Rio Tinto and Hitachi's Strategic Partnership: Revolutionizing Mining with Remote Operation Technologies
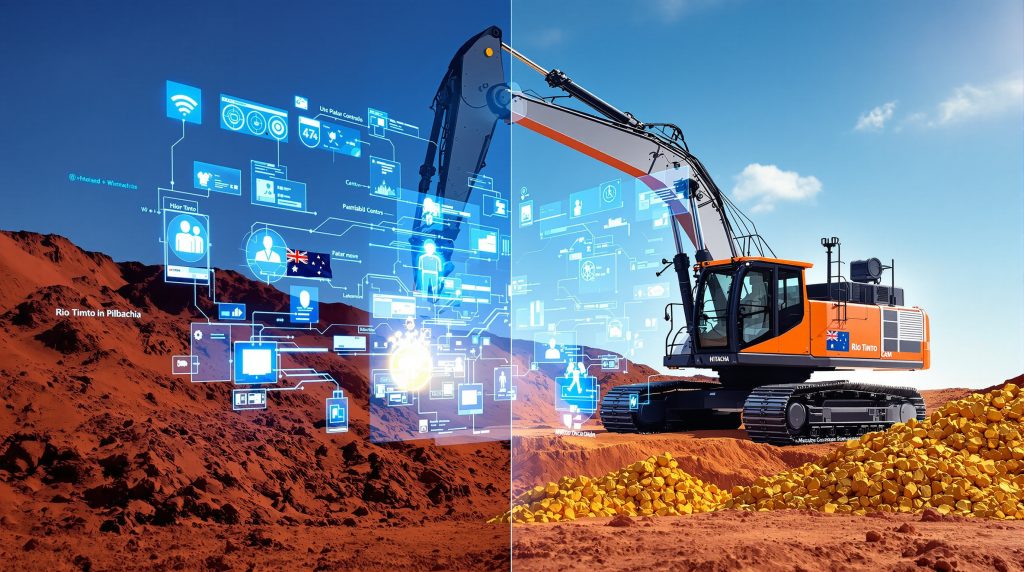
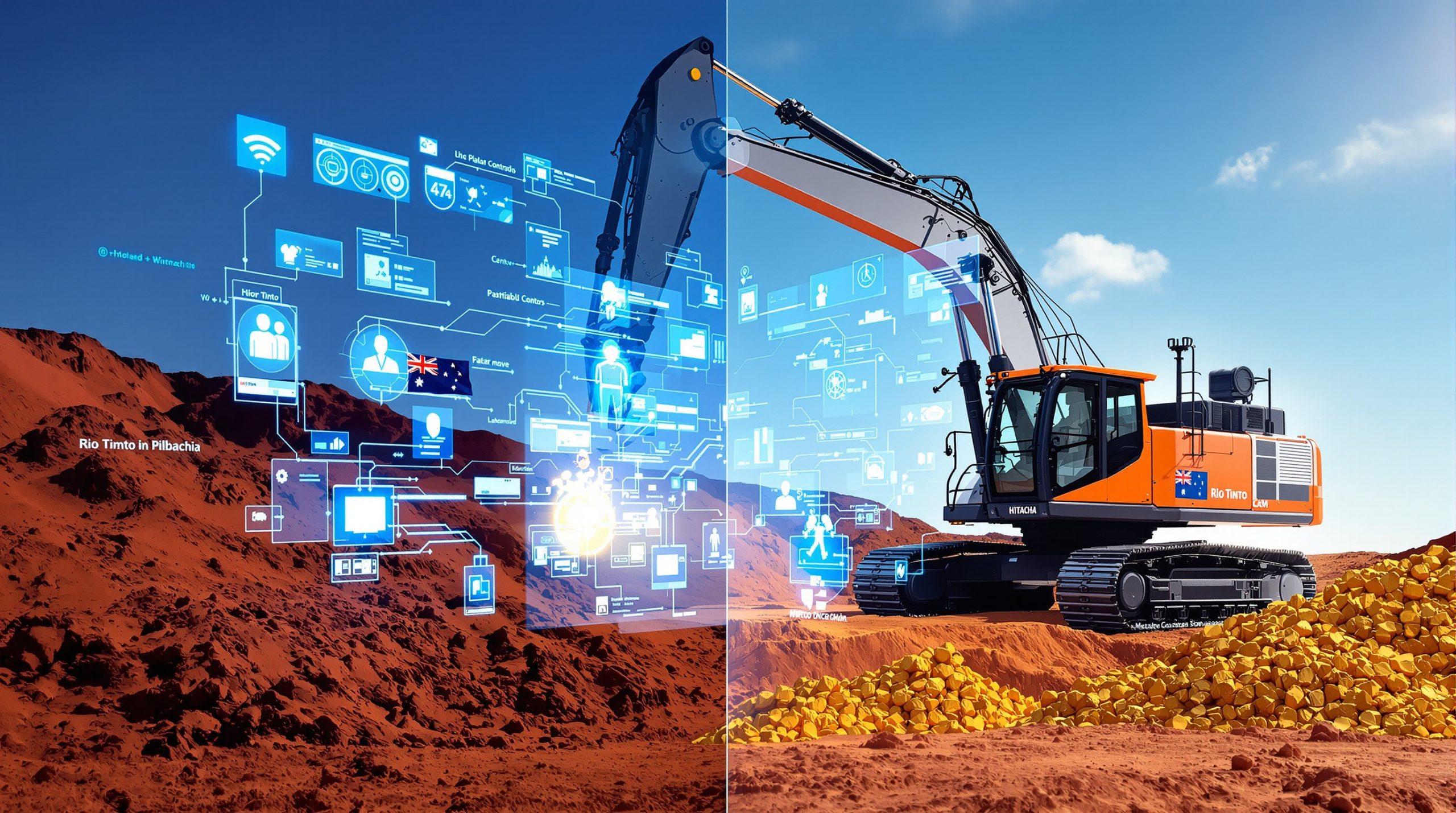
The Rio Tinto-Hitachi partnership represents a significant advancement in mining automation, formalized through a five-year charter agreement signed in Tokyo on October 8, 2025. This strategic collaboration focuses on developing sophisticated remote operation technologies for ultra-large hydraulic excavators used in mining operations. Technological Resources Limited, Rio Tinto's Melbourne-based subsidiary, will work closely with Hitachi Construction Machinery to create next-generation mining solutions that include operator assist functions, remote operation capabilities, and partial autonomy for digging and loading operations.
According to the official Hitachi Construction Machinery press release, this partnership builds upon Hitachi's long history of innovation in the ultra-large hydraulic excavator sector, which began in the late 1970s. The partnership's formalization marks an important milestone in both companies' automation journeys.
Key Components of the Partnership Agreement
- Five-year collaborative framework (2025-2030)
- Focus on ultra-large hydraulic excavator automation
- Development of operator assist technologies
- Implementation of remote operation capabilities
- Creation of partial autonomy for repetitive tasks
- Testing and deployment in Western Australia's Pilbara region impact
The agreement's structure allows for extensive testing and refinement of technologies under real mining conditions, with Rio Tinto's Pilbara operations serving as the primary testing ground. This arrangement enables immediate operational feedback that can be incorporated into ongoing development efforts.
How This Technology Transforms Mining Operations
The implementation of remote operation technologies for ultra-large hydraulic excavators represents a fundamental shift in how mining excavation is conducted. By removing operators from potentially hazardous environments while maintaining operational control, these systems address one of the industry's most persistent challenges: balancing safety with productivity.
According to Hitachi Construction Machinery, prioritizing both safety and productivity is essential at mine sites where continuous operation is required around the clock. The company states that the adoption of remote operation technologies for ultra-large hydraulic excavators represents a significant advancement toward these critical goals.
Safety and Productivity Enhancements
Remote operation technologies enable operators to control excavators from secure control centers, significantly reducing exposure to common mining hazards including dust, noise, vibration, and potential equipment failures. This arrangement creates multiple benefits:
- Reduced operator fatigue through improved working conditions
- Consistent operation regardless of environmental challenges
- Enhanced visibility through multiple camera angles and sensor feeds
- Ability to quickly switch between different machines as needed
- Improved operator retention through better working environments
These improvements directly address the mining industry's twin imperatives of enhanced safety and increased productivity, creating a solution that advances both priorities simultaneously.
