Secondary Lead Market: Production Challenges and Inventory Trends (July 2025)
Secondary Lead Market: Production Challenges and Inventory Trends (July 2025)
The secondary lead market is experiencing significant supply constraints as smelters across China maintain reduced production levels amid continuing profitability challenges. This operational pullback has triggered a notable decline in finished product inventories, creating ripple effects throughout the supply chain that affect both producers and consumers in this critical metals segment.
Current Inventory Levels and Recent Trends
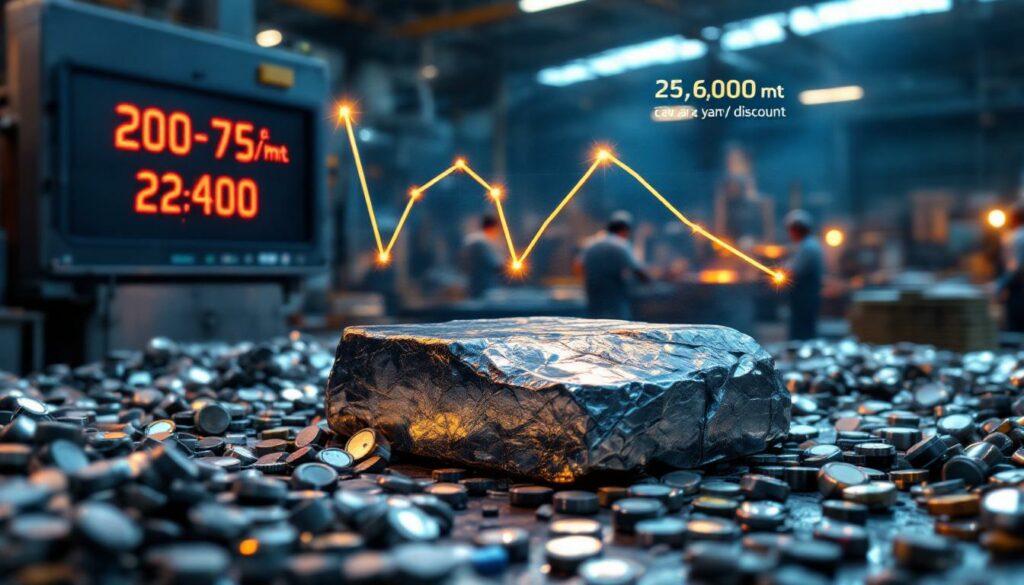
As of July 10, 2025, finished product inventories at secondary lead smelters have dropped to 22,400 metric tons, representing a substantial weekly decrease of approximately 3,500 metric tons. This inventory reduction reflects a continuing downward trajectory that has characterized the market in recent months.
In terms of pricing, secondary lead producers in central China and parts of eastern China are currently offering discounts ranging from 200-75 yuan/mt against the SMM 1# lead average price. These discount levels indicate producers' attempts to balance inventory management with cash flow needs amid challenging market conditions.
"The continued inventory decline reflects fundamental structural challenges in the secondary lead sector rather than a surge in demand. This distinction is critical for understanding current market dynamics." — SMM Market Analysis, July 2025
The regional variation in discount rates highlights localized supply-demand imbalances, with central China producers generally offering deeper discounts than their eastern counterparts due to logistical factors and regional competition dynamics.
Why Are Secondary Lead Smelters Operating at Low Production Levels?
The primary driver behind reduced production rates is straightforward but significant: persistent unprofitability across the secondary lead smelting sector. This economic pressure has forced strategic operational adjustments throughout the industry.
Economic Challenges Facing Smelters
Secondary lead producers are contending with a challenging cost structure that has compressed margins to unsustainable levels:
- Raw material cost volatility – Battery scrap prices haven't decreased proportionally with finished product values
- Energy cost inflation – Power represents 15-20% of total production costs for most smelters
- Environmental compliance expenses – Emissions control requirements add significant operational overhead
- Labor cost pressures – Skilled workforce retention requires competitive compensation despite margin compression
The resulting financial strain has pushed many facilities into loss-making territory, with industry-wide operating losses confirmed by the latest SMM analysis. These losses have persisted despite various efficiency initiatives and cost-reduction programs.
Strategic Responses by Smelters
In response to these economic pressures, smelters have implemented several strategic adaptations:
- Extended shutdown periods at multiple facilities to minimize losses during the most challenging market conditions
- External procurement of lead ingots to fulfill contractual obligations without incurring production losses
- Selective production scheduling focused on highest-margin products and most profitable customer segments
- Maintenance acceleration to position facilities for eventual market improvement
These tactics represent a calculated approach to weathering current market conditions while maintaining the capability to respond when profitability returns.
"Secondary lead smelters are generally running at low production levels, with some even choosing to extend their shutdown periods and purchasing external lead ingots to fulfill long-term contracts." — SMM Industry Report, July 11, 2025
The practice of sourcing finished products externally to meet contractual commitments is particularly noteworthy, as it indicates smelters' determination to maintain customer relationships despite operational challenges.
How Are Downstream Buyers Responding to Market Conditions?
The inventory contraction has created a nuanced purchasing environment for downstream consumers, who are balancing price opportunities against supply security concerns.
