Silver market backwardation represents a critical disruption in normal trading patterns where immediate delivery prices exceed future contract values. This phenomenon signals acute physical metal scarcity and often precedes significant price movements that reshape precious metals markets. Furthermore, understanding these conditions becomes essential as they increasingly influence the broader silver market squeeze dynamics affecting global financial systems.
According to Keith Weiner, founder and CEO of Monetary Metals, backwardation indicates a real scarcity or shortage to the market, not necessarily of the metal overall. He emphasizes that while virtually all silver mined throughout human history remains in existence, scarcity in the market context refers specifically to whether metal holders are willing to bring inventory to market for available returns.
Recent market conditions have demonstrated this principle dramatically. On October 10, 2025, silver market backwardation reached a remarkable 20% annualized rate, representing what market observers characterize as a severe and unusual occurrence following an extended period without such conditions.
How Does Silver Backwardation Differ From Normal Market Conditions?
Normal Market Structure vs. Backwardation
Under typical circumstances, silver futures trade at premiums to spot prices due to storage costs, insurance, and financing expenses. This structure, called contango, reflects the natural cost of holding physical metal over time. Moreover, these conditions often coincide with periods where record backwardation creates significant trading opportunities.
Backwardation reverses this relationship:
-
Spot prices exceed futures prices
-
Immediate delivery commands premium pricing
-
Physical metal becomes scarce relative to paper contracts
-
Market participants prioritise tangible assets over financial instruments
Key Market Mechanics During Backwardation
The technical analysis reveals fascinating market dynamics during backwardation periods. Weiner describes the basis as the futures market price minus the spot market price. When basis rises alongside rising prices, this indicates buying pressure concentrated in futures contracts rather than physical metal.
Current market conditions show a fundamental shift from historical patterns. Previously, every price increase would trigger rising basis with futures bidding driving the action while the co-basis (measure of scarcity) would fall. This pattern persisted through what market participants characterised as challenging years following silver's 2011 price peak.
However, recent weeks have witnessed a complete reversal. As prices have risen, the silver co-basis has been rising simultaneously, indicating buying action concentrated in physical metal rather than futures contracts. Additionally, these dynamics contribute to the ongoing silver supply deficits that market analysts are closely monitoring.
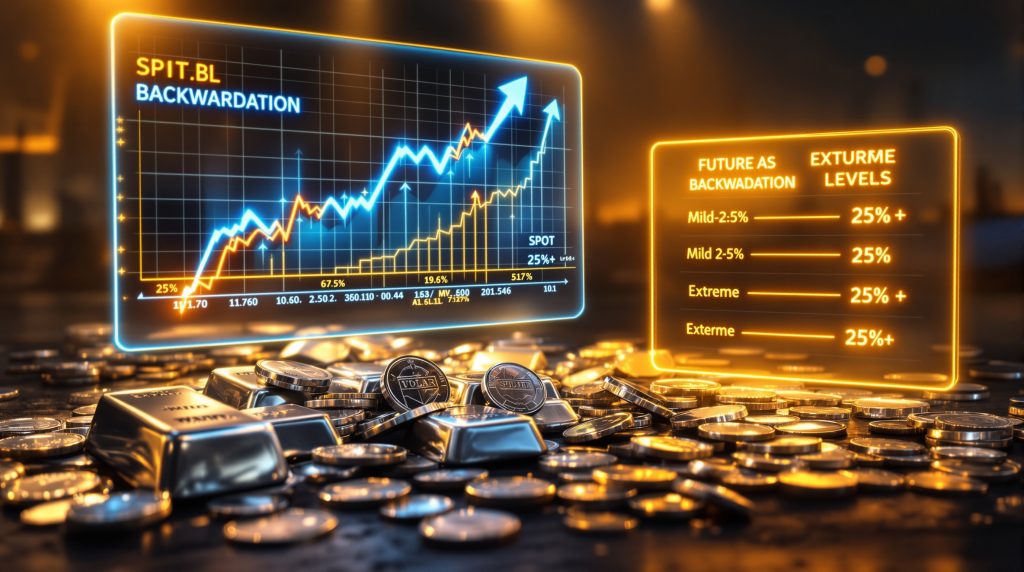
| Backwardation Level | Annualised Percentage | Market Implication |
|---|---|---|
| Mild | 2-5% | Temporary supply tightness |
| Moderate | 5-15% | Sustained physical demand |
| Severe | 15-25% | Critical shortage conditions |
| Extreme | 25%+ | Potential market disruption |
What Triggers Silver Market Backwardation?
Physical vs. Futures Market Dynamics
Understanding the distinction between futures trading and physical metal acquisition reveals why backwardation develops. Futures represent short-term trading vehicles offering up to 20:1 leverage, making them unsuitable for long-term holding due to margin call risks and carrying costs.
Physical metal purchases represent fundamentally different market behaviour. When investors buy physical silver, the metal often disappears from active markets, stored in private vaults, safety deposit boxes, or personal storage. This removal from available supply creates sustained upward pressure on prices.
Industrial and Investment Demand Patterns
Industrial Accumulation Factors:
-
Manufacturing sectors securing supply chains
-
Technology companies building strategic reserves
-
Solar panel producers anticipating shortages
-
Medical device manufacturers stockpiling materials
Investment Behaviour Shifts:
-
Portfolio managers allocating to tangible assets
-
Retail investors preferring physical ownership
-
Institutional buyers seeking delivery mechanisms
-
Sovereign wealth funds diversifying reserves
The current environment demonstrates these dynamics clearly. Unlike speculative futures trading, physical metal acquisition removes inventory from markets permanently, creating the scarcity conditions that drive backwardation.
Why Is Current Silver Backwardation Historically Significant?
Historical Context and Precedents
Silver backwardation episodes remain relatively rare occurrences, making current conditions historically noteworthy. Previous significant episodes include brief backwardation during the period when UK Chancellor Gordon Brown authorised the sale of approximately half of Britain's gold reserves between 1999-2002.
More substantially, backwardation became serious during fall 2008 and regularly reoccurred for several years following the financial crisis. These episodes coincided with banking system stress, counterparty risk concerns, and dramatic increases in physical precious metals demand. Understanding this relationship helps investors interpret current contango versus backwardation patterns in the broader market context.
Current Market Characteristics
The October 2025 backwardation exhibits unique features distinguishing it from previous episodes. Market observers note that gold remains in normal contango conditions while silver demonstrates severe backwardation, suggesting silver-specific supply and demand imbalances rather than broad precious metals market stress.
The 20% annualised backwardation rate recorded on October 10, 2025, represents one of the most severe episodes in recent market history, suggesting fundamental supply-demand disruptions beyond typical trading anomalies.
This divergence between gold and silver market structures indicates that current conditions stem from factors specific to silver markets rather than broad-based monetary or financial system concerns. Consequently, the gold‐silver ratio analysis becomes increasingly relevant for understanding these market dynamics.
How Does Backwardation Impact Silver Price Discovery?
Arbitrage Mechanism Breakdown
Traditional arbitrage opportunities should theoretically eliminate backwardation through profit-seeking activities. The standard process involves selling physical silver at premium spot prices, purchasing equivalent futures contracts at discounts, and profiting from price convergence at contract maturity.
During the October 10, 2025 backwardation event, market participants could execute trades offering approximately 4-5% returns over 1.5-2 months, equivalent to 20% annualised returns. At silver prices around $48 per ounce, this represented approximately $2 per ounce premiums for immediate delivery.
Current Market Obstacles:
-
Limited physical metal availability for selling
-
Concerns about futures contract delivery reliability
-
Storage and insurance cost uncertainties
-
Counterparty risk considerations
Market Participant Behaviour
Despite apparent risk-free returns in conventional terms, market observation revealed reluctance among participants to execute arbitrage trades. This hesitancy suggests deeper concerns about market structure and metal availability beyond normal supply-demand considerations.
The reluctance indicates that metal holders recognise current scarcity conditions and prefer maintaining physical positions rather than trading for paper profits. This behaviour reinforces upward price pressure by reducing available supply for arbitrage activities.
What Are the Investment Implications of Silver Backwardation?
Portfolio Strategy Considerations
Backwardation conditions require adjusted investment approaches recognising fundamental market structure changes. The distinction between physical and paper exposure becomes crucial during these periods.
Physical vs. Paper Exposure Analysis:
-
Physical silver ownership provides direct exposure to scarcity premiums
-
ETF holdings may not capture full backwardation benefits
-
Mining stocks offer leveraged exposure but introduce operational risks
-
Futures positions require careful roll management during backwardation
Institutional vs. Retail Approach
Market analysis reveals fundamental differences in how institutional and retail investors approach precious metals during backwardation periods. Retail investors typically focus on physical metal acquisition, viewing high price targets as signals to buy tangible assets for long-term holdings.
Institutional investors pursue different strategies, seeking quality gold and silver-linked assets with leverage to metal prices. Rather than parking physical metal and paying storage fees, institutions prefer investments offering five to ten-times leverage to underlying metal price movements.
| Risk Factor | Mitigation Strategy | Implementation Method |
|---|---|---|
| Liquidity Constraints | Diversify exit strategies | Multiple selling channels |
| Storage Costs | Optimise holding periods | Professional vault services |
| Insurance Requirements | Comprehensive coverage | Specialised precious metals policies |
| Market Volatility | Position sizing discipline | Gradual accumulation approach |
Alternative Yield Strategies
Current market conditions present unique challenges for precious metals investors. Traditional approaches involve purchasing metals for capital appreciation, but rising prices create profit-taking dilemmas. Selling metals to realise gains defeats the original purpose of holding them as dollar alternatives.
Innovative approaches involve putting metals to productive use through yield-generating strategies. Some companies now offer programmes allowing metal owners to earn returns whilst maintaining exposure to price appreciation, potentially earning 2-5% yields on precious metals holdings.
How Long Does Silver Backwardation Typically Last?
Duration Patterns and Resolution Mechanisms
Backwardation episodes vary significantly in length depending on underlying causes and market responses. Understanding these patterns helps investors develop appropriate strategies for different scenario outcomes.
Short-Term Events (1-3 months):
-
Temporary supply disruptions
-
Seasonal demand fluctuations
-
Speculative trading anomalies
-
Technical market factors
Extended Periods (6-18 months):
-
Structural supply deficits
-
Major economic transitions
-
Geopolitical instability
-
Monetary policy shifts
Price-Driven Resolution Dynamics
Market resolution depends significantly on supply response to elevated price levels. The critical question involves whether silver remains as scarce to markets at higher prices or whether increased prices draw additional metal into circulation.
Historical patterns suggest that substantially higher prices eventually incentivise increased selling activity, potentially flooding markets and normalising conditions. However, timing this response remains extremely difficult to predict accurately.
Backwardation typically resolves through several pathways:
-
Supply Response: Higher prices incentivise increased production
-
Demand Moderation: Elevated costs reduce consumption patterns
-
Inventory Release: Previously held stocks enter markets
-
Substitution Effects: Alternative materials replace silver usage
What Does Current Backwardation Signal for Future Silver Prices?
Technical and Momentum Analysis
Current market conditions provide strong technical signals for continued price appreciation. Physical buying pressure suggests sustained upward momentum, whilst historical support levels strengthen during scarcity periods.
Market observers recommend respecting current momentum rather than attempting contrarian positions. The combination of fundamental scarcity signals and technical price action suggests continued upward pressure until underlying supply-demand imbalances resolve.
Price Target Projections
Based on current market dynamics and historical precedents, silver prices could easily reach $60-65 per ounce, according to market analysts. These projections assume continued backwardation conditions and sustained physical buying pressure. Furthermore, these movements often correlate with broader gold prices analysis trends affecting precious metals markets.
Current Market Context (October 2025):
-
Silver price: $53 per ounce
-
Gold price: $4,250 per ounce
-
Revised targets: $60-65 silver, $4,600-4,700 gold
Important Disclaimer: These represent analytical projections based on current market conditions and should not be construed as definitive predictions. Precious metals markets remain highly volatile and subject to numerous unpredictable factors.
Fundamental Analysis Framework
Long-term price implications depend on addressing underlying supply-demand imbalances through various market mechanisms. Current conditions suggest several supportive factors for continued appreciation.
Bullish Factors:
-
Industrial demand growth exceeding mine production
-
Investment allocation increases from institutional sources
-
Currency debasement concerns driving precious metals interest
-
Supply chain regionalisation reducing available inventory
Potential Headwinds:
-
Economic slowdown reducing industrial consumption
-
Interest rate changes affecting opportunity costs
-
Technology substitution limiting silver requirements
-
Recycling improvements increasing secondary supply
Macroeconomic Context and Global Demand Drivers
US Debt and Dollar Debasement Concerns
Current macroeconomic conditions provide crucial context for understanding precious metals demand drivers. US government debt has reached $37 trillion, creating what many analysts view as an unsustainable fiscal situation.
Breaking down this debt burden reveals staggering per-capita obligations. With approximately 100 million private sector workers supporting government operations, each worker faces a theoretical debt burden of $370,000. For dual-income households, this translates to $740,000 in government debt obligations.
These calculations highlight the mathematical impossibility of debt repayment through conventional means, driving increased interest in alternative stores of value including precious metals.
Institutional Portfolio Allocation Shifts
Major financial institutions have begun recommending significant portfolio allocation changes reflecting growing precious metals acceptance. Morgan Stanley's Chief Investment Officer recently recommended abandoning traditional 60% equity, 40% bond allocations in favour of 60% equity, 20% bond, 20% gold portfolios.
This recommendation represents a watershed moment for precious metals acceptance within mainstream financial institutions. The significance lies not in the specific 20% allocation recommendation, but in the institutional source of the guidance. Moreover, these shifts often influence central bank precious metals policies and purchasing decisions.
International Precious Metals Adoption
Global precious metals adoption varies dramatically by region, with some countries demonstrating extraordinary individual participation rates. Turkey offers gold-denominated bank accounts through its banking system, creating 120 million gold accounts for a population of 80-90 million people.
This represents more than one gold account per person, indicating widespread precious metals adoption rivalling American gun ownership patterns in terms of per-capita prevalence.
International Market Data:
-
Turkey: 120 million gold bank accounts, 80-90 million population
-
India: 1.4 billion population, $3,000 per capita GDP
-
Indian Rupee: Declining 7-9% annually vs. US dollar
India presents a fascinating contrast with very low per-capita GDP but enormous aggregate precious metals demand. Despite individual purchasing power limitations, 1.4 billion people buying even small amounts of gold creates massive market impact exceeding US demand despite Americans' significantly higher individual wealth levels.
Investment Strategy Considerations During Backwardation
Risk Management Framework
Investing during backwardation periods requires careful risk management acknowledging both opportunities and potential pitfalls. Market conditions can change rapidly, requiring flexible strategies adaptable to evolving circumstances.
Position Sizing Discipline:
-
Gradual accumulation approaches reduce timing risk
-
Diversified acquisition channels improve execution flexibility
-
Professional storage solutions optimise security and insurance
-
Exit strategy planning prevents forced selling during unfavourable conditions
Physical vs. Leveraged Exposure Trade-offs
Backwardation creates unique considerations for different investment approaches. Physical metal ownership provides direct exposure to scarcity premiums but involves storage costs and liquidity constraints.
Mining equity investments offer leveraged exposure to metal price movements but introduce operational risks, management quality considerations, and broader equity market correlations that may not align with precious metals fundamentals.
Exchange-traded fund holdings provide convenience and liquidity but may not capture the full benefits of physical metal scarcity during backwardation periods, particularly if underlying funds face delivery constraints or premium market conditions.
Market Timing Considerations
Current momentum analysis suggests respecting upward price trends rather than attempting contrarian timing strategies. Silver market backwardation indicates fundamental supply-demand imbalances requiring resolution through higher prices or increased supply response.
However, investors should avoid short-term trading approaches during volatile conditions, particularly given the leverage risks associated with futures positions and margin requirements. Long-term physical accumulation strategies generally prove more suitable for capitalising on backwardation conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions About Silver Backwardation
Is Backwardation Always Bullish for Silver Prices?
Whilst backwardation typically indicates upward price pressure, outcomes depend significantly on duration and severity. Short-term episodes may resolve quickly without sustained price gains, whilst extended backwardation often leads to significant appreciation as supply-demand imbalances require time to correct.
The key distinction involves understanding whether backwardation reflects temporary market dislocations or fundamental structural changes in supply and demand dynamics.
How Can Retail Investors Benefit From Backwardation Conditions?
Retail investors can capitalise on backwardation through strategic physical silver purchases, recognising that premiums may remain elevated during scarcity periods. However, timing exits becomes crucial as conditions eventually normalise and premiums may disappear rapidly.
Successful strategies typically involve gradual accumulation during backwardation onset rather than attempting to time precise entry and exit points. Storage planning and exit strategy development should occur before market conditions become extreme.
What Role Do Central Banks Play During Silver Backwardation?
Central banks primarily influence silver markets indirectly through monetary policy affecting currency values and investment demand. Unlike gold, silver receives limited direct central bank intervention during backwardation episodes.
However, central bank gold purchases may create secondary buying interest in silver as investors seek precious metals exposure across the complex. Central bank activity often provides psychological support for broader precious metals investment themes.
Can Backwardation Predict Major Economic Events?
Historical evidence suggests backwardation often precedes or coincides with significant economic stress periods. However, using it as a standalone predictor requires careful analysis of supporting economic indicators.
Silver market backwardation should be viewed as one component of a comprehensive analytical framework rather than a definitive forecasting tool. Combined with macroeconomic analysis, debt sustainability concerns, and currency debasement trends, backwardation provides valuable market intelligence.
Future Market Outlook and Strategic Implications
Technological and Industrial Demand Factors
Silver's unique industrial properties create fundamental demand that distinguishes it from purely monetary metals. Electronic applications, solar panel manufacturing, medical devices, and emerging technologies require silver's specific conductivity and antimicrobial properties.
This industrial demand base provides price support during economic expansions whilst monetary demand increases during economic uncertainty, creating multiple demand drivers across different economic cycles.
Supply Chain Regionalisation Trends
Geopolitical tensions and supply chain security concerns are driving regionalisation of critical mineral supply chains. Countries increasingly prioritise domestic or allied nation sourcing for strategic materials, potentially reducing silver availability in global markets.
This trend toward supply chain regionalisation could extend backwardation periods by limiting cross-border metal flows and creating regional scarcity conditions even when global supplies appear adequate.
Currency Competition and Digital Assets
The emergence of dollar-denominated stablecoins creates new dynamics for international currency competition. Citizens of countries with weak currencies may increasingly access dollar-based digital assets, potentially accelerating local currency devaluation.
This development could drive additional precious metals demand as populations seek alternatives to both local currencies and centralised digital systems, supporting long-term silver demand growth.
Conclusion: Navigating Silver Market Backwardation
Silver market backwardation represents a powerful signal of underlying market stress and potential price appreciation opportunities. Current conditions suggest sustained physical demand exceeding available supply, creating investment opportunities for informed participants whilst requiring careful risk management approaches.
Understanding backwardation mechanics enables better investment decisions during these critical market periods. Whether pursuing physical ownership, mining equity exposure, or alternative strategies, recognising backwardation's implications provides valuable market intelligence for precious metals portfolios.
The combination of industrial demand growth, investment allocation increases, and supply constraints suggests current backwardation conditions may persist longer than historical averages. This persistence could drive silver prices significantly higher as market participants compete for limited physical inventory.
Key Strategic Considerations:
-
Respect current market momentum and scarcity signals
-
Implement gradual accumulation strategies rather than timing-based approaches
-
Consider storage and liquidity requirements for physical holdings
-
Monitor resolution mechanisms and supply response to higher prices
-
Maintain diversified exposure across physical and paper alternatives
Market Outlook: Current backwardation conditions reflecting 20% annualised rates represent severe market stress suggesting continued upward pressure on silver prices. Resolution timing remains uncertain, but historical precedents suggest extended periods may be required for supply-demand rebalancing.
Investment Implications: Backwardation provides compelling evidence for silver's scarcity value whilst highlighting the importance of physical ownership during periods of paper market stress. Investors should prepare for extended volatility whilst positioning for potential sustained price appreciation.
Risk Management: Success during backwardation periods requires balancing opportunity recognition with prudent risk controls. Overleveraged positions and short-term trading approaches generally prove counterproductive during highly volatile conditions driven by fundamental supply constraints.
The convergence of macroeconomic uncertainty, institutional adoption, international demand growth, and current silver market backwardation creates a unique environment for silver market development. Understanding these dynamics provides essential context for navigating precious metals investments during this potentially transformative period.
Ready to Position Yourself in Silver's Supply Squeeze Before it Intensifies?
Silver backwardation conditions demand swift action, and Discovery Alert's proprietary Discovery IQ model ensures you stay ahead of critical ASX silver mining discoveries as scarcity drives opportunity. Visit Discovery Alert's discoveries page to understand how major mineral discoveries can generate substantial returns, then begin your 30-day free trial to gain the market edge essential during these extraordinary silver market conditions.