Understanding the Global Lead Market: Recent Deficit Trends and Future Outlook
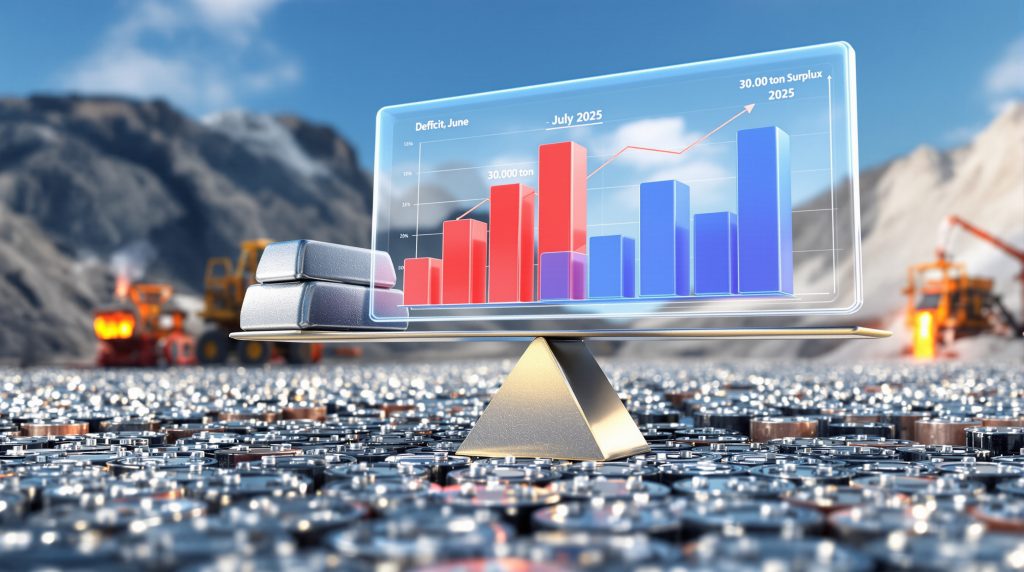
The global lead market has experienced significant shifts in 2025, with the deficit narrowing to 5,600 metric tons in July from a more substantial 19,100 tons in June, according to recent International Lead and Zinc Study Group (ILZSG) data. This reduction represents a 70.7% decrease in the monthly global lead market deficit, signaling important changes in market dynamics.
Despite these monthly deficits, the broader picture for 2025 reveals a different trend. The first seven months of the year actually recorded a 30,000-ton surplus of refined lead metal, tripling the 10,000-ton surplus observed during the same period in 2024.
Key Lead Market Statistics for 2025 (January-July)
| Metric | 2025 (Jan-Jul) | 2024 (Jan-Jul) | Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mine Production | 2,571,000 tons | 2,562,000 tons | +0.35% |
| Metal Production | 7,702,000 tons | 7,537,000 tons | +2.19% |
| Metal Usage | 7,672,000 tons | 7,527,000 tons | +1.93% |
| Market Balance | +30,000 tons | +10,000 tons | +200% |
What's Driving Changes in the Lead Market Balance?
The global lead market has undergone significant transformations in recent months, with numerous factors contributing to the shift from monthly deficits to an overall surplus position. Understanding these drivers is essential for stakeholders across the supply chain.
Supply-Side Factors Influencing Lead Production
Mining Output Fluctuations
Despite the overall increase in mine production for the January-July period, monthly data shows significant volatility. July's mine production (379,300 tons) decreased by 3.2% compared to June (391,900 tons), highlighting ongoing supply challenges.
Several key mining regions have experienced operational disruptions, including weather-related events and labor disputes, contributing to the inconsistent production levels. The mining industry evolution has been particularly evident in how these challenges are being addressed with new technologies and approaches. These disruptions have been partially offset by increased output from secondary sources, primarily recycling operations.
Refined Metal Production Growth
Metal production has shown greater resilience, with July's output (1,094,000 tons) increasing by 0.8% over June (1,085,100 tons). This growth in refined lead production has helped ease some supply constraints despite mining fluctuations.
