Understanding Teck Resources' Copper Production Challenges and Market Impact
Teck Resources, a major player in the global mining sector, has recently made headlines with significant downward revisions to its copper production forecasts. These adjustments reflect ongoing operational difficulties that carry substantial implications for the broader copper market, particularly as the world faces rising copper demand amid tightening supplies.
The Canadian mining giant's struggle to meet production targets comes at a critical time when copper remains fundamental to global electrification efforts, renewable energy infrastructure, and the electric vehicle revolution. Understanding these challenges provides valuable insights into the current state and future outlook of global copper supply.
How Significant Are Teck Resources' Copper Output Reductions?
The scale of Teck Resources' production forecast revisions reveals a concerning trend for copper supply fundamentals. The company has substantially cut its copper production targets across multiple years, with reductions becoming increasingly significant through the medium term.
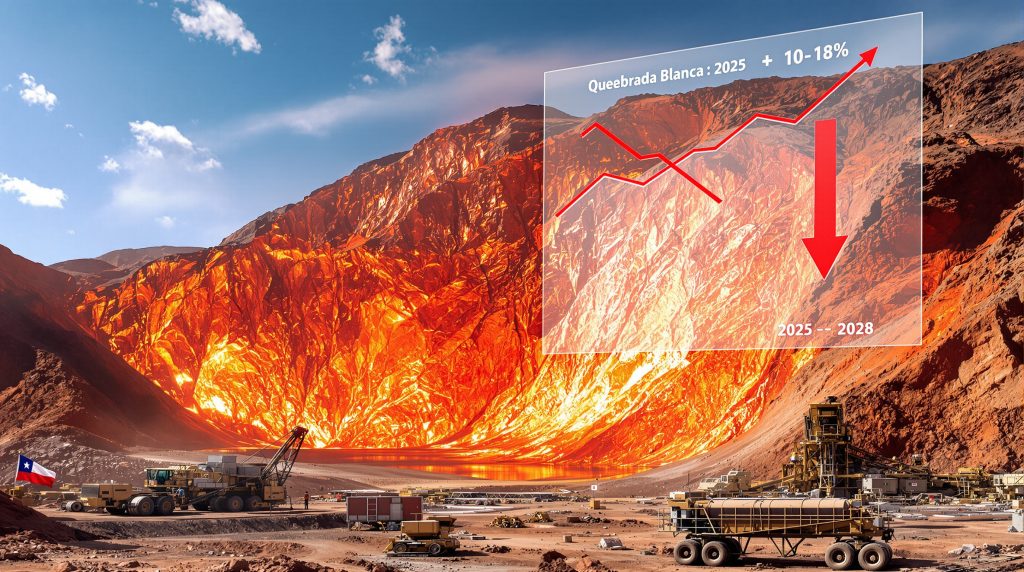
For 2025, Teck now anticipates producing between 415,000-465,000 tonnes of copper, down from its previous guidance of 470,000-525,000 tonnes. This represents a substantial reduction of approximately 55,000-60,000 tonnes (10-12%) from original projections. The company initially targeted raising output to 490,000-565,000 tonnes from 446,000 tonnes in 2024.
Revised Production Targets Through 2028
| Year | Previous Guidance (tonnes) | Revised Guidance (tonnes) | Reduction (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2025 | 470,000-525,000 | 415,000-465,000 | 10-12% |
| 2026 | 550,000-620,000 | 455,000-530,000 | 17-18% |
| 2028 | 475,000-545,000 | 435,000-510,000 | 8-10% |
The 2026 revisions are particularly alarming, with production estimates slashed by approximately 95,000 tonnes at the midpoint. This represents a reduction of nearly one-fifth of planned output, highlighting significant obstacles in Teck's copper growth strategy.
Beyond copper, Teck's output of zinc concentrates is also expected to decline dramatically, falling to 275,000-325,000 tonnes by 2028 from 525,000-575,000 tonnes in 2025—a drop of nearly 50% over three years.
What's Causing Teck Resources' Copper Output Reduction?
Quebrada Blanca Mine Challenges
At the heart of Teck's copper production shortfalls lies its Quebrada Blanca (QB) mine in northern Chile. This operation was intended to be the cornerstone of Teck's copper growth strategy but has consistently underperformed against expectations.
The primary bottleneck has been identified as the "pace of development" of the tailings storage facility. Notably, the company has indicated that the mine's processing plant itself has adequate capacity to meet production targets, but operations are constrained by limitations in tailings management infrastructure.
For the QB mine specifically, Teck has revised its 2025 output forecast down to 170,000-190,000 tonnes from the previous 210,000-230,000 tonnes. Looking ahead to 2026, QB production estimates were dramatically cut from 280,000-310,000 tonnes to just 200,000-235,000 tonnes—a reduction of approximately 80,000 tonnes or 27% at the midpoint.
