Fire at Glencore's Lomas Bayas Copper Mine: Impact and Industry Implications
The Fire Incident Details
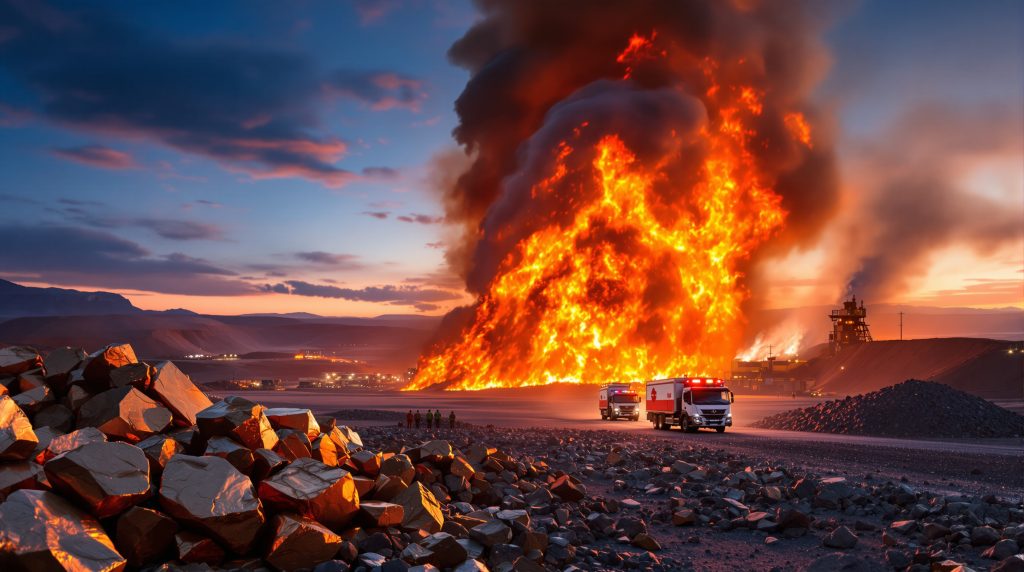
A fire erupted at Glencore's Lomas Bayas copper mine in Chile on September 30, 2025. The incident was first reported by Chilean media outlet Radio Biobio, with mine representatives not immediately available for official comment. Located in Chile's mineral-rich Atacama Desert region, this operational disruption affects a significant copper producing facility during a period of already constrained global supply.
The fire's exact cause remains under investigation, and preliminary assessments indicate the blaze originated in the mine's processing facilities, though this awaits official confirmation from Glencore representatives.
Immediate Response and Safety Concerns
Emergency response protocols were swiftly activated following the fire outbreak, with local firefighting teams dispatched to the mining complex. While details regarding potential injuries remain limited, industry sources familiar with the operation indicated the mine had been evacuated according to standard safety procedures.
This incident is particularly notable as Lomas Bayas had recently celebrated an impressive safety milestone, having achieved 2 million hours without lost-time accidents earlier in 2025. This achievement had positioned the mine as a safety leader within Glencore's global portfolio of operations.
How Important is the Lomas Bayas Operation?
Production Capacity and Output
The Lomas Bayas operation represents a significant contributor to Glencore's copper portfolio, producing approximately 74,000 metric tons of copper cathodes in 2024. This output, while modest compared to Chile's largest operations, still accounts for roughly 1.5% of the country's total copper production.
What makes Lomas Bayas particularly remarkable is its operational efficiency despite challenging geological conditions. The open-pit mine processes exceptionally low-grade copper ore—averaging just 0.25% copper content—through sophisticated heap leaching technology. This grade is among the lowest commercially viable copper operations globally, yet through innovative processing methods, the mine maintains consistent and profitable production.
Strategic Value in Glencore's Portfolio
Glencore acquired the Lomas Bayas operation during its landmark $90 billion merger with Xstrata in 2013. The mine represents an important strategic asset within Glencore's diversified mining portfolio, particularly as copper continues gaining prominence in global markets driven by rising copper demand.
