The shifting leverage in prime steel scrap market represents a fundamental transformation from pandemic-era procurement practices to more balanced buyer-seller dynamics. Mills are reasserting negotiating power as oversupply concerns dissipate and premium structures face intense scrutiny. Furthermore, this market correction reflects broader economic adjustments affecting steel industry profitability.
Understanding Prime Steel Scrap Market Fundamentals
Prime steel scrap refers to high-grade steel byproducts generated primarily from manufacturing processes, typically classified as No. 1 busheling and bundles. These grades are known for their uniformity, low residual levels, and high ferrous content, making them an essential raw material for electric arc furnace (EAF) steelmaking.
EAF mills depend on prime scrap for its predictable chemistry and yield, helping achieve desired steel specifications while minimising impurities. Historical data shows that prime scrap often commands significant premiums over obsolete grades due to its reliability and demand from flat-rolled steel producers.
In North America, tracking the American Metal Market (AMM) benchmark has long established a clear baseline. However, North American market trends indicate prime scrap pricing typically reflects market cycles, demand spikes, and downstream sector activity (especially automotive and construction). The past decade has witnessed pronounced premium structures amid shifts in manufacturing outputs and raw material sourcing strategies.
How Have Contract Terms Evolved Since the 2020 Market Disruption?
Pre-2020 Market Dynamics
Traditionally, prime scrap contracts featured formula-based pricing using AMM settlements plus a negotiated premium, reflective of supply-demand imbalances or regional scarcity. Contract lengths often spanned one to two years, with routine renewal patterns.
Mills and scrap suppliers maintained a balanced negotiation environment, with leverage shifting according to broader steel market cycles. Consequently, predictable premium structures emerged based on historical precedent rather than speculative positioning.
Post-Pandemic Contract Inflation
The onset of the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 triggered significant anxiety in scrap markets. Mills scrambled for raw material security, resulting in heightened premiums, lengthier contract commitments, and widespread adoption of guaranteed tonnage agreements.
Disrupted supply chains amplified the drive to lock in supply, pushing some premiums as high as AMM+$50/ton during the peak demand period. Market psychology shifted dramatically: fear of a prime scrap shortage led both mills and suppliers to overcommit on price and volume.
Notably, some arrangements were executed more out of perceived necessity than actual market fundamentals. This development sowed the seeds for the current contractual correction affecting the shifting leverage in prime steel scrap market.
Why Are Steel Mills Reassessing Their Scrap Procurement Strategies?
Current Market Conditions Favouring Buyers
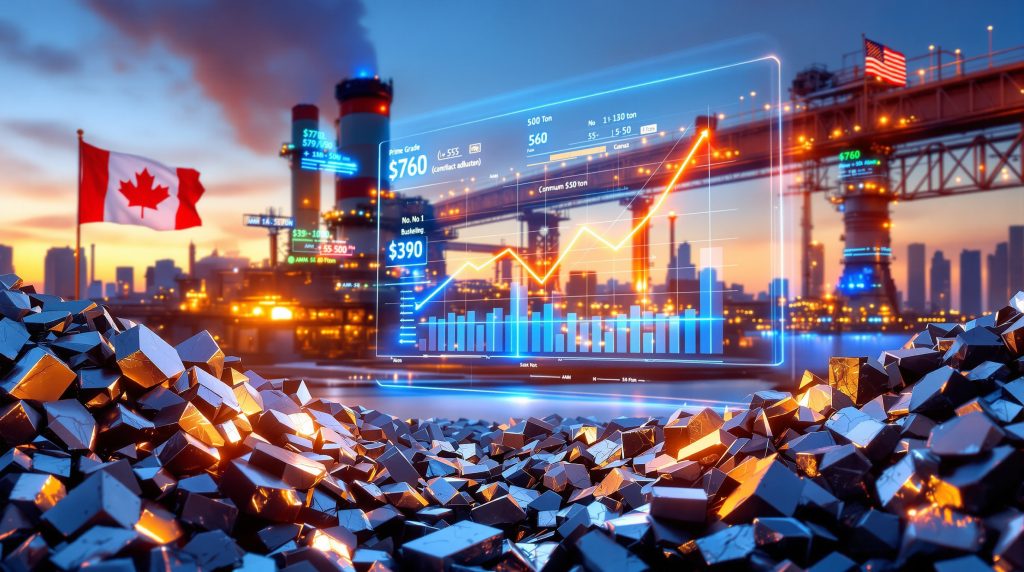
The market landscape in late 2025 presents a stark contrast from the prior two years. Prime scrap pricing has fallen from a peak of $760 per gross ton (April 2022) to **$390 per gross ton (October 2025)**—a drop of nearly 50%.