Purchasing Behavior Patterns
Downstream enterprises, particularly battery manufacturers and other industrial consumers, have demonstrated:
- Moderate inquiry activity – Maintaining regular market engagement without aggressive purchasing
- Strategic purchasing at preferential prices – Leveraging current discounts for necessary volume
- Cautious inventory management – Avoiding excessive stockpiling given uncertain price trajectories
- Contract renegotiation initiatives – Seeking more flexible terms amid supply uncertainties
This measured approach reflects buyers' understanding of market dynamics and their reluctance to commit to large purchases without greater price certainty.
Impact on Transaction Volumes
The current price discounts (200-75 yuan/mt against SMM 1# lead benchmarks) have stimulated some opportunistic buying, but transaction volumes remain insufficient to reverse production slowdowns. This dynamic creates a feedback loop: reduced production leads to inventory declines, yet buyers remain selective, preventing inventory rebuilding.
Regional variations in transaction activity are notable:
- Central China: More active purchasing, leveraging deeper discounts
- Eastern China: More selective buying, with greater focus on quality and reliability
- Southern regions: Increased reliance on strategic inventory positions due to logistics considerations
The overall pattern indicates buyers are exercising market power but stopping short of aggressive stockpiling that might stabilize the market.
What Factors Are Influencing Secondary Lead Production?
Multiple interconnected factors are constraining secondary lead production capacity, creating a complex operational environment for smelters.
Raw Material Supply Challenges
The recycled battery supply chain faces several obstacles that complicate production planning:
- Battery scrap availability fluctuations – Collection volumes vary significantly by region and season
- Quality inconsistencies – Variable lead content and contaminant levels affect process efficiency
- Collection network disruptions – Transportation bottlenecks and labor shortages impact reliable supply
- Price discovery challenges – Rapid market changes complicate fair value determination for recycled materials
These raw material challenges directly impact production economics, with inconsistent supply creating both quality control issues and utilization inefficiencies.
Operational Constraints
Beyond raw material considerations, smelters face numerous operational challenges:
- Energy cost volatility – Power prices represent a significant portion of production costs
- Environmental compliance requirements – Emissions standards require sophisticated control technologies
- Technical maintenance needs – Complex equipment requires regular downtime for optimal performance
- Skilled labor availability – Specialized roles demand competitive compensation despite margin pressure
The combined effect of these constraints has reduced operational flexibility, forcing difficult production decisions as smelters prioritize financial sustainability over volume.
How Does This Compare to Historical Market Patterns?
Current market conditions represent a deviation from typical seasonal patterns, suggesting structural rather than cyclical challenges.
Seasonal Factors and Cyclical Trends
Secondary lead markets typically follow predictable seasonal rhythms:
- Mid-year stability – Production and inventory levels usually stabilize during summer months
- Q3 gradual build – Inventories typically rise ahead of fall demand increases
- Q4 consumption peak – Battery replacement season typically drives year-end demand
- Q1 reset – Post-holiday adjustments often bring production recalibrations
The current inventory decline during what should be a stabilization period indicates fundamental market imbalances rather than normal seasonal fluctuation.
Year-over-Year Comparison
When compared to July 2024, several key metrics highlight concerning trends:
- Inventory levels are approximately 10% lower than the same period last year
- Production capacity utilization has declined from approximately 75% to below 65%
- Discount ranges have widened compared to the 150-50 yuan/mt typical in 2024
- External procurement volumes have increased significantly year-over-year
These comparative metrics indicate a market experiencing more structural challenges than in previous cycles, with smelters implementing more aggressive operational adjustments.
What Are the Short-Term Market Outlook Projections?
Industry analysis points to continued inventory pressure in the near term, with several key indicators suggesting persistent challenges.
Expected Inventory Trajectories
Projections for the coming 30-60 days indicate:
- Continued downward trend in in-plant inventories of lead ingot finished products
- Potential supply tightening in specific product categories, particularly high-purity grades
- Regional inventory imbalances with central regions experiencing more significant drawdowns
- Extended lead times for non-contract orders as smelters prioritize existing commitments
These inventory projections reflect both production constraints and selective procurement patterns by downstream consumers.
Price Trend Indicators
Key pricing dynamics expected in the near term include:
- Persistent discount structure against SMM 1# lead benchmarks
- Potential narrowing of discount ranges as inventories decline further
- Regional price differential expansion reflecting localized supply-demand imbalances
- Contract versus spot spread widening as smelters prioritize relationship preservation
These price forecast insights suggest continued market tension as smelters balance production economics against customer relationships.
"It is expected that the in-plant inventory of lead ingot finished products will maintain a downward trend in the short term, creating potential supply challenges for spot market buyers." — SMM Forward Outlook, July 2025
The most likely stabilization scenario involves a combination of improved raw material economics and modest energy cost relief, potentially enabling incremental production increases by late Q3 2025.
How Does Secondary Lead Performance Impact the Broader Metals Market?
The secondary lead sector's challenges create ripple effects throughout related metal markets and downstream industries.