Located approximately 120 kilometers northeast of Antofagasta in northern Chile, the mine benefits from proximity to port infrastructure and established logistics networks. With over 500 direct employees and hundreds more contractors, Lomas Bayas also represents a significant economic contributor to Chile's Antofagasta region.
What Are the Potential Market Implications?
Impact on Copper Supply and Pricing
The timing of this incident is particularly significant as it coincides with an already constrained global copper market. Copper prices had been experiencing notable volatility throughout 2025, with September marking the metal's strongest monthly performance since June, rising 4.2% on persistent supply concerns.
Multiple factors had already been pressuring copper supplies before this incident, including operational disruptions at major mines in Peru, labor disputes in Panama, and processing bottlenecks in Africa's Copper Belt. Industry analysts now suggest the Lomas Bayas disruption could potentially remove between 20,000-30,000 tons of copper from global markets if the shutdown extends beyond a few weeks.
| Indicator | Value | Change |
|---|---|---|
| Copper Price | $4.866/lb | -0.81% daily |
| Monthly Performance | +4.2% | Best since June |
| Global Supply Disruptions | Multiple | Increasing |
| Market Sentiment | Bullish | Supply concerns |
Broader Industry Context
The fire at Lomas Bayas adds to a troubling series of operational challenges facing major copper producers in 2025. Weather events, technical failures, and labor disputes have increasingly affected output across key producing regions. These supply constraints come at a particularly sensitive time for copper markets, with demand growing steadily due to energy transition technologies and infrastructure development.
"The global copper market was already facing a deficit of approximately 150,000 tons for 2025 before this incident. Any prolonged disruption at Lomas Bayas will only exacerbate the tightness in an already strained market." – Mining analyst from a leading financial institution
The market implications extend beyond immediate price reactions. Copper cathodes from Lomas Bayas are primarily exported to Asian markets, where fabricators may now face additional sourcing challenges amid already tight inventories. With LME copper inventories sitting near multi-year lows, the market has limited buffer against supply disruptions.
How Does This Fit Into Chile's Copper Sector Challenges?
Chile's Copper Production Landscape
Chile remains the world's copper powerhouse, accounting for approximately 28% of global copper supply forecast. However, the country has been facing mounting challenges in maintaining its production dominance. Aging mines, declining ore grades, and severe water constraints in the Atacama Desert region have all contributed to production pressures.
The Chilean Copper Commission (Cochilco) had already revised down its 2025 production forecast from 5.9 million to 5.8 million tons before this incident, citing operational challenges across several major mines. The Lomas Bayas disruption now threatens to further reduce this output, potentially dropping Chile below the symbolic 5.7 million ton threshold for the first time since 2018.
Regulatory and Environmental Considerations
Chilean authorities have implemented increasingly stringent safety and environmental regulations for mining operations following several high-profile incidents in recent years. The fire at Lomas Bayas will likely trigger heightened regulatory scrutiny and potentially new compliance requirements.
Water management has become particularly critical for Chilean copper operations, with mines competing for scarce resources in one of the world's driest regions. Lomas Bayas had invested significantly in water efficiency technologies, including advanced recycling systems that allow it to operate with approximately 45% less water per ton of copper produced compared to conventional operations.
The Chilean government's increasing focus on sustainability credentials for mining operations means the post-fire recovery efforts will likely need to demonstrate enhanced environmental controls to secure necessary approvals for resuming full operations.
What Technologies Are Being Implemented at Lomas Bayas?
Technological Innovations and Efficiency Improvements
Prior to the fire incident, Lomas Bayas had been implementing significant technological upgrades to enhance operational efficiency and safety. Most notably, the mine had deployed Hexagon's Smart Center technology—an integrated monitoring and control system that provides real-time visibility across data-driven mining operations.
This technology implementation included:
- Advanced fleet management systems reducing fuel consumption by 7%
- Predictive maintenance algorithms that had decreased unplanned downtime by 18%
- Autonomous drilling operations in select areas of the mine
- Enhanced metallurgical controls improving copper recovery rates by 3.2%
These digital transformation initiatives were crucial for maintaining profitability while processing such low-grade ore bodies, essentially allowing Lomas Bayas to "do more with less" in challenging geological conditions.