The discrepancy between declining mine output and increasing refined production suggests processors are drawing from existing concentrate inventories and improving operational efficiencies. Technological improvements in smelting processes have also contributed to higher metal recovery rates at major refineries.
Demand-Side Dynamics Affecting Market Balance
Consumption Patterns and Trends
Metal usage decreased by 0.4% from June to July 2025, dropping from 1,104,200 tons to 1,099,600 tons. This slight reduction in consumption has contributed to the narrowing deficit.
Seasonal factors typically influence lead consumption, with summer months often showing reduced demand from the automotive sector in particular. The minor contraction in July usage follows historical patterns, though at a less pronounced rate than in previous years.
Regional Consumption Variations
While global data shows an overall surplus, regional markets are experiencing varied conditions:
-
Asia-Pacific: Remains the dominant consumption region with strong battery manufacturing demand, particularly in China and India where industrial battery applications continue to expand.
-
Europe: Facing pressure from automotive industry slowdowns, with vehicle production numbers remaining below pre-pandemic levels in several key markets.
-
North America: Showing steady demand supported by infrastructure investments under the Trump administration's renewed focus on domestic manufacturing and energy independence policies.
How Do Historical Lead Market Trends Compare to Current Conditions?
Understanding the current lead market requires examining its historical context and cyclical patterns that have defined this metal's supply-demand dynamics over time.
Long-Term Market Balance Patterns
The lead market has historically alternated between periods of surplus and deficit. The current situation—monthly deficits within an overall surplus period—reflects this cyclical nature. Since 2020, the market has experienced:
-
2020-2021: Significant deficits due to pandemic-related supply disruptions that severely impacted mining operations worldwide
-
2022-2023: Gradual return to balance as supply chains normalized and production capacity recovered
-
2024: Small surplus (10,000 tons in first seven months) as production increases outpaced demand recovery
-
2025: Larger surplus (30,000 tons in first seven months) with decreasing monthly deficits indicating continued supply chain stabilization
This pattern demonstrates the market's typical 3-5 year cycle between tight and oversupplied conditions, a characteristic that distinguishes lead from some other base metals with longer cycle periods.
Price Response to Changing Market Conditions
Lead prices have responded to these shifting supply-demand dynamics:
-
Price Volatility: Fluctuations reflecting monthly deficit/surplus changes have created trading opportunities but challenges for consumers requiring price stability
-
Overall Trend: Moderate price pressure despite the year-to-date surplus, with prices remaining above historical averages due to broader inflationary pressures
-
Regional Premiums: Varying based on local supply conditions, with particularly high premiums in regions experiencing localized shortages despite the global surplus
Unlike some other metals that have seen dramatic price increases, lead's price movements have remained relatively constrained, reflecting both its surplus position and the metal's mature market status with established recycling channels. Recent copper price insights reveal a stark contrast to lead's more modest valuation trends.
What Are the Key Applications Driving Lead Demand?
Understanding demand patterns requires analyzing the diverse applications that consume lead in today's global economy.
Battery Sector Dominance
The lead-acid battery industry continues to account for approximately 80% of global lead consumption, with demand driven by:
-
Automotive Batteries: Still the largest application despite EV growth, with traditional internal combustion engine vehicles requiring lead-acid starter batteries and hybrid vehicles often incorporating lead-acid auxiliary systems
-
Industrial Batteries: Growing demand for backup power systems, particularly in telecommunications infrastructure and data centers where reliability requirements continue to increase
-
Energy Storage Solutions: Increasing use in renewable energy installations, with lead-acid batteries providing cost-effective storage for smaller-scale solar and wind installations
The resilience of lead-acid battery demand demonstrates the technology's continued relevance despite competition from alternative chemistries. Improvements in lead-acid technology, including enhanced energy density and cycle life, have helped maintain its market position. Additionally, battery recycling innovations are extending the lifecycle value of lead-acid batteries.
Non-Battery Applications
The remaining 20% of lead consumption comes from:
-
Construction Materials: Lead sheets and radiation shielding used in healthcare facilities, laboratories, and nuclear installations
-
Cable Sheathing: For underwater and underground applications where lead's corrosion resistance and flexibility provide unique advantages
-
Ammunition and Alloys: Specialized industrial uses including ammunition production, ballast applications, and specialized alloys
These diverse applications provide stability to lead demand, creating a buffer against fluctuations in any single sector. The construction sector in particular has shown increased demand as infrastructure spending rises globally.