At the same time, manufacturing and construction sector demand remains subdued, increasing the availability of cheaper spot market options. Mills, in response to falling prices and overcommitted supply contracts, are reevaluating their procurement models.
Greater access to prime scrap, alongside recognition that guaranteed tonnage agreements may tie up capital for little marginal benefit, is spurring a transition toward more flexible, profit-focused sourcing. Additionally, metal price declines analysis reveals broader commodity market pressures affecting steel input costs.
Premium Structure Recalibration
As contract reviews accelerate, the mathematics of premium payments are coming into sharp focus. While a $50/ton premium represented just 6.58% of the headline price at the 2022 peak, it now equates to 12.82% of October 2025 pricing.
This shift exacerbates mills' resistance to maintaining elevated premiums. For instance, the relative cost burden of premiums has doubled, driving a collective pushback against inflated, legacy contracts in favour of renegotiated and reduced premium structures.
What Contract Renegotiation Strategies Are Emerging Across North America?
Mill-Side Negotiation Tactics
Amid this correction, steel mills are proactively renegotiating or abandoning unprofitable long-term deals. Key tactics include:
- Walking away from legacy contracts with excessively high premiums
- Using spot market liquidity and price transparency to obtain better terms
- Actively targeting arrangements where premiums exceed AMM+$20/ton
- Leveraging current scrap metal price trends to justify renegotiation requests
Mills are increasingly prepared to orphan accounts if mutually agreeable terms cannot be reached. Furthermore, there's a strong emphasis on restoring profitability over maintaining volume commitments.
Supplier Response Mechanisms
Scrap suppliers, in turn, are approaching contract reviews with heightened scrutiny. The likelihood and nature of contract adjustments are closely correlated with the existing premium level:
| Premium Level | Likelihood of Renegotiation | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| AMM + $10/ton | Low | Likely maintained |
| AMM + $20-30/ton | Moderate | Potential reduction |
| AMM + $40-50/ton | High | Significant cuts or termination |
Industrial Account Restructuring
Other strategies include:
- Reverting recent contract modifications for greater flexibility
- Lowering formula pricing for industrial scrap accounts
- Abandoning chronically unprofitable or overly restrictive contracts
- Implementing more rigorous quality specifications to justify premium payments
These strategies reflect a broader shift in industry behaviour, emphasising margin management over top-line tonnage growth. However, industry consolidation trends suggest smaller operators may struggle to adapt.
How Is the Canadian Market Influencing US Scrap Dynamics?
Cross-Border Supply Implications
Canadian scrap inventories have become a focal point in North American supply dynamics. Industry data indicates that an estimated 500,000 tons of prime scrap currently rest in Canadian scrapyards, refuting earlier fears regarding structural scarcity.
This surplus has altered pricing psychology, as US buyers weigh new sources against domestic options. The flow of Canadian material has created opportunities for arbitrage, balancing regional supply-demand and resisting runaway premium escalation south of the border.
Moreover, US-Canada tariff effects continue to influence cross-border scrap trade patterns and pricing mechanisms.
Regional Arbitrage Opportunities
Regional price differentials between Canada and the US have widened, sometimes justifying cross-border transactions even after factoring in transportation and currency costs. Scrap contracts are now increasingly structured to consider:
- Freight rates and logistical bottlenecks
- Exchange rate fluctuations between CAD and USD
- Provincial and federal regulatory variations impacting cross-border scrap flows
- Quality specifications differences between markets
Such complexities require sophisticated contract management and risk assessment. Consequently, these factors foster more dynamic trade flows within North America while affecting the shifting leverage in prime steel scrap market.
What Market Correction Indicators Signal Long-Term Structural Changes?
Oversupply Evidence and Market Psychology
The narrative of a chronic prime scrap shortage has been effectively disproven by ample supply and persistent downward price pressure. Mills and suppliers alike are migrating from aggressive volume procurement to disciplined, margin-focused sourcing.
These behaviours signal the onset of a deeper structural shift. In addition, profitability, transparency, and flexibility are supplanting the premium-centric mindset typical of recent years. The correction demonstrates how quickly market psychology can shift when fundamental supply-demand dynamics change.
Competitive Dynamics Reshaping
Mills previously competed against themselves, inadvertently enabling intermediaries to claim spreads of up to $20 per ton for minimal added value. This inefficiency is now being systematically eliminated as buyers take a more disciplined approach to procurement.
The steel scrap market analysis reveals that such intermediary margins are becoming increasingly unsustainable under current market conditions.
Leverage Transfer Mechanisms
As sellers' market conditions wane, mills enjoy increased negotiating leverage by:
- Reducing or eliminating contractual tonnage guarantees
- Diversifying sourcing via spot markets or direct industrial accounts
- Prioritising only quality-driven or strategically advantageous long-term arrangements
- Implementing stricter payment terms and delivery specifications
Which Pricing Methodologies Will Define Future Scrap Contracts?
