The global tungsten supply chain represents one of the most strategically concentrated mineral systems in modern industrial production. This critical metal underpins everything from defence manufacturing to everyday construction tools, yet its production remains overwhelmingly centralised in ways that create significant geopolitical vulnerabilities for consuming nations. Furthermore, recent developments in Australia's defense materials strategy highlight the growing importance of supply chain security for strategic minerals.
Understanding tungsten's supply dynamics requires examining not just production statistics, but the underlying geological, technological, and political factors that have shaped this extraordinary market concentration.
Tungsten's Industrial Significance and Unique Properties
Physical Characteristics That Drive Strategic Importance
Tungsten possesses a combination of physical properties that make it irreplaceable in critical applications. With the highest melting point of any metal at 3,422°C, tungsten maintains structural integrity under extreme thermal conditions that would destroy alternative materials.
• Tungsten carbide applications consume approximately 60% of global production, leveraging hardness levels approaching diamond characteristics
• Industrial cutting tools rely on tungsten's durability for machining hardened steels and specialised alloys
• Mining equipment utilises tungsten carbide for drill bits and wear-resistant components in harsh extraction environments
• High-temperature industrial processes depend on tungsten electrodes and heating elements for consistent performance
Defence and Aerospace Applications
Military applications create inelastic demand for tungsten products, regardless of price fluctuations. The metal's extreme density of 19.3 grams per cubic centimetre makes it essential for specialised defence applications where weight and penetration capabilities are critical.
Aerospace manufacturers incorporate tungsten into vibration dampening systems and counterweight applications, where its density provides optimal performance in confined spaces. These applications often require materials meeting stringent quality specifications that limit supplier alternatives.
Global Production Geography and Market Dominance
China's Overwhelming Market Position
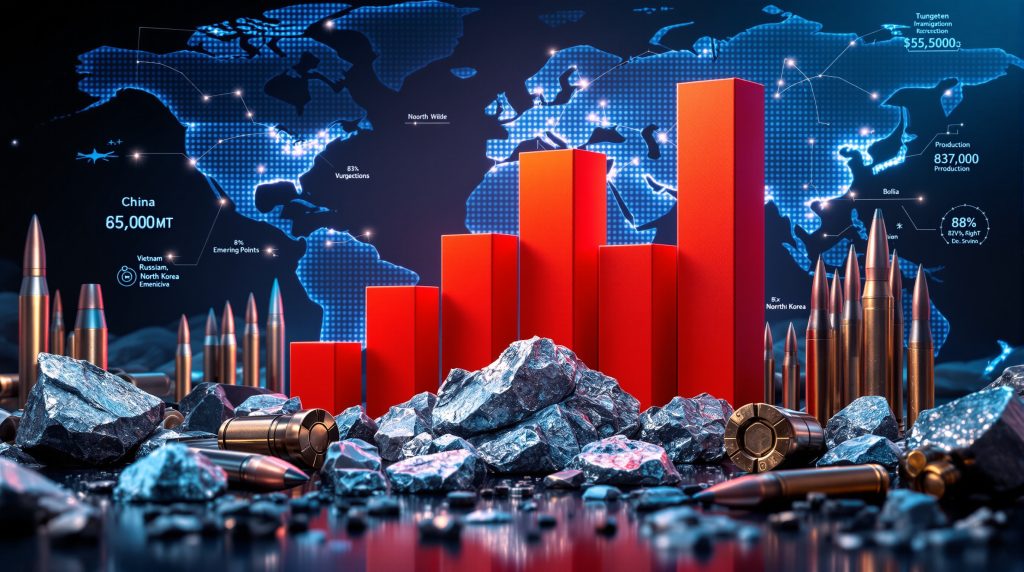
According to the USGS Mineral Commodity Summaries, global tungsten production in 2024 demonstrated unprecedented concentration:
| Producer | Production (MT) | Market Share | Regional Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| China | 67,000 | 82.7% | Complete supply chain integration |
| Vietnam | 3,400 | 4.2% | Limited processing capability |
| Russia | 2,000 | 2.5% | Strategic reserves priority |
| North Korea | 1,700 | 2.1% | Export restrictions apply |
| Bolivia | 1,600 | 2.0% | Small-scale operations |
| Other nations | 3,300 | 4.1% | Fragmented production |
This concentration exceeds that of most other critical minerals, creating supply chain vulnerabilities that extend beyond simple market dynamics into strategic security considerations. In addition, the global tungsten supply chain faces challenges that mirror those discussed in broader critical minerals pivot strategies.
Western Production Limitations
Traditional mining nations maintain minimal tungsten production capacity. Australia, Austria, Spain, and Portugal collectively produce approximately 2,800 metric tons annually, representing merely 3.5% of global output. This production gap cannot be bridged quickly due to geological constraints and processing infrastructure limitations.
The absence of significant Western production reflects both geological realities and economic factors. Many historical tungsten mining regions became uneconomical as Chinese production expanded, leading to mine closures and infrastructure deterioration that would require substantial investment to restore.
Reserve Distribution and Long-Term Supply Security
Global Reserve Analysis
While production concentration remains extreme, tungsten reserves show somewhat broader geographic distribution. China controls approximately 2.4 million tons of identified tungsten reserves, representing 52% of the global total of 4.6 million tons.
This reserve-to-production ratio reveals important strategic implications:
• China's reserve dominance exceeds its production share, indicating potential for sustained market control
• Alternative reserve locations exist but lack developed extraction and processing infrastructure
• Western reserve development requires significant capital investment and multi-year development timelines
• Secondary supply sources through recycling offer limited but growing alternatives
Emerging Production Centres
South Korea's Sangdong tungsten project represents the most significant non-Chinese development in decades. Following its operational restart, this facility potentially supplies 8-10% of global tungsten demand once reaching full production capacity.
Australian tungsten operations, particularly the Mt. Carbine facility in Queensland, provide Western-aligned supply sources. However, these operations produce at scales significantly smaller than Asian facilities, limiting their impact on overall supply security. Moreover, the broader mining industry evolution trends suggest increasing focus on strategic mineral security.
Supply Chain Vulnerabilities and Risk Factors
Multi-Level Risk Assessment
The global tungsten supply chain faces interconnected vulnerabilities across three critical levels:
Primary Production Risks:
• Environmental regulations in China affect production consistency and costs
• Political instability in secondary producing nations creates supply uncertainty
• Limited geological exploration outside established mining regions
• Climate change impacts on mining infrastructure and operations
Processing and Refining Bottlenecks:
• Tungsten concentrate processing requires specialised metallurgical expertise
• European processing facilities operate at limited capacity compared to Chinese facilities
• Technical knowledge transfer restrictions limit processing capability development
• Quality control standards vary significantly between processing centres
End-User Manufacturing Dependencies:
• Defence contractors require consistent tungsten carbide specifications
• Industrial tool manufacturers face inventory management challenges
• High-technology electronics production vulnerable to supply disruptions
• Substitution possibilities remain limited for critical applications
Export Controls and Trade Policy Impacts
Recent Policy Developments
China's implementation of export control measures targeting tungsten and other critical minerals creates immediate supply security concerns for Western manufacturers. These restrictions demonstrate how concentrated production enables policy leverage in international trade relationships.
Export controls typically include:
• Licensing requirements for tungsten product exports to specific countries
• Quantity restrictions during periods of domestic supply prioritisation
• Technical specification limitations affecting high-purity tungsten availability
• Price manipulation potential through administrative supply management
Western Response Strategies
Strategic minerals policy requires long-term thinking and sustained investment commitment to achieve meaningful supply chain diversification results.
The United States and European Union have initiated various programmes to address tungsten supply vulnerability:
- Domestic mining incentives through tax credits and development support
- International partnership agreements with alternative supplier countries
- Research funding for tungsten substitution and recycling technologies
- Strategic stockpiling programmes to buffer against supply disruptions
- Anti-dumping measures to protect domestic tungsten industry development
These initiatives align with broader energy security insights regarding critical mineral dependencies.
Alternative Supply Development and Market Evolution
Recycling and Secondary Supply Growth
Tungsten recycling represents an increasingly important supply source, though still limited compared to primary production. Industrial recycling programmes recover tungsten from:
• Worn cutting tools and industrial equipment
• Military hardware and ammunition manufacturing waste
• Electronic components and specialised alloys
• Construction and mining equipment replacement
Recovery rates for tungsten recycling can reach 85-90% under optimal conditions, making circular economy approaches economically viable for high-value applications.
Investment in Alternative Production
New tungsten mining projects require substantial capital investment and extended development timelines. According to analysis from Aranca's global tungsten supply study, typical project development involves:
• 5-7 years for exploration and feasibility studies
• 3-5 years for permitting and construction phases
• $100-500 million in capital requirements depending on scale
• Specialised workforce development for tungsten metallurgy and processing
These timeframes mean that supply chain diversification represents a decade-long commitment requiring sustained political and financial support.
Market Pricing Dynamics and Volatility Factors
Price Formation Mechanisms
European tungsten spot prices reached historically high levels during 2023, driven by multiple convergent factors:
• Geopolitical supply uncertainty affecting long-term contract negotiations
• Increased defence spending boosting tungsten demand across NATO countries
• Limited alternative supplier capacity constraining price competition
• Speculation in commodity markets amplifying price volatility
Demand Growth Drivers
Several trends support sustained tungsten demand growth:
• Defence modernisation programmes requiring advanced tungsten alloys
• Green technology transitions utilising tungsten in renewable energy infrastructure
• Industrial automation expansion increasing tungsten carbide tool consumption
• Infrastructure development in emerging economies driving construction equipment demand
Furthermore, industry events such as the mining innovation expo showcase technological advances that may influence future demand patterns.
Future Supply Chain Development Scenarios
Short-Term Outlook (2025-2030)
The next five years will likely see limited fundamental change in tungsten supply chain structure. China's production dominance will persist whilst alternative projects undergo development phases.
Key developments may include:
• Sangdong mine expansion reaching full production capacity
• European processing facility investments to reduce Chinese dependence
• Recycling technology improvements increasing secondary supply contributions
• Strategic stockpile accumulation by Western governments
Medium-Term Transformation (2030-2040)
Successful supply chain diversification requires sustained investment and policy support throughout this period:
• New mining projects in Australia, Canada, and South America reaching production
• Processing infrastructure development outside China
• Advanced recycling technologies achieving higher recovery rates
• Potential breakthrough in tungsten substitution research for specific applications
Strategic Implications for Stakeholders
Manufacturer Risk Management
Companies dependent on tungsten supplies should implement comprehensive risk management strategies:
• Supplier diversification programmes even at higher cost premiums
• Inventory buffering for critical tungsten components
• Long-term supply contracts with multiple geographic sources
• Investment in recycling capabilities to reduce primary material dependence
Government Policy Priorities
National security considerations require coordinated policy approaches:
• Strategic reserve policies balancing cost and security objectives
• Mining industry development incentives for tungsten projects
• International cooperation agreements with alternative supplier countries
• Research funding for substitution and recycling technologies
The global tungsten supply chain's extreme concentration creates systemic vulnerabilities that extend far beyond normal market dynamics. While China's production efficiency provides cost advantages under stable conditions, geopolitical tensions and export restrictions demonstrate the strategic risks of such concentrated dependence.
Consequently, achieving meaningful supply chain resilience requires coordinated efforts spanning decades, involving substantial investment in alternative production, processing capabilities, and recycling infrastructure. The timeline for supply chain rebalancing makes immediate risk mitigation strategies essential for tungsten-dependent industries and national security planning.
Disclaimer: This analysis is based on publicly available data and industry reports. Tungsten market conditions and geopolitical factors can change rapidly, affecting supply chain dynamics and pricing. Readers should consult current market data and professional advisors for investment or strategic planning decisions.
Could Tungsten Supply Disruptions Create Major Investment Opportunities?
Strategic mineral supply chains