Understanding Metallurgical Coal Markets: Coronado Global Resources and Price Volatility
Amid the global push for decarbonization, metallurgical coal markets have experienced unprecedented volatility, with prices plummeting from record highs in 2022 to multi-year lows in 2025. This dramatic shift has severely impacted producers like Coronado Global Resources (ASX:CRN), whose share price has collapsed by 85% in just twelve months. Understanding this complex market requires examining both industry-specific factors and broader economic trends affecting the steel manufacturing supply chain.
What Is Metallurgical Coal and How Does It Differ from Thermal Coal?
Defining Metallurgical Coal's Role in Steel Production
Metallurgical coal, often called coking coal, serves as an irreplaceable component in traditional steel manufacturing processes. Unlike thermal coal used primarily for electricity generation, metallurgical coal undergoes a specialized transformation into coke—a carbon-rich material that provides both the heat and chemical reactants necessary for iron ore reduction in blast furnaces.
The fundamental difference lies in their applications: thermal coal generates heat and steam for power plants, while metallurgical coal creates the essential reducing agent (coke) that converts iron ore into liquid iron for steelmaking. This critical role in industrial manufacturing explains why metallurgical coal typically commands premium pricing compared to its thermal counterpart.
"Metallurgical coal is fundamentally tied to steel production in a way that thermal coal isn't to electricity generation," explains Nick Sundich of Stocks Down Under. "While thermal coal faces competition from renewable energy sources, metallurgical coal faces fewer immediate substitutes in traditional steelmaking."
Key Quality Parameters That Determine Value
Not all metallurgical coal is created equal. Premium hard coking coal varieties command substantially higher prices based on several crucial quality parameters:
- Volatile matter content: Ideally between 20-26% to ensure proper coking properties
- Ash content: Premium grades contain less than 10% ash
- Sulfur levels: High-quality coking coal contains under 1% sulfur
- Caking properties: Measured by indices like CSR (Coke Strength after Reaction)
- Fluidity: Determines how well the coal melts during the coking process
These chemical and physical properties directly impact the efficiency and quality of steel production. Higher-grade metallurgical coal creates stronger coke with better structural integrity inside blast furnaces, resulting in more efficient steel production and higher-quality final products.
The specialized nature of metallurgical coal, with its specific chemical requirements and limited global availability, creates a distinct market dynamic separate from the broader thermal coal industry. This specialization has historically protected metallurgical coal from some of the market pressures affecting thermal coal, though recent price volatility suggests this insulation may be weakening.
How Have Metallurgical Coal Prices Performed Historically?
The Dramatic Price Volatility Since 2020
Metallurgical coal has experienced extreme price volatility that even seasoned industry participants describe as unprecedented. Consider these dramatic swings:
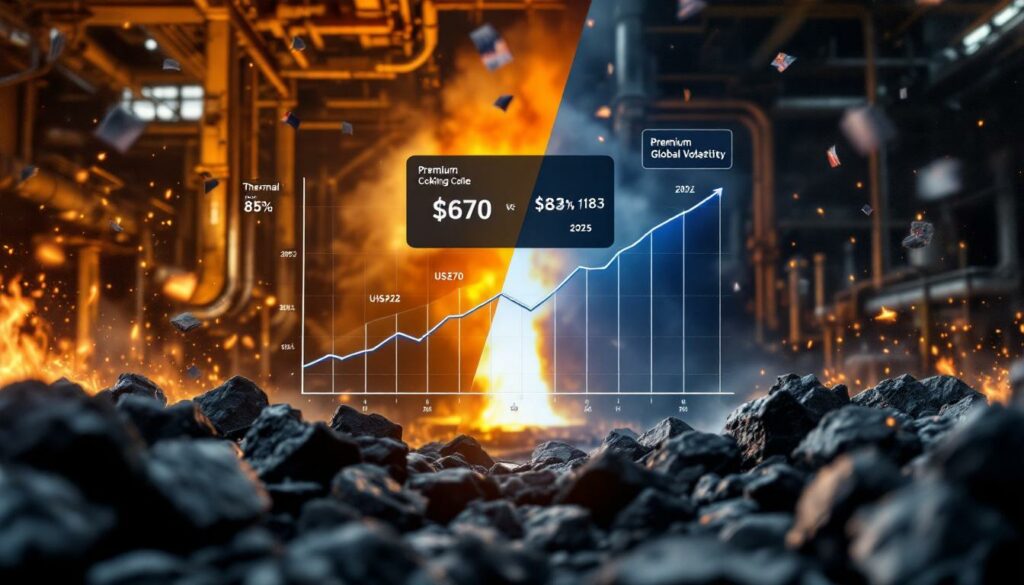
- 2022 Peak: Prices reached an extraordinary US$670 per tonne
- July 2025: Prices plummeted to approximately US$183 per tonne
- Overall Decline: A staggering 72.7% drop from peak to current levels
This volatility far exceeds historical norms for the industry, which typically saw more moderate fluctuations tied to steel production cycles. The COVID-19 pandemic initially disrupted supply chains, creating shortages that drove prices upward. The Russia-Ukraine conflict further exacerbated supply concerns, pushing prices to all-time highs in 2022.