Partial Autonomy Functionality
A cornerstone innovation of this collaboration is the development of partial autonomy capabilities. According to Australian Mining's coverage of the agreement, this technology enables operators to:
- Set initial digging positions
- Establish dump truck loading positions
- Allow the system to automatically repeat subsequent operations
This semi-autonomous approach balances human oversight with machine efficiency, creating a hybrid operational model that leverages the strengths of both human decision-making and automated precision. The operator maintains strategic control while the system handles repetitive tasks with consistent performance.
Unlike fully autonomous systems that may struggle with the variability inherent in excavation work, this partial autonomy approach allows human operators to address unexpected conditions while delegating standardized operations to automated systems.
Hitachi's LANDCROS Concept Explained
Vision and Framework
The LANDCROS concept, which combines the word "land" with "CROS" (Hitachi's abbreviated goals), represents Hitachi's vision for creating reliable and open solutions for mining customers. According to Hitachi Vice President and Executive Officer Hiroshi Kanezawa, this framework embodies the company's commitment to designing versatile technologies that benefit the entire mining industry.
As reported in the Hitachi Construction Machinery press release from October 8, 2025, Kanezawa emphasized that the LANDCROS concept reflects their aim to design reliable and open solutions for customers, with open collaboration expected to accelerate the development of highly versatile autonomous operation technologies.
Key Elements of LANDCROS
- Customer-centric design philosophy prioritizing real-world operational needs
- Reliable performance engineered for the challenging conditions of mining environments
- Open collaboration approach that embraces partnership with industry leaders
- Solutions-oriented development targeting specific mining challenges
This comprehensive framework guides all aspects of Hitachi's development work in the mining sector, ensuring that technologies address actual industry needs rather than simply showcasing technical capabilities.
Previous Testing and Development
The LANDCROS concept has already undergone significant real-world testing, with Australian Mining reporting two major test phases:
- August 2023: Durability tests of enhanced boom and arm components for ultra-large hydraulic excavators in the Pilbara region
- March 2024: Verification tests of operator assist systems for digging and loading tasks
These testing phases demonstrate Hitachi's methodical approach to technology development, with each component rigorously evaluated in actual mining conditions before being integrated into comprehensive systems. This iterative testing process ensures that technologies are robust and reliable before full-scale deployment.
Western Australia's Pilbara Region: The Ideal Testing Ground
Strategic Testing Location
The Pilbara region serves as the primary testing and implementation site for this collaborative technology development. This remote, resource-rich area of Western Australia provides ideal conditions for evaluating the performance of remote operation technologies in actual mining environments for several key reasons:
- Diverse geological conditions that test equipment adaptability
- Extreme climate conditions that challenge system durability
- Remote location that highlights telecommunications requirements
- Large-scale operations that demonstrate scalability
- Existing automation infrastructure that allows for integration testing
These factors combine to create a comprehensive testing environment that challenges technologies in ways that controlled testing facilities cannot replicate.
Implementation Strategy
According to the Hitachi Construction Machinery press release, the collaborative testing framework will see Hitachi develop remote operation technologies while Rio Tinto deploys excavators equipped with these technologies in the Pilbara region. This arrangement will:
- Generate valuable operational data from actual mining activities
- Provide immediate user feedback from experienced operators
- Test system performance under diverse site conditions
- Validate durability in challenging environmental conditions
This real-world testing approach accelerates the development cycle by identifying practical issues that might not emerge in laboratory settings, allowing for rapid iteration and improvement.
The Partnership's Significance for the Mining Industry
Industry-Wide Implications
This collaboration between a major mining company and a leading equipment manufacturer has far-reaching implications for the mining sector:
- Establishes new standards for mining excavation automation
- Creates pathways for broader implementation of remote technologies
- Demonstrates the value of cross-industry partnerships in technology development
- Accelerates industry innovation trends
By combining Rio Tinto's operational expertise with Hitachi's manufacturing capabilities, this partnership creates a development environment that addresses practical mining challenges while advancing technological boundaries.
Competitive Advantage
For both companies, this partnership offers distinct competitive advantages:
For Rio Tinto:
- Early access to cutting-edge automation technology
- Potential productivity gains through optimized excavation
- Enhanced safety protocols for mining operations
- Reduced operational costs through efficiency improvements
For Hitachi:
- Real-world testing environment for new technologies
- Access to operational expertise from a mining leader
- Platform to showcase innovation capabilities
- Potential to establish industry standards for automation
As noted in Hitachi's press release, open collaboration with Rio Tinto, which has extensive expertise in mining operations, will accelerate the development of highly versatile autonomous operation technologies for the benefit of the whole mining industry.
Environmental Benefits of Remote Operation Technologies
Operational Sustainability
Remote operation technologies and partial automation can contribute to more sustainable mining practices through several mechanisms:
- More precise excavation that reduces unnecessary material movement
- Optimized truck loading that minimizes fuel consumption
- Consistent operation that reduces equipment wear and extends service life
- Reduced on-site infrastructure requirements for operator facilities
While specific environmental metrics were not detailed in the source material, these operational improvements align with the mining industry's increasing focus on sustainability and resource efficiency.
Long-Term Sustainability Impact
The implementation of these technologies supports broader industry goals for sustainable resource extraction:
- Improved resource recovery rates through more precise excavation
- Reduced energy consumption through optimized operations
- Decreased environmental footprint from smaller on-site workforce requirements
- Extended equipment lifecycle through consistent operation
These benefits contribute to mining companies' efforts to reduce their environmental impact while maintaining or improving productivity, addressing growing stakeholder expectations for responsible resource extraction.
Technology Implementation Timeline
Development Roadmap
The five-year agreement establishes a clear timeframe for technology development and implementation. While specific milestones were not outlined in the source material, a typical progression for technology of this nature would include:
- Initial deployment and testing of base systems
- Refinement based on operational feedback
- Expanded implementation across additional sites
- Integration with existing mining systems
- Full-scale deployment and operational standardization
This phased approach allows for careful evaluation and refinement at each stage, ensuring that technologies perform reliably before widespread deployment.
Key Milestones to Watch
Several critical indicators will signal the partnership's progress:
- First successful remote operation of ultra-large excavators in production settings
- Initial implementation of partial autonomy functions
- Quantifiable productivity improvements compared to traditional operations
- Safety performance metrics demonstrating risk reduction
- Integration with existing fleet management systems
These milestones will provide visible evidence of the partnership's success and indicate the technology's readiness for broader industry adoption.
Mining Automation Landscape and Competitive Context
Current Industry Automation Trends
The Rio Tinto-Hitachi partnership exists within a broader context of mining automation initiatives that have transformed various aspects of the mining value chain. The industry has seen significant advancements in areas such as:
- Autonomous haulage systems for material transport
- Automated drilling for exploration and production
- Remote operations centers controlling multiple sites
- Autonomous rail systems for product transport
- Automated processing facilities for resource extraction
Each of these technologies addresses different operational challenges, with varying levels of industry adoption and maturity.
The Excavation Automation Frontier
What distinguishes this partnership is its focus on excavation operations, which have received less attention in previous automation efforts due to their complexity. Unlike haulage operations that follow relatively predictable paths, excavation requires adaptive responses to variable material conditions.
The emphasis on partial autonomy rather than full automation represents a pragmatic approach that acknowledges the complexity of excavation tasks while still capturing significant operational benefits. This hybrid model may prove more effective than complete automation attempts that have struggled with the variability inherent in mining excavation.
Technical Challenges and Solutions Approach
Engineering Obstacles
Developing remote operation technologies for ultra-large hydraulic excavators presents several technical challenges:
- Creating real-time control systems with minimal latency
- Establishing reliable communication infrastructure in remote locations
- Integrating multiple sensors for comprehensive environmental awareness
- Developing robust fail-safe mechanisms for system interruptions
- Designing intuitive operator interfaces that maintain situational awareness
These challenges require sophisticated engineering solutions that balance technological capabilities with practical operational requirements.
Solutions Approach
According to the Hitachi press release, the partnership will address these challenges through continuous testing under diverse site conditions in the Pilbara region. This approach includes:
- Iterative testing in actual mining conditions to identify practical issues
- Continuous refinement based on operator feedback from production environments
- Progressive implementation that builds on successful components
- Development of specialized training protocols for remote operators
This methodical, field-based development process increases the likelihood of creating technologies that perform reliably in the challenging conditions of actual mining operations.
Workforce Transformation in Mining Automation
Evolving Skill Requirements
The implementation of remote operation technologies will transform workforce requirements in mining operations, creating new opportunities while changing traditional roles. These changes include:
- Increased demand for technologically skilled operators
- Need for systems maintenance specialists with both mechanical and digital expertise
- Reduced requirement for on-site physical labor in harsh conditions
- Development of new roles in remote operations centers
These changes represent an evolution of mining employment rather than simple displacement, with many traditional skills remaining valuable within new operational contexts.
Training and Transition Strategies
Successfully implementing these technologies will require comprehensive approaches to workforce development:
- Transitional training for existing operators moving from in-cab to remote operation
- Technical training for maintenance personnel on new systems
- Development of new operational protocols and procedures
- Creation of specialized career pathways for automation specialists
These strategies ensure that workforce evolution keeps pace with technological implementation, maintaining operational continuity while building capabilities for future development.
FAQ: Rio Tinto and Hitachi Remote Operation Technologies
What is the primary goal of the Rio Tinto-Hitachi partnership?
The partnership aims to develop advanced remote operation technologies for ultra-large hydraulic excavators, including operator assist functions, remote operation capabilities, and partial autonomy for digging and loading operations, as detailed in the Hitachi Construction Machinery press release.
Where will these technologies be tested and implemented?
The technologies will be primarily tested and implemented at Rio Tinto's mining operations in the Pilbara region of Western Australia, leveraging the diverse site conditions to ensure technology reliability.
What is partial autonomy in the context of excavator operations?
Partial autonomy allows operators to set initial parameters (such as digging position and truck loading position) after which the system can automatically repeat subsequent operations without continuous operator input, creating a hybrid operational model.
How long is the partnership agreement between Rio Tinto and Hitachi?
The charter agreement between Rio Tinto and Hitachi Construction Machinery spans five years, beginning with the signing on October 8, 2025.
What benefits does remote operation technology provide to mining operations?
Remote operation technology enhances safety by reducing operator exposure to hazardous environments, improves productivity through consistent operations, reduces operator fatigue, and enables operations in challenging conditions that might otherwise limit mining activities.
The Future of Mining Automation: A New Paradigm
The strategic partnership between Rio Tinto and Hitachi Construction Machinery represents a significant advancement in mining automation technology. By focusing on remote operation and partial autonomy for ultra-large hydraulic excavators, this collaboration addresses critical industry challenges related to safety, productivity, and operational efficiency.
As Hitachi's Kanezawa noted in the company's press release, open collaboration with Rio Tinto will accelerate the development of highly versatile autonomous operation technologies that benefit the entire mining industry. This collaborative approach recognizes that the most effective innovation emerges from combining operational expertise with manufacturing capabilities.
The emphasis on partial autonomy rather than full automation reflects a pragmatic approach that balances technological innovation with practical operational requirements. This hybrid model, combining human expertise with machine precision, may prove to be the most effective path forward for complex mining operations that require adaptability and judgment alongside consistency and precision.
Furthermore, the integration of AI in mining automation and modern mine planning technology will likely enhance these remote operation systems in the coming years. Additionally, the shift toward data-driven operations in the mining industry complements these technological advancements, creating a more integrated and efficient mining ecosystem.
Industry Perspective:
Mining automation continues to evolve from simple task automation to sophisticated systems that augment human capabilities. The Rio Tinto-Hitachi partnership represents the next stage in this evolution, focusing on the complex challenge of excavation automation while maintaining the human judgment essential for adapting to variable mining conditions.
As implementation progresses, the mining industry will be watching closely to see how this partnership transforms excavation operations and what lessons can be applied to other aspects of mining automation. The potential benefits in safety, productivity, and sustainability make this development particularly significant for an industry navigating increasing operational challenges and stakeholder expectations.
Interested in Capturing Real-Time ASX Mining Discoveries?
Discover significant ASX mining announcements before the market moves with Discovery Alert's proprietary Discovery IQ model, which instantly identifies high-potential mineral discoveries from daily ASX announcements. Visit the Discovery Alert discoveries page to understand how major mineral discoveries can generate substantial investment returns.