Interconnections with Primary Lead Production
The relationship between secondary and primary lead markets shows several important dynamics:
- Substitution effects – Some consumers shift toward primary lead when secondary discounts narrow
- Total market supply considerations – Secondary production represents approximately 45% of total lead supply
- Quality differential impacts – High-purity secondary lead competes directly with primary for premium applications
- Production cost comparisons – Energy efficiency advantages of secondary processes are partially offset by other costs
These interconnections mean that secondary lead production shutdown insights inevitably influence the broader lead market structure.
Downstream Industry Implications
Several key industries face direct impacts from secondary lead market conditions:
- Battery manufacturing – Lead-acid battery producers face input cost and availability uncertainties
- Automotive sector – Vehicle production planning must account for potential battery supply constraints
- Construction industry – Lead products used in building applications face potential delivery delays
- Export markets – International competitiveness affected by domestic supply-chain reliability
The extended impact of secondary lead market conditions highlights the metal's continued importance in multiple industrial applications despite alternatives in some segments.
FAQ: Secondary Lead Market Conditions
What is causing the decline in secondary lead finished product inventories?
The inventory decline is primarily driven by smelters operate at low production levels and in-plant inventory of secondary lead finished products continues to decline due to persistent profitability challenges. Many facilities have extended shutdown periods and resorted to purchasing external lead ingots to fulfill contractual obligations without incurring production losses. This production pullback, rather than a surge in demand, is the primary driver behind falling inventories.
How are pricing discounts affecting market dynamics?
The current discounts of 200-75 yuan/mt against SMM 1# lead average prices represent a significant value opportunity for buyers. These discounts have attracted moderate interest from downstream consumers who are strategically purchasing at these preferential rates. However, transaction volumes remain insufficient to reverse production slowdowns or stabilize inventory levels, creating a feedback loop of continued inventory decline.
What strategies are smelters employing to manage current market conditions?
Smelters are implementing various strategic adaptations to navigate challenging market conditions:
- Reduced production schedules to minimize losses
- Selective external procurement to fulfill contractual obligations
- Extended maintenance periods during unprofitable market conditions
- Focused production on highest-margin products and customers
- Preservation of key customer relationships through alternative sourcing when necessary
These approaches represent efforts to balance financial sustainability with market position maintenance.
When might the secondary lead market stabilize?
Market stabilization will depend on several interconnected factors:
- Improvement in smelter profitability through cost structure changes
- Adjustments in raw material economics, particularly battery scrap pricing
- Energy cost developments that impact production economics
- Downstream demand patterns in key consuming industries
While short-term projections indicate continued inventory declines, early signs of stabilization could emerge if raw material costs align better with finished product values or if energy costs moderate. Most industry analysts anticipate potential stabilization beginning in late Q3 or early Q4 2025.
Key Metrics for Secondary Lead Market Analysis (July 2025)
| Indicator | Current Value | Weekly Change | Market Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Finished Product Inventory | 22,400 mt | -3,500 mt | Supply tightening |
| Price Discount Range | 200-75 yuan/mt | Varies by region | Moderate buying interest |
| Smelter Operating Rates | Low levels | Some extended shutdowns | Reduced production output |
| Downstream Purchase Activity | Moderate | Selective buying | Strategic procurement |
| External Procurement | Increasing | Fulfilling contracts | Maintaining customer relationships |
Market Insight: The continued operation of secondary lead smelters at low production levels, combined with strategic external procurement to fulfill contracts, suggests that the industry is prioritizing financial sustainability over volume production in the current challenging economic environment.
Future Considerations for Secondary Lead Market Participants
Several key factors will shape market developments in coming months, requiring strategic planning by all participants.
Potential Market Stabilization Factors
The most likely path to market stabilization includes:
- Raw material cost adjustments – More balanced pricing between battery scrap and finished products
- Energy efficiency improvements – Technological advances reducing production energy intensity
- Environmental compliance optimization – More cost-effective approaches to emissions control
- Value chain integration – Closer coordination between collection networks and smelters
These factors could gradually improve smelter economics, enabling production increases that would stabilize inventory levels.
Strategic Planning Recommendations
Market participants should consider several strategic approaches:
- Inventory management optimization – Balanced positions that hedge against both shortages and price declines
- Contract structure reassessment – More flexible terms that share market risks between buyers and sellers
- Supply chain diversification – Multiple sourcing relationships to mitigate regional disruptions
- Production flexibility enhancements – Capability to adjust quickly to changing market conditions
These strategic considerations can help both producers and consumers navigate the current challenging mining industry evolution while positioning for eventual stabilization. Furthermore, understanding the beneficiation economic insights and inflation and cost pressures facing the industry is essential for making informed business decisions.
Disclaimer: This analysis reflects current market conditions and projections based on available data as of July 2025. Future developments may be influenced by factors not currently evident, and all market participants should conduct independent research before making significant business decisions.
Looking for Early Intelligence on Mineral Discoveries?
Stay ahead of the market with Discovery Alert's proprietary Discovery IQ model, which provides real-time notifications on significant ASX mineral discoveries before they make headlines. Visit https://discoveryalert.com.au/discoveries/ to explore how major mineral discoveries have historically generated substantial returns for early investors.