"The peak-to-trough movement we've witnessed since 2022 represents the most dramatic price collapse in metallurgical coal markets in recent memory," notes industry analyst Nick Sundich. "Even veteran producers were caught off guard by the severity of the decline."
Factors Driving Recent Price Declines
Multiple interconnected factors have contributed to the collapse in iron ore price trends and metallurgical coal prices:
-
Chinese Steel Production Decline: Steel production in China has fallen to seven-year lows in 2025, with the government actively curtailing output to reduce emissions and address overcapacity issues. As the world's largest steel producer, China's reduced demand has created significant ripple effects.
-
Global Supply Increases: Production expansions planned during the high-price environment of 2022 have now come online, flooding the market with additional supply just as demand weakens.
-
U.S. Production Potential: The specter of increased American coal production under protectionist policies has created oversupply concerns among market participants.
-
Economic Uncertainty: Broader economic headwinds have reduced steel demand in construction, automotive, and infrastructure sectors globally.
-
Alternative Supplier Availability: Increased competition from emerging suppliers in Mongolia and Mozambique has disrupted traditional market dynamics.
This perfect storm of declining demand and increasing supply has created persistent downward pressure on prices, with few signs of immediate relief for producers like Coronado Global Resources.
Who Is Coronado Global Resources and What Are Their Operations?
Company Overview and Global Footprint
Coronado Global Resources (ASX:CRN) operates as a specialized metallurgical coal producer with a strategic presence spanning two continents. Established through a series of acquisitions, the company has positioned itself as a significant supplier to steel manufacturers across multiple global regions.
The company's business model centers on extracting, processing, and exporting high-quality metallurgical coal from its operations in Australia and the United States. This dual-hemisphere approach provides Coronado with geographical diversification and access to different customer markets, including:
- North American steel mills
- European manufacturing centers
- Asian industrial hubs (particularly Japan, South Korea, and India)
- South American steel producers
This global footprint initially provided Coronado with resilience against regional market fluctuations. However, the synchronized global downturn in steel production has minimized these diversification benefits in recent years.
Key Mining Assets and Production Capacity
Coronado's operational portfolio includes three primary mining complexes across two countries:
| Operation | Location | Resources | Reserves | Operating Since | Acquisition Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Logan | Central Appalachian region (Virginia/West Virginia, USA) | 248Mt | 135Mt | 2005 | 2014 |
| Buchanan | Central Appalachian region (Virginia/West Virginia, USA) | 203Mt | 154Mt | 1983 | 2016 |
| Curragh Complex | Bowen Basin, Queensland, Australia | 936Mt | 290Mt | Varies | Not specified |
The Curragh Complex represents Coronado's crown jewel by resource volume, containing nearly 1 billion tonnes of coal resources. This operation produces both metallurgical coal for export markets and thermal coal, which is sold domestically to Stanwell Corporation for Queensland's electricity generation.
Each mining complex features different coal quality characteristics:
- Buchanan: Produces premium low-volatile hard coking coal with excellent caking properties
- Logan: Yields mid-volatile and high-volatile coking coal varieties
- Curragh: Delivers a diverse range of metallurgical coal products, from premium hard coking to semi-soft coking coal
This product diversity historically allowed Coronado to serve various customer specifications and optimize its sales mix based on prevailing market conditions. However, the company's extensive fixed-cost base across these operations has created significant financial pressure during the current price downturn.
Why Has Coronado's Stock Price Collapsed by 85%?