Life Extension Projects
Glencore had been actively exploring technologies to extend Lomas Bayas' operational life beyond its currently projected closure date of 2029. A notable partnership with Chilean technology provider Ceibo had been established to test advanced copper bioleaching techniques that could potentially extend the mine's productive life by at least seven years.
The innovative bioleaching approach uses specialized bacteria to extract copper from previously uneconomical low-grade material, potentially unlocking access to an additional 250,000 tons of recoverable copper from existing waste dumps and tailings. Initial pilot tests had shown promising results, with recovery rates exceeding 65% from material previously considered uneconomical.
These life extension initiatives take on new significance following the fire, as they may influence Glencore's decision-making regarding the scale and timing of investments in rebuilding affected infrastructure.
How Will This Affect Glencore's Strategic Position?
Glencore's Copper Strategy
Glencore has positioned copper as a core component of its future growth strategy, particularly given the metal's critical role in energy transition technologies. The company has been actively rebalancing its portfolio toward copper and other battery metals while reducing exposure to thermal coal.
In its most recent strategic update, Glencore indicated plans to increase copper production by approximately 15% by 2028 through a combination of brownfield expansions and operational improvements across its global portfolio. While Lomas Bayas represents a relatively modest portion of Glencore's total copper output, the mine's consistent performance and low operating costs made it an important cash generator within the company's Chilean operations.
The fire now presents Glencore with strategic decisions regarding not only the restoration of operations but potentially the acceleration of previously planned upgrades and expansions that might be more efficiently implemented during an extended shutdown period.
Asset Optimization Considerations
Prior to this incident, industry analysts had occasionally speculated about Glencore potentially divesting Lomas Bayas as part of broader portfolio optimization efforts. The company had been reducing debt and focusing capital on its highest-return opportunities, leading to questions about whether smaller operations like Lomas Bayas remained core to its long-term strategy.
The Glencore smelter impact on global copper markets is already significant, and this fire could potentially accelerate Glencore's strategic review of the asset, particularly if restoration costs prove substantial or production impacts extend beyond initial estimates. However, with copper price prediction remaining strong due to energy transition demand, the economic case for rebuilding and potentially expanding Lomas Bayas remains compelling despite the current setback.
Industry observers note that Glencore may also use this opportunity to negotiate favorable terms with Chilean authorities regarding permitting for future expansions or life extension projects in exchange for commitments to enhanced safety and environmental controls during the rebuilding process.
What Are the Recovery Prospects and Timeline?
Damage Assessment and Recovery Planning
The immediate priority following the fire involves comprehensive damage assessment and development of a phased recovery plan. While official statements regarding the extent of damage remain pending, similar incidents at copper processing facilities typically require:
- Initial safety stabilization and site security (1-2 weeks)
- Comprehensive structural and equipment assessment (2-4 weeks)
- Development of detailed recovery engineering plans (4-8 weeks)
- Equipment procurement and replacement (timeframe dependent on damage extent)
- Reconstruction of affected facilities (3-9 months depending on severity)
- Commissioning and gradual return to full production (1-3 months)
Historical precedents suggest recovery timelines ranging from 3-12 months depending on the extent of damage to critical infrastructure. The most comparable recent incident occurred at another Chilean copper facility in 2023, which resulted in a three-week production suspension and approximately $45 million in repair costs after a fire affected a secondary processing area.
Operational Continuity Measures
Glencore will likely implement various contingency measures to maintain some level of operational continuity during the recovery period:
- Focusing on mining activities while processing facilities are rebuilt
- Stockpiling ore for future processing when facilities return online
- Potentially utilizing excess capacity at other regional facilities through toll processing arrangements
- Accelerating planned maintenance activities across unaffected parts of the operation
Insurance coverage will play a critical role in the recovery economics. Most major mining operations maintain comprehensive business interruption insurance that covers both physical damage and lost production value. However, policy specifics including deductibles, waiting periods, and coverage limits will significantly influence the financial impact on Glencore's global copper operations.