What Are the Environmental and Regulatory Factors Affecting Lead Markets?
Environmental considerations and evolving regulations significantly impact both the supply and demand sides of the global lead market.
Recycling's Impact on Supply
Lead has one of the highest recycling rates among metals, with secondary (recycled) lead accounting for over 60% of global supply. Recent developments include:
-
Recycling Efficiency Improvements: New technologies increasing recovery rates, with advanced sorting and processing methods capturing a higher percentage of available lead from end-of-life products
-
Collection System Expansion: Better battery return programs in developing markets, particularly in Southeast Asia and Africa where formal collection systems are maturing
-
Quality Standards: Stricter requirements for recycled lead, with manufacturers demanding higher purity levels to meet performance specifications
The recycling sector's efficiency directly impacts the supply-demand balance, with improvements in collection rates effectively increasing available supply without additional mining activity. Industry estimates suggest recycling rates could reach 70% by 2030, according to recent analysis by GMI.
Regulatory Pressures and Responses
Environmental regulations continue to shape the lead industry:
-
Emissions Standards: Tightening controls on smelter operations, particularly in China where environmental enforcement has intensified
-
Battery Directive Updates: Extended producer responsibility requirements creating more comprehensive collection systems across Europe and increasingly in North America
-
Substitution Pressures: Research into alternatives for some applications, though technical limitations and cost considerations have limited widespread substitution
Regulatory compliance costs have risen significantly, particularly for primary producers, creating a competitive advantage for modernized recycling operations with lower environmental footprints. This dynamic has accelerated investment in secondary production capacity. The focus on sustainability in mining has become a crucial aspect of the lead market's evolution.
What's the Outlook for the Global Lead Market?
Analyzing current trends and underlying factors provides insight into the likely future direction of the global lead market.
Short-Term Market Projections
For the remainder of 2025 and early 2026, analysts project:
-
Continuing Surplus: The overall surplus trend is likely to persist, with production growth continuing to outpace demand increases
-
Decreasing Monthly Deficits: Further narrowing of monthly deficits expected, with potential for consistent monthly surpluses by early 2026
-
Price Stabilization: Reduced volatility as market balance improves, though regional variations will persist based on localized supply chains
These projections suggest a period of relative market stability, with predictable pricing beneficial for both producers and consumers making long-term investment decisions.
Long-Term Supply-Demand Forecast
Looking beyond 2025, key factors shaping the lead market include:
-
Battery Technology Evolution: Potential impact of new energy storage technologies, though lead-acid batteries are expected to maintain significant market share in automotive and industrial applications
-
Mining Project Pipeline: Limited new primary lead mining projects, with most new production expected to come from expansion of existing operations rather than greenfield developments
-
Secondary Supply Growth: Increasing importance of recycling infrastructure, particularly in emerging markets where collection systems are developing rapidly
-
Regional Demand Shifts: Emerging market growth offsetting developed market stability, with India and Southeast Asia expected to show the strongest demand growth rates
The long-term outlook suggests a market in gradual transition, with recycling becoming increasingly dominant in the supply mix and application technologies evolving to maintain lead's relevance despite competition from alternative materials.
How Does the Lead Market Compare to Other Metal Markets?
The lead market exhibits distinct characteristics when compared to other metals, providing important context for investors and industry stakeholders.
Comparative Market Conditions
Unlike many other base metals experiencing significant deficits in 2025, lead stands out with its overall surplus position:
| Metal | 2025 Market Balance | Price Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Lead | 30,000-ton surplus | Moderate pressure |
| Copper | Significant deficit | Strong upward pressure |
| Zinc | Small deficit | Moderate upward pressure |
| Nickel | Surplus | Downward pressure |
This divergence highlights how different supply-demand fundamentals can lead to contrasting market conditions even among closely related metals. While copper prices have surged due to supply constraints, lead has maintained relatively stable pricing reflective of its surplus position.