Analyzing the Multifaceted Causes of the Share Price Decline
Coronado Global Resources has experienced a catastrophic share price collapse, with its stock plummeting approximately 85% over the twelve months leading to July 2025. This precipitous decline stems from several interconnected factors:
-
Metallurgical Coal Price Collapse: The 72.7% drop in metallurgical coal prices from 2022 peaks has directly impacted Coronado's revenue and profitability. With prices falling from US$670 to US$183 per tonne, the company's core product has lost significant value.
-
Long-Term Viability Concerns: Market participants have raised serious questions about metallurgical coal's future in a decarbonizing world, compressing valuation multiples for all producers in the sector.
-
Increasing Operational Costs: While coal prices have fallen, many input costs (energy, labor, equipment) have remained elevated, squeezing profit margins from both directions.
-
Index Exclusion: Coronado's removal from the ASX 200 index triggered automatic selling by index-tracking funds, creating additional downward pressure on the share price.
-
Failed Acquisition Attempt: A 2023 acquisition offer from Czech billionaire Pavel Tykac's Sev.en Global Investments failed to materialize, removing a potential price floor for the stock.
"The market is pricing in not just current metallurgical coal weakness, but fundamental questions about whether metallurgical coal even has a future in a 'Net Zero' world," notes Nick Sundich of Stocks Down Under.
This combination of immediate operational challenges and existential long-term concerns has created a perfect storm for Coronado's share price.
The Impact of Financial Performance Deterioration
Coronado's financial trajectory tells a story of rapid deterioration:
| Year | Revenue | Profit/Loss | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2022 | US$3.6bn | US$771.1m profit | Peak coal prices drove record profits |
| 2023 | US$2.9bn | US$156.1m profit | Declining but still profitable |
| 2024 | US$2.5bn | US$108.9m loss | Shifted to substantial losses |
This dramatic reversal from substantial profitability to significant losses within just two years illustrates the operational leverage inherent in mining businesses. With high fixed costs across its mining operations, Coronado's profitability demonstrates extreme sensitivity to metallurgical coal prices.
The company's efforts to reduce costs have proven insufficient to offset the revenue decline. Despite achieving approximately US$7 million in cost savings per tonne sold, these efficiency gains have been overwhelmed by the magnitude of the price collapse.
Market concerns about Coronado's financial sustainability have created a negative feedback loop, where declining share prices limit access to capital markets just when the company most needs financial flexibility.
What Financial Challenges Is Coronado Currently Facing?
Credit Rating Downgrades and Financing Difficulties
Coronado's financial position has deteriorated significantly, leading to formal credit rating downgrades that further complicate its outlook. In July 2025, S&P downgraded Coronado's credit rating, citing concerns about the company's ability to service its debt obligations if metallurgical coal prices remain depressed.
This downgrade came at a particularly inopportune moment, as Coronado was attempting to secure approximately US$1 billion in debt financing to strengthen its balance sheet. The credit rating agency specifically warned that Coronado would continue burning cash if metallurgical coal prices remained below US$200 per tonne—a concerning forecast given current market prices hovering around US$183 per tonne.
The downgrade creates several cascading problems:
- Higher borrowing costs: Any new debt will come with substantially higher interest rates
- Restricted access to capital markets: Fewer lenders willing to extend credit
- Covenant concerns: Risk of violating existing debt agreements if financial metrics deteriorate further
- Refinancing challenges: Difficulty rolling over existing debt as it matures
These financing difficulties create a challenging environment for Coronado to navigate, particularly as operational cash flows remain under pressure from low coal prices.
Cash Burn Rate and Strategic Responses
Facing deteriorating market conditions, Coronado has implemented several strategic initiatives to address its cash burn rate:
-
Workforce Reduction: Implemented a 30% headcount reduction at Australian operations to lower fixed costs.
-
Operational Efficiencies: Achieved cost reductions of approximately US$7 million per tonne sold through various optimization initiatives.
-
Asset Sale Exploration: Actively investigating potential stake sales, particularly involving the Curragh Complex, to generate immediate capital.
-
Production Adjustments: Optimizing production volumes to focus on higher-margin coal varieties and reduce overall output.
-
Capital Expenditure Deferral: Postponing non-essential growth projects to preserve cash.
"These conditions are among the most challenging we've seen in many years," acknowledged Coronado's chairman Gerry Spindler in a recent ASX announcement, underscoring the severity of the situation.
Despite these efforts, the company faces significant headwinds. Its removal from the ASX 200 index has triggered additional institutional selling pressure, complicating efforts to stabilize the share price and access equity markets.