FAQ: Key Questions About the Lomas Bayas Fire Incident
How does this fire compare to other mining incidents in Chile?
Chile has experienced several significant mining incidents in recent years, though fires at major copper operations have been relatively rare. The most comparable recent incident occurred in 2023 at another major copper facility, which resulted in a three-week production suspension and approximately $45 million in repair costs.
More severe was the 2022 processing plant fire at a northern Chilean operation that resulted in a six-month partial shutdown and over $120 million in reconstruction costs. The Lomas Bayas incident appears potentially more significant than the 2023 event but likely less severe than the 2022 case, though official damage assessments remain pending.
What safety systems were in place at Lomas Bayas?
Prior to the incident, Lomas Bayas had implemented comprehensive safety management systems, including advanced monitoring technology through Hexagon's Smart Center. The mine had achieved significant safety milestones, including 2 million hours without lost-time accidents earlier in 2025.
Key safety systems included:
- Advanced fire detection and suppression systems
- Regular emergency response drills and trained emergency teams
- Continuous environmental monitoring systems
- Integrated operations center with real-time monitoring capabilities
The investigation will likely focus on whether these systems functioned as designed and if any improvements are needed in future installations.
How might this affect Chile's copper export targets?
Chile had projected copper exports of approximately 5.8 million metric tons for 2025. While Lomas Bayas represents less than 2% of this total, any prolonged disruption would contribute to cumulative production shortfalls that have challenged the country's export targets in recent years.
The impact becomes more significant when considered alongside other operational issues affecting Chilean production, including water constraints at several major operations and ongoing grade deterioration at aging mines. Analysts suggest the combined effect could potentially reduce Chilean exports by 2-3% compared to initial 2025 projections.
What are the environmental implications of the fire?
Mining fires can potentially release hazardous substances and create air quality concerns. Chilean environmental authorities typically conduct independent assessments following such incidents to evaluate potential impacts and determine if additional remediation measures are required beyond the immediate fire response.
Key environmental concerns include:
- Potential air quality impacts from smoke and particulates
- Risk of contaminated water from firefighting efforts
- Chemical releases from damaged processing facilities
- Soil contamination in affected areas
The mine's location in the Atacama Desert somewhat reduces certain environmental risks due to the absence of significant surface water resources, but increases concerns about potential impacts to the region's fragile desert ecosystem.
Industry-Wide Implications of the Lomas Bayas Fire
The fire at Glencore's Lomas Bayas copper mine represents more than just an isolated operational incident. It highlights the ongoing challenges facing copper producers globally, particularly in maintaining consistent production amid aging infrastructure, declining ore grades, and increasing operational complexities. The incident occurs against a backdrop of tight copper supply and growing demand, potentially exacerbating market volatility.
For Glencore specifically, the fire presents both immediate operational challenges and longer-term strategic considerations regarding the future of Lomas Bayas within its portfolio. The company's response and recovery efficiency will be closely monitored by investors and industry analysts as an indicator of operational resilience.
More broadly, the incident underscores the importance of robust risk management, technological innovation, and operational redundancy in modern mining operations. As the industry continues to navigate the complex intersection of production pressures, safety requirements, and sustainability expectations, events like the Lomas Bayas fire serve as important reminders of the inherent challenges in resource extraction.
The increasing frequency of operational disruptions across the copper industry suggests companies may need to reassess their approach to redundancy and contingency planning. With copper playing a crucial role in the global energy transition, ensuring supply chain resilience becomes increasingly critical not only for mining companies but for the broader manufacturing sectors dependent on reliable copper supplies.
Want to Stay Ahead of the Next Major Mineral Discovery?
Discovery Alert's proprietary Discovery IQ model delivers instant notifications for significant ASX mineral discoveries, providing crucial insights before the wider market. Visit our discoveries page to see why historic discoveries have generated substantial returns for early investors.