Correlation with Economic Indicators
Lead demand shows distinct patterns compared to other metals:
-
Less Sensitive to construction activity than copper or steel, making it less responsive to housing market fluctuations
-
More Closely Tied to automotive production and replacement cycles, creating a more predictable demand pattern
-
Moderately Affected by general economic growth indicators, with a higher percentage of demand coming from replacement applications rather than new product manufacturing
These characteristics make lead a somewhat counter-cyclical metal compared to others, often experiencing different market phases and price movements. This distinction provides portfolio diversification benefits for investors with exposure to multiple metal markets.
FAQ: Global Lead Market Conditions
What caused the lead market deficit to narrow in July 2025?
The narrowing deficit resulted from a combination of slightly increased metal production (up 0.8% from June) and decreased consumption (down 0.4%), creating a more balanced monthly market condition. These changes reflect both operational improvements at refineries and typical seasonal demand patterns.
Is the global lead market currently in deficit or surplus?
While July 2025 showed a 5,600-ton deficit, the overall market for the first seven months of 2025 recorded a 30,000-ton surplus, indicating that production has generally exceeded consumption across the broader period. This pattern of monthly deficits within an overall surplus highlights the importance of analyzing longer timeframes when assessing market conditions.
How does the 2025 lead market compare to previous years?
The 2025 market shows a larger surplus (30,000 tons) compared to the same period in 2024 (10,000 tons), suggesting improving supply conditions relative to demand. This continues the gradual shift toward oversupply that began in late 2023 as production capacity recovered from earlier disruptions.
What regions are driving lead demand growth?
Emerging markets in Asia continue to lead demand growth, particularly in the automotive and energy storage sectors, while mature markets show more stable consumption patterns. India and Southeast Asian nations are showing particularly strong growth rates as vehicle ownership expands and industrial applications increase.
How significant is recycled lead to the overall market?
Secondary (recycled) lead accounts for over 60% of global supply, making the recycling sector a critical component of market balance and increasingly important as environmental regulations tighten. The high recycling rate distinguishes lead from many other metals and provides significant supply stability.
Future Challenges and Opportunities in the Lead Market
The lead industry faces a complex landscape of both challenges and opportunities that will shape its evolution in coming years.
Technological Disruption Potential
The lead industry faces both challenges and opportunities from technological changes:
-
Challenge: Competition from lithium-ion and other battery technologies, particularly in electric vehicle applications where lead-acid batteries have limited presence
-
Opportunity: Lead-acid battery improvements for specific applications, including advanced carbon additives that enhance performance characteristics
-
Adaptation: Development of lead-carbon hybrid technologies that combine lead-acid reliability with improved energy density and cycle life
Industry investment in research and development has accelerated, with major manufacturers recognizing the need for continuous innovation to maintain lead's competitive position in evolving energy storage markets.
Sustainability Initiatives
Environmental considerations are reshaping industry practices:
-
Carbon Footprint Reduction: Energy efficiency improvements in smelting, with modernized facilities achieving significantly lower emissions per ton of output
-
Closed-Loop Systems: Enhanced battery collection and recycling, with industry initiatives promoting near-100% recovery rates in developed markets
-
Product Design: Innovations to improve recyclability and reduce material usage, including more efficient battery designs that deliver the same performance with less lead content
These sustainability efforts represent both a response to regulatory pressure and a proactive strategy to maintain lead's social license to operate in an increasingly environmentally conscious marketplace. The mining decarbonisation benefits are becoming increasingly apparent throughout the supply chain.
The global lead market deficit continues to evolve through a complex interplay of supply-demand dynamics, technological developments, and environmental considerations. While currently in surplus territory, the market's cyclical nature suggests potential rebalancing in the coming years as production and consumption patterns adjust to changing economic and regulatory landscapes.
Further Exploration:
Readers interested in learning more about global metal markets and commodity trends can explore Trading Economics' lead price data, which regularly publishes market analysis and industry reports on various metals including lead.
Want to Spot the Next Major Mineral Discovery Before the Market?
Discover how ASX investors can gain an immediate edge with real-time alerts on significant mineral discoveries through Discovery Alert's proprietary Discovery IQ model. Explore our dedicated discoveries page to understand how historic mineral discoveries have generated substantial returns for early investors.