's international operations and revenue streams.
2027 Self-Sufficiency Strategy Components
The pathway toward PEMEX financial independence involves several interconnected initiatives:
Debt Management Reforms:
- Refinancing existing obligations at favourable terms
- Reducing foreign exchange exposure through peso-denominated instruments
- Extending maturity profiles to reduce annual service requirements
- Potentially restructuring obligations with government guarantees
Operational Efficiency Improvements:
- Integration of refining operations to capture downstream margins
- Enhanced export capacity through infrastructure investments
- Cost reduction programmes targeting administrative and operational expenses
- Technology upgrades to improve production efficiency
Tax and Regulatory Simplification:
- Streamlined tax regime reducing compliance costs and administrative burden
- Regulatory reforms enhancing operational flexibility
- Modified royalty and tax structures aligned with production economics
- Simplified reporting and compliance requirements
International Competitiveness Challenges
PEMEX's path to financial independence occurs within an increasingly competitive international energy market characterised by price volatility, environmental regulations, and technological disruption. The company must balance traditional oil operations with emerging energy transition requirements.
Market positioning factors include:
- Competition from private sector operators in Mexican energy markets
- International oil price volatility affecting revenue predictability
- Environmental compliance costs increasing operational expenses
- Technology investment requirements to maintain production efficiency
Alternative Fiscal Strategies for Revenue Diversification
Mexico's experience with the PEMEX support revenue gap highlights the importance of developing resilient fiscal frameworks less dependent on volatile commodity revenues. Several alternative strategies could enhance fiscal stability while supporting energy sector transformation.
Non-Oil Revenue Expansion Opportunities
The strong performance of non-tax revenues (16.4% growth) suggests potential for further diversification beyond traditional taxation and oil revenues:
Digital economy taxation:
- Enhanced collection from digital services and e-commerce platforms
- Improved taxation of digital advertising and data monetisation activities
- Streamlined compliance for digital nomad and remote work taxation
Regulatory fee optimisation:
- Increased cost recovery from regulated industries (telecommunications, financial services)
- Enhanced environmental permit and compliance fee structures
- Improved customs and trade facilitation fee collection
Public asset monetisation:
- Strategic partnerships for infrastructure development and operation
- Concession arrangements that generate ongoing revenue streams
- Real estate optimisation for government-owned properties
International Benchmarking for State Enterprise Management
Comparative analysis with other national oil companies reveals diverse approaches to balancing commercial objectives with social responsibilities:
| Country | NOC Fiscal Model | Government Support Level | Financial Independence Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brazil (Petrobras) | Mixed ownership with private shareholders | Limited direct transfers | Operationally independent |
| Colombia (Ecopetrol) | Partially privatised with state control | Minimal budget support | Self-financing operations |
| Norway (Equinor) | State ownership with commercial operations | No direct fiscal support | Contributes to sovereign wealth fund |
| Mexico (PEMEX) | Full state ownership | High support requirements | Projected independence by 2027 |
This comparison suggests that ownership structure and operational autonomy significantly influence state enterprise financial performance and fiscal contributions.
Navigating Mexico's Fiscal Transformation
The PEMEX support revenue gap represents more than a temporary fiscal challenge; it reflects fundamental questions about the role of state enterprises in modern economies and the balance between energy security and fiscal sustainability. Mexico's path forward requires careful calibration of short-term stabilisation measures with long-term structural reforms.
Critical Decision Points for Energy and Fiscal Policy
Several key decisions will determine whether Mexico successfully transitions from oil revenue dependence to a more diversified fiscal foundation:
Timing of support phase-out:
- Whether the 2027 self-sufficiency timeline proves realistic given current financial trajectories
- Contingency planning if PEMEX requires continued support beyond projected timelines
- Integration of support reduction with broader energy sector reforms
Alternative investment prioritisation:
- Reallocation of resources freed from PEMEX support toward infrastructure and social programmes
- Balance between traditional infrastructure and energy transition investments
- Regional distribution of federal investment to support economic diversification
Institutional governance reforms:
- Enhanced oversight mechanisms for state enterprise financial performance
- Improved integration of state enterprise budgeting with federal fiscal planning
- Strengthened congressional oversight of emergency support mechanisms
Mexico's fiscal future depends on successfully managing this transition while maintaining energy security and supporting broader economic development objectives. The lessons learned from addressing the PEMEX support revenue gap will influence fiscal policy frameworks for years to come, potentially serving as a model for other emerging economies facing similar challenges with state-owned enterprises and commodity revenue dependence.
Disclaimer: This analysis is based on fiscal data through October 2025 and government projections that may change due to economic conditions, policy modifications, or operational performance variations. Future financial performance of state enterprises involves inherent uncertainties that could affect projected timelines and outcomes.
Looking for Opportunities in Mexican Energy Sector Transitions?
Discovery Alert's proprietary Discovery IQ model delivers real-time notifications on significant ASX mineral discoveries, helping investors identify actionable opportunities whilst broader markets navigate global energy transitions. Explore how major mineral discoveries have historically generated substantial returns by visiting Discovery Alert's dedicated discoveries page and begin your 30-day free trial today to position yourself ahead of the market.