Strategic Mineral Partnerships in a Multipolar World
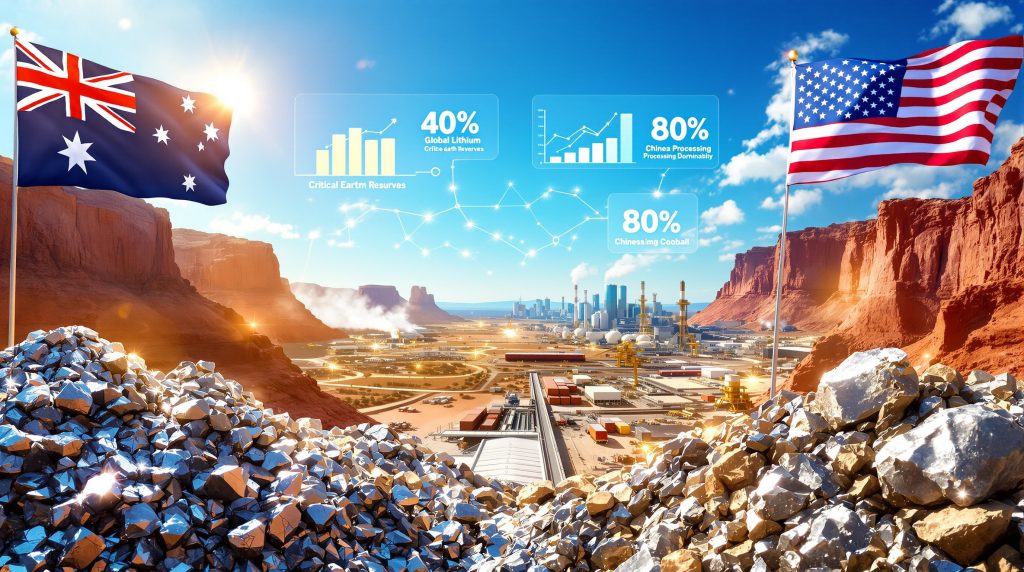
The global landscape for critical minerals has transformed dramatically as nations prioritise supply chain security over traditional cost considerations. Australia's emergence as a key alternative supplier comes at a crucial moment when geopolitical tensions highlight vulnerabilities in mineral-dependent industries. The timing of high-level diplomatic discussions, such as the potential Albanese Trump meeting critical minerals dialogue, reflects growing recognition that mineral security represents a cornerstone of both economic competitiveness and national defence capability.
Modern technology infrastructure depends fundamentally on materials that are geographically concentrated and politically sensitive. Electric vehicle batteries, renewable energy systems, and advanced defence platforms all require consistent access to lithium, rare earth elements, and other strategic materials. Australia's substantial mineral endowments position it as an essential partner for nations seeking to diversify away from concentrated supply sources.
The shift toward supply chain resilience over pure economic optimisation represents a fundamental change in global procurement strategies. Companies increasingly demonstrate willingness to pay premiums for guaranteed delivery schedules and politically stable sourcing arrangements.
China's Market Dominance Creates Strategic Vulnerabilities
Chinese control over critical mineral processing creates significant dependencies for consuming nations. The country processes approximately 87-90% of global rare earth elements and maintains 60-65% of lithium refining capacity as of 2024. This concentration extends beyond raw materials to encompass 75-77% of lithium-ion battery cell manufacturing globally.
Recent trade measures demonstrate how mineral dependencies can become geopolitical leverage points. China implemented export controls on gallium and germanium in August 2023, followed by graphite restrictions in December 2023. These actions highlighted the strategic importance of developing alternative supply networks through trusted partnerships.
The concept of friend-shoring, articulated by former U.S. Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen in April 2022, describes strategies to build supply chains through trusted partners rather than seeking lowest-cost options globally. This approach prioritises political stability and shared values alongside economic considerations.
Market dynamics increasingly favour suppliers who can guarantee consistent quality standards and delivery reliability. The COVID-19 pandemic demonstrated how supply chain disruptions can cascade through interconnected global systems, reinforcing the value of diversified sourcing strategies. Furthermore, the importance of developing a comprehensive critical minerals strategy becomes evident when examining these vulnerabilities.
Bilateral Cooperation Framework Opportunities
The U.S.-Australia Climate, Critical Minerals and Clean Energy Transformation Compact, announced during the May 2023 Quad Leaders Summit, establishes formal mechanisms for enhanced cooperation in strategic mineral supply chains. This framework creates pathways for joint investments and technology sharing initiatives.
Australia's A$2 billion Critical Minerals Facility through Export Finance Australia represents substantial government commitment to developing domestic processing capabilities. This investment platform creates opportunities for international partnerships in establishing supply chains that bypass traditional Chinese processing routes. In addition, valuable CRM facility insights demonstrate how similar initiatives in Europe are shaping global mineral supply strategies.
Strategic investment areas offering the greatest potential include:
- Midstream processing facilities for lithium hydroxide and battery-grade materials
- Rare earth separation and refining infrastructure to compete with Chinese facilities
- Joint research and development programmes for next-generation extraction technologies
- Integrated supply chain solutions connecting mining, processing, and manufacturing
The existing U.S.-Australia Free Trade Agreement (AUSFTA) provides preferential access frameworks that can accelerate mineral trade development. Under the Inflation Reduction Act, Australian-sourced critical minerals qualify for domestic content requirements, with 40% critical mineral value requirements in 2023 rising to 80% by 2027. However, any future critical minerals executive order could significantly reshape these arrangements.
Defence and Security Considerations Drive Partnership Logic
The AUKUS partnership, representing an estimated AUD $368 billion investment over 30 years, demonstrates the depth of Australia-U.S. defence cooperation. Critical minerals supply chains support both submarine cooperation and advanced capabilities including quantum technologies, artificial intelligence, and hypersonic weapons systems.
Defence applications create specific quality and security requirements that favour trusted suppliers over cost-optimised alternatives. Neodymium enables permanent magnets in precision-guided missiles and jet engines. Erbium supports fiber-optic communications systems. Europium functions in nuclear reactor control systems.
Australian producer Lynas Corporation received U.S. Department of Defense funding through Defense Production Act investments for building heavy rare earth separation facilities in Texas. This project demonstrates how defence requirements can drive commercial infrastructure development in allied nations.
The U.S. Department of Defense identified 50 critical minerals as essential for national security applications. Australia possesses significant reserves or production capabilities for many of these materials, creating natural partnership opportunities. Consequently, the role of energy transition security becomes paramount in long-term strategic planning.
Mineral-Specific Partnership Assessment
| Mineral Category | Australian Position | Strategic Value | Partnership Potential |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lithium | 47% global mine production | EV battery security | Very High |
| Rare Earth Elements | 6th largest reserves globally | Defence applications | High |
| Cobalt | 5th largest producer | Battery cathodes | Moderate |
| Nickel | 6th largest producer | Stainless steel, batteries | Moderate |
Lithium represents the most immediate opportunity, with Australia producing 86,000 tonnes in 2023, representing nearly half of global mine production. However, most Australian lithium exports as spodumene concentrate to Chinese processing facilities, highlighting the need for domestic processing development. Recent lithium industry innovations provide additional context for understanding sector development potential.
Rare earth elements offer strategic value despite Australia's smaller market share. The country produced 18,000 tonnes of rare earth oxides in 2023 compared to China's 240,000 tonnes, but geological surveys suggest substantial undeveloped resources.
Converting spodumene concentrate to battery-grade lithium hydroxide requires significant chemical processing infrastructure involving roasting, leaching, purification, and precipitation steps. Building such facilities with 20,000-25,000 tonne annual capacity typically requires USD $400-600 million in capital investment.
Investment Mechanisms and Funding Structures
Several financing mechanisms could accelerate partnership development between Australian mineral producers and U.S. strategic objectives:
Government-Backed Facilities
Export-Import Bank of the United States China and Transformational Exports Program makes $27 billion available for projects countering Chinese economic influence. Australian Modern Manufacturing Initiative provides AU$1.3 billion through Resources Technology and Critical Minerals Processing streams.
U.S. Defense Production Act Title III enables loans, guarantees, and purchase commitments for defence-critical materials. These mechanisms provide substantial financial backing for infrastructure development initiatives.
Public-Private Partnership Models
Joint venture structures combining government risk mitigation with private sector efficiency offer promising pathways. Technology transfer agreements with equity participation components create shared incentives for success.
Strategic stockpiling arrangements providing long-term purchase commitments reduce investment risks. Infrastructure development partnerships sharing capital requirements distribute financial burdens across multiple stakeholders.
The Defense Production Act framework allows the U.S. government to provide direct financial support for establishing domestic production capabilities. Combined with Australia's critical minerals facility, these mechanisms could create synergistic investment opportunities benefiting both nations' strategic objectives.
Market Transformation Potential and Global Influence
Successful Australia-U.S. cooperation could establish templates for broader democratic nation collaboration in critical minerals. The Minerals Security Partnership (MSP), launched in June 2022, brings together 14 countries including the United States, Australia, Canada, and European nations to coordinate investments in alternative supply chains.
Global lithium demand projections from the International Energy Agency suggest 42 times growth between 2020 and 2040 under stated policies scenarios. Rare earth demand could increase from approximately 125,000 tonnes in 2020 to 315,000 tonnes by 2030.
These growth projections create market opportunities for new suppliers who can achieve cost competitiveness with established Chinese facilities. Australian producers benefit from stable political environments, established mining infrastructure, and existing trade relationships with consuming nations.
Market transformation indicators include:
- Development of alternative processing capacity outside China
- Creation of certification standards emphasising supply chain transparency
- Enhanced price discovery mechanisms in critical mineral markets
- Improved supply security for allied industrial capabilities
The strategic importance of an Albanese Trump meeting critical minerals discussion becomes evident when considering these transformation opportunities and their potential global impact.
Implementation Challenges and Cost Competitiveness
Technical and economic hurdles must be overcome for successful partnership implementation. Chinese rare earth processing costs are estimated 30-50% lower than equivalent facilities in developed economies due to labour costs, environmental standards, and economies of scale advantages.
Technical Requirements
Scaling processing capabilities to commercial production levels presents significant challenges. Achieving consistent quality standards across new supply chains requires substantial investment in technology and training.
Developing cost-competitive alternatives to established facilities demands innovation in processing techniques. Coordinating regulatory frameworks between partner nations adds complexity to implementation planning.
Economic Considerations
Securing sufficient investment capital for infrastructure development remains a primary concern. Managing higher initial costs compared to Chinese suppliers requires careful financial planning and government support.
Balancing commercial viability with strategic security objectives creates tension between short-term costs and long-term benefits. Creating sustainable long-term market demand ensures project success beyond initial government commitments.
Regulatory Coordination
Harmonising environmental standards and permitting processes streamlines development timelines. Streamlining export-import procedures for strategic materials reduces transaction costs and delays.
Developing mutual recognition frameworks for quality certifications eliminates duplicative testing requirements. Creating preferential procurement policies for allied suppliers provides market incentives for investment.
Container shipping costs increased 300-400% during 2020-2021 pandemic disruptions, demonstrating how supply chain vulnerabilities can impact global trade flows. These experiences reinforce the value proposition of geographically diversified supply networks.
Timeline and Performance Measurement Framework
Realistic implementation timelines require phased approaches balancing ambitious objectives with practical constraints:
Short-term Milestones (1-2 years)
Formal partnership agreement finalisation and framework establishment represent immediate priorities. Initial investment commitments and priority project identification create momentum for broader cooperation.
Regulatory pathway development and bureaucratic streamlining reduce implementation barriers. Pilot project launches demonstrating commercial viability provide proof of concept for larger investments.
Medium-term Objectives (3-5 years)
Commercial-scale processing facility commissioning and operations mark significant progress milestones. Measurable supply chain diversification achievements for key materials demonstrate partnership effectiveness.
Technology transfer programme implementation and knowledge sharing strengthen bilateral cooperation. Significant reduction in Chinese supply chain dependencies achieves strategic objectives.
Long-term Vision (5-10 years)
Fully integrated alternative supply networks operational at scale transform global mineral markets. Cost parity achievement with traditional suppliers through efficiency gains ensures commercial sustainability.
Leadership development in next-generation mineral processing technologies creates competitive advantages. Replicable model establishment for broader democratic nation cooperation extends partnership benefits globally.
Success measurement criteria might include percentage reductions in Chinese supply dependencies and volumes of minerals processed through bilateral facilities. The U.S. Geological Survey provides standardised metrics for tracking progress against these objectives.
Strategic Implications for Global Mineral Markets
The broader implications of successful Australia-U.S. critical minerals cooperation extend beyond bilateral trade relationships. This partnership could catalyse fundamental changes in how strategic materials are sourced, processed, and distributed globally.
Democratic supply chain networks emphasising political stability and shared values could emerge as alternatives to purely cost-optimised procurement strategies. This shift reflects growing recognition that supply security considerations often outweigh marginal cost advantages, particularly for materials essential to national security and economic competitiveness.
The development of alternative processing hubs outside China could increase price transparency and competition in critical mineral markets. Currently, Chinese dominance in processing creates information asymmetries and potential pricing power that consuming nations seek to counterbalance through diversified sourcing strategies.
Investment flows into Australian mineral processing infrastructure could demonstrate the commercial viability of alternatives to Chinese facilities. Success stories would likely attract additional private sector capital and encourage similar developments in other allied nations with mineral endowments.
The potential for an Albanese Trump meeting critical minerals dialogue to establish new precedents in international mineral cooperation highlights the strategic importance of these developments. Furthermore, such high-level discussions could accelerate implementation timelines and create additional funding mechanisms for partnership projects.
The Albanese Trump meeting critical minerals framework represents a critical juncture for reshaping global mineral supply chains. Success in this endeavour could establish Australia as the cornerstone of a new democratic minerals alliance, fundamentally altering the geopolitical landscape of strategic materials trade.
Disclaimer: This analysis involves forecasts and speculative assessments about future market developments, government policies, and international trade relationships. Actual outcomes may differ significantly from projections due to changing political circumstances, technological developments, market conditions, and other factors beyond current knowledge or control. Investment decisions should not be based solely on this analysis and require independent professional advice.
Ready to Capitalise on Critical Minerals Market Opportunities?
As Australia positions itself as a strategic alternative to Chinese mineral dominance, identifying emerging opportunities in ASX-listed critical minerals companies becomes crucial for investors. Discovery Alert's proprietary Discovery IQ model delivers instant notifications on significant mineral discoveries across the ASX, helping subscribers uncover actionable opportunities in lithium, rare earths, and other strategic commodities before broader market recognition. Begin your 30-day free trial today to position yourself ahead of this transformative market shift and explore how historic mineral discoveries have generated substantial returns for early investors.