The situation mirrors challenges faced by other metallurgical coal producers, including Bowen Coking Coal, which has also experienced severe financial distress amid the sector downturn. This industry-wide pressure suggests the issues are structural rather than company-specific, though Coronado's particular debt profile creates additional challenges.
How Does Trump's Trade Policy Impact Metallurgical Coal Markets?
Potential Tariff Effects on Global Coal Trade
The implementation of protectionist trade policies under the Trump administration presents a complex and potentially disruptive force for metallurgical coal markets. While the specific tariff structures remain under development, their impact could fundamentally reshape global coal trade flows.
For Coronado Global Resources, the US tariff impacts create a mixed outlook:
-
Positive: The company's U.S. operations (Logan and Buchanan) could benefit from increased domestic demand if tariffs restrict imports.
-
Negative: Its Australian operations (Curragh) could face challenges accessing U.S. markets and potentially see increased competition in Asian markets from diverted U.S. exports.
The broader market implications extend beyond individual companies:
-
Trade Flow Disruption: Established patterns of metallurgical coal shipments would likely reconfigure as producers seek to minimize tariff exposure.
-
Regional Price Differentials: Price disparities between U.S. domestic coal and international markets could widen, creating arbitrage opportunities but also market inefficiencies.
-
Contract Renegotiations: Existing long-term supply agreements might require modification to address changing economic realities.
-
Increased Volatility: Market uncertainty during policy implementation would likely amplify price swings in an already volatile commodity.
"Trump's plan is to take America back to dominating global coal production," notes Nick Sundich. "This creates particular challenges for Australian exporters who historically relied on stable trade relationships."
Supply-Demand Imbalance Concerns
The potential for increased U.S. coal production under protectionist policies raises significant concerns about market oversupply. With Chinese steel production already at seven-year lows and global demand showing persistent weakness, any substantial increase in metallurgical coal supply would likely exert additional downward pressure on prices.
Several key dynamics warrant consideration:
-
Production Response Time: While policy changes might be announced quickly, ramping up shuttered U.S. coal production requires significant time and capital investment.
-
Quality Differentials: Not all metallurgical coal is fungible; quality differences between U.S. and Australian coal mean they aren't perfect substitutes for specific steelmaking requirements.
-
Cost Structure Variations: U.S. production generally operates higher on the global cost curve than Australian operations, potentially limiting the extent of production increases at current price levels.
-
Transport Infrastructure Constraints: Logistical bottlenecks in rail and port capacity could restrict the speed and volume of increased U.S. exports.
For companies like Coronado with operations in both countries, the ability to strategically adjust production between regions provides some flexibility to navigate these policy shifts. However, the overall impact of potential oversupply on global prices creates significant challenges for all producers, regardless of their geographical diversification.
What Is the Long-Term Outlook for Metallurgical Coal in a Decarbonizing World?
Steel Industry Decarbonization Efforts
The global steel industry faces mounting pressure to reduce carbon emissions, creating existential questions for traditional metallurgical coal producers. With steel production accounting for approximately 7-9% of global CO2 emissions, decarbonization of this sector represents a critical component of climate change mitigation efforts.
Several technological alternatives to traditional coal-based steelmaking are gaining momentum:
-
Hydrogen-Based Direct Reduction of Iron (H-DRI): This process uses hydrogen rather than carbon as the reducing agent, eliminating coal from the steelmaking process entirely. Companies like SSAB, ArcelorMittal, and Thyssenkrupp are investing heavily in developing and scaling this technology.
-
Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) Production: This method primarily uses recycled scrap steel and electricity rather than virgin iron ore and coal. While already established, EAF production faces limitations in producing certain high-grade steel varieties.
-
Carbon Capture Utilization and Storage (CCUS): This approach maintains traditional blast furnace technology but captures and sequesters the resulting CO2 emissions. While technically feasible, the economics remain challenging without carbon pricing or regulatory mandates.
-
Biomass Substitution: Replacing fossil coal with sustainably produced biochar or charcoal offers another pathway to
Ready to Catch the Next Big Mineral Discovery?
Discover how investors gain a significant market edge through real-time alerts on major ASX mineral discoveries with Discovery Alert's proprietary Discovery IQ model, turning complex exploration data into actionable investment opportunities. Visit the Discovery Alert discoveries page to explore historic examples of exceptional returns from game-changing mineral discoveries.