Benchmark-Based Pricing Evolution
The AMM settlement remains the backbone of North American scrap pricing. Nevertheless, evolving market dynamics suggest several potential modifications:
- Incorporating spot market inputs alongside monthly benchmarks
- Tying premiums to measurable quality or logistics metrics (e.g., moisture content, delivery reliability)
- Introducing more agile formula pricing to rapidly adjust to market swings
- Establishing regional pricing differentials to reflect local supply-demand conditions
Premium Justification Frameworks
The next generation of contracts will likely assign premiums based on:
- Consistency and certainty of grade specifications
- Robustness and predictability of delivery performance
- Alignment with strategic supplier-partner initiatives rather than market excesses
- Value-added services such as sorting, processing, or logistics support
Furthermore, tariffs and market impact considerations will increasingly influence premium structures as trade policies evolve.
How Will January 2026 Contract Renewals Shape Market Direction?
Expected Negotiation Outcomes
Market consensus points to a broad reduction in premiums across most contract segments during the imminent January 2026 renewal window. Industry feedback indicates that the major contract reset will transpire over a two to six-month period.
This transition will drive greater transparency and alignment between suppliers and consumers. However, the extent of premium reductions will vary significantly based on regional dynamics, supplier relationships, and contract specifics.
Strategic Positioning for Market Participants
The following strategies are emerging:
- Mills fortifying low-cost procurement options and evaluating alternative suppliers
- Scrap suppliers adjusting business models to accommodate thinner margins and reduced volumes
- Increased likelihood of industry consolidation as smaller or higher-cost operators struggle to compete
- Enhanced focus on operational efficiency and cost management across the supply chain
What Are the Broader Implications for North American Steel Supply Chains?
Manufacturing Sector Impact Assessment
Persistent downward pressure on prime scrap premiums will deliver cost relief for downstream steel consumers, including fabricators and OEMs in the construction and automotive sectors. This shift is likely to affect:
- Inventory management philosophies, with reduced incentive to overstock high-cost material
- Emphasis on supply chain resilience and diversification rather than single-channel sourcing
- Renewed focus on just-in-time procurement strategies where feasible
Investment and Capacity Planning
Scrap processing facilities are reevaluating capital investments, given forecasted margin compression and shifting demand characteristics. EAF operators are recalculating input cost models, seeking efficiency to offset lower finished steel prices.
Simultaneously, the raw material security paradigm is changing—from guarantee at all costs, to flexible, opportunistic buying informed by real-time market data. This represents a fundamental shift in how the shifting leverage in prime steel scrap market affects long-term strategic planning.
FAQ: Prime Steel Scrap Market Reset
How long will the current buyer's market conditions persist?
The prevailing buyer advantage is projected to continue through 2026, with the January renewal cycle serving as a decisive reference point. However, market conditions remain fluid and subject to broader economic influences.
What premium levels are considered sustainable in the current environment?
Market participants agree that AMM+$10-20/ton is a more tenable range for contracts. Higher premiums are unlikely to survive active renegotiation unless justified by exceptional quality or service provisions.
How does this market reset affect smaller scrap suppliers?
Smaller firms face greater pressure to compete on cost and consistently deliver quality. This raises barriers to ongoing participation and increases the risk of industry consolidation, particularly among operators with limited scale advantages.
Conclusion: Navigating the New Prime Scrap Market Reality
The current reset in the prime steel scrap market signifies a structural evolution away from pandemic-driven procurement and pricing practices. Mills are reclaiming leverage, driving downgraded premium expectations, and fostering market dynamics centred on profit and agility instead of sheer volume.
While this correction poses challenges—especially for suppliers dependent on inflated premiums—it also opens pathways for more efficient, transparent, and sustainable industry relationships. The coming months, particularly the January 2026 contract renewals, will reveal the durability and scope of these market shifts.
Disclaimer: This article contains forecasts and speculative analysis. Market conditions, pricing trends, and contractual arrangements described herein are subject to rapid change. Always consult with industry specialists and review the latest market data before making strategic or financial decisions.
Further Exploration: Readers seeking a deeper dive into prime steel scrap pricing and strategic trends should consult Fastmarkets' methodologies and comprehensive market reports at Fastmarkets.com.
Want to Stay Ahead of Industrial Metal Market Shifts?
The shifting leverage in prime steel scrap market demonstrates how quickly fundamental supply-demand dynamics can reshape entire commodity sectors. Discovery Alert's proprietary Discovery IQ model delivers real-time alerts on significant ASX mineral discoveries across steel-related commodities, instantly empowering subscribers to identify actionable opportunities ahead of broader market movements and begin your 30-day free trial today to position yourself advantageously as industrial markets evolve.