Technical and Operational Complexities
While tailings facility constraints represent the immediate bottleneck, several underlying factors likely contribute to the ongoing difficulties:
- Complex Geology: Chilean copper deposits often feature challenging mineralogical characteristics that complicate extraction and processing
- Water Limitations: Northern Chile's arid conditions create ongoing challenges for water-intensive mining operations
- Ramp-Up Difficulties: New mining operations frequently encounter unforeseen technical obstacles during production scaling
- Labor and Supply Chain Issues: Post-pandemic disruptions continue to affect specialized equipment and skilled labor availability
The persistent nature of these challenges suggests that resolving them will require significant capital investment and technical solutions beyond simple operational adjustments.
How Does Teck's Reduction Impact Global Copper Supply?
Widening Global Supply Deficit
Teck's production cuts contribute to an already concerning global copper supply outlook. The company's 2026 reduction alone removes approximately 73,000 tonnes from the global concentrates market, according to market analyst assessments. While smaller than some other major disruptions, such as Freeport McMoRan's Grasberg mine force majeure (estimated at 270,000 tonnes), it represents another significant supply contraction in an already tight market.
This reduction comes at a particularly inopportune time, as several major copper producers are simultaneously experiencing production challenges. Companies including Anglo American and Glencore are struggling with similar issues stemming from declining ore grades and inadequate water supplies, especially in Latin America.
Market Indicators of Tightening Supply
The impact of these collective production shortfalls is already visible in key market indicators:
- Treatment Charges Declining: Fastmarkets' copper concentrates TC index was assessed at $65.40 per tonne on October 3, 2025, down by $2 per tonne from $63.40 per tonne just one week earlier on September 26
- Accelerating TC Decline: This represents the deepest level since the index stood at $65.80 per tonne in July 2025, highlighting rapidly tightening concentrate availability
- Smelter Competition Intensifying: Copper smelters are facing increasing difficulty securing sufficient concentrate supplies
These market signals suggest that the copper concentrate supply chain is experiencing significant pressure, with downstream processors likely to face ongoing challenges maintaining adequate feedstock levels.
Why Are Major Copper Producers Struggling to Meet Targets?
Industry-Wide Production Challenges
Teck's difficulties mirror broader issues affecting global copper miners. Several critical factors are constraining production growth across the industry:
- Declining Ore Grades: Many established mines are producing lower-grade material as higher-grade zones are depleted, requiring more ore processing for the same metal output
- Water Constraints: Particularly in Latin America, inadequate water supplies limit processing capacity at many operations
- Technical Complications: Complex geology and engineering challenges at depth create extraction difficulties
- Infrastructure Limitations: Inadequate power, water, and logistics infrastructure in remote mining regions hampers efficient operations
Notable Industry Examples
Several major copper producers are experiencing similar challenges:
- Freeport McMoRan: The company declared force majeure at Grasberg, the world's second-largest copper mine, creating a 270,000-tonne supply deficit
- Codelco: Chile's state miner continues to struggle with aging mines and declining grades
- Anglo American: Facing production difficulties across multiple operations
- Glencore: Experiencing challenges meeting production targets at various copper assets
Industry analysts have noted that "this year's mines supply is likely to come in below virtually every forecast made over the past 15 years," highlighting the systemic nature of these production shortfalls.
What Strategic Moves Is Teck Making to Address Production Challenges?
Merger with Anglo American's Chilean Assets
Teck is pursuing strategic consolidation to improve operational efficiency and overcome production constraints:
- The company has agreed to merge its QB operation with the adjacent Collahuasi mine (owned by Anglo American and Glencore)
- This consolidation aims to create the world's fifth-largest copper supplier
- The merger is expected to help the companies cut costs and boost copper production through shared infrastructure and expertise
This strategic realignment represents a significant shift in Teck's approach, recognizing that collaboration may offer better supply crunch strategies to the complex challenges facing its Chilean operations than going it alone.
Operational Recalibration
Beyond the merger, Teck appears to be adopting a more conservative and realistic approach to production forecasting:
- Revising targets to reflect actual operational capabilities rather than aspirational goals
- Focusing on resolving fundamental bottlenecks before pursuing aggressive production growth
- Potentially reassessing capital allocation to prioritize infrastructure development, particularly around tailings management
- Implementing more conservative ramp-up timelines for new projects and expansions
This pragmatic shift suggests Teck is prioritizing operational stability over ambitious growth targets—a prudent approach given the persistent challenges.
How Will Teck's Production Cuts Affect Copper Market Dynamics?
Near-Term Market Implications
Teck's reduced output contributes to several important market trends:
- Tighter Concentrate Supply: Smelters will face increased competition for available material, potentially leading to operational constraints at processing facilities
- Treatment Charge Pressure: Continued downward pressure on TC/RCs as miners gain negotiating leverage over smelters
- Price Support: Fundamental supply constraints provide underlying support for copper price predictions
- Strategic Significance: Heightened concerns about copper availability for energy transition technologies, potentially accelerating investment in recycling and substitution
The rapid decline in treatment charges—a key indicator of concentrate availability—signals that market tightness is already materializing.
Long-Term Supply Concerns
The production challenges highlight deeper structural issues in copper supply:
- Chronic Underperformance: Actual mine supply consistently falling below forecasts over the past decade and a half
- Investment Gap: Insufficient capital allocation to new copper projects, particularly during previous cyclical downturns
- Development Timelines: Long lead times for bringing new mines online (typically 7-10 years) create persistent supply lag
- Resource Nationalism: Increasing government intervention in major copper-producing regions adds complexity to project development
These structural constraints suggest that supply tightness could persist well beyond current operational issues, creating longer-term implications for copper availability and pricing.
What Does This Mean for Copper Market Participants?
Implications for Different Stakeholders
The ongoing supply constraints create varied impacts across the copper value chain:
- Miners with Stable Production: Companies that can maintain reliable output will benefit from higher prices despite volume challenges
- Smelters and Refiners: Face margin pressure from higher concentrate procurement costs and potential throughput reductions
- End Users: May experience higher prices and potential supply security concerns, potentially driving inventory building
- Investors: Could see increased interest in copper and uranium investment as supply constraints support prices
- Project Developers: Enhanced economic viability for new copper projects, potentially accelerating development timelines
Strategic Considerations
Market participants should consider several strategic responses:
- Supply Diversification: Reducing dependence on single sources of copper concentrate to mitigate disruption risks
- Vertical Integration: Exploring advantages of controlling multiple stages of the value chain to ensure supply security
- Technological Innovation: Investing in new processing technologies to maximize recovery from lower-grade resources
- Strategic Partnerships: Collaborating across the value chain to overcome shared infrastructure challenges
- Long-Term Contracting: Securing future supply through extended offtake agreements
- Secondary Supply: Increasing focus on recycled copper sources as a supplement to primary production
For investors, the sustained nature of these supply constraints may warrant a reassessment of long-term copper price assumptions and their implications for project economics and company valuations.
FAQ: Teck Resources Copper Production Challenges
Why is Teck Resources struggling to meet its copper production targets?
Teck faces persistent operational challenges at its Quebrada Blanca mine in Chile, primarily related to tailings facility constraints that limit processing throughput. While the processing plant itself has adequate capacity, the pace of tailings facility development has created a bottleneck that restricts overall production.
How much copper production has Teck Resources lost due to these challenges?
For 2025, Teck has reduced its copper production forecast by approximately 55,000-60,000 tonnes (10-12%). The 2026 reduction is even more significant at about 95,000 tonnes (17-18%), with ongoing reductions through 2028.
Are other major copper producers facing similar challenges?
Yes, companies including Freeport McMoRan, Codelco, Anglo American, and Glencore are all struggling with production shortfalls due to declining ore grades, water constraints, and technical complications, particularly in Latin America.
What does Teck's production reduction mean for global copper supply?
Teck's cuts contribute to an already tight global copper market, removing approximately 73,000 tonnes from the 2026 concentrate market alone. Combined with other disruptions like Freeport's Grasberg force majeure (270,000 tonnes), these reductions significantly widen the projected supply deficit.
How are copper treatment charges (TCs) affected by these production issues?
Treatment charges are declining as concentrate availability shrinks. Fastmarkets' copper concentrates TC index fell to $65.40 per tonne in early October 2025, reflecting tightening supply conditions that strengthen miners' negotiating position relative to smelters.
What strategic moves is Teck making to address these challenges?
Teck has agreed to merge its QB operation with Anglo American and Glencore's adjacent Collahuasi mine, aiming to create the world's fifth-largest copper supplier. This consolidation is expected to help cut costs and boost production through shared infrastructure and expertise.
When might copper supply constraints begin to ease?
Industry analysts suggest that supply tightness could persist for several years given the 7-10 year timeline typically required to develop new copper projects and the current underinvestment in the sector. Near-term relief would likely depend on existing producers overcoming current operational challenges.
Further Exploration
Market participants seeking deeper insights into copper market dynamics and supply constraints can access additional resources from industry information providers. These resources offer detailed analysis of price trends, supply-demand balances, and project development timelines.
The copper market's structural challenges highlight the strategic importance of this metal for global electrification efforts and suggest that supply security will remain a critical consideration for downstream users in the years ahead. Companies throughout the value chain will need to develop robust strategies to navigate these constraints while supporting the transition to a more electrified global economy.
Disclaimer: This article contains market analysis and forward-looking statements about copper supply and demand. Readers should be aware that market conditions can change rapidly, and projections about future supply, demand, or prices involve inherent uncertainty.
Seeking Early Insights Into Major Mineral Discoveries?
Don't miss the next transformative copper discovery on the ASX—Discovery Alert's proprietary Discovery IQ model provides instant notifications on significant mineral finds, empowering investors to act before the broader market. Visit our discoveries page to see how early identification of game-changing resources can generate substantial returns for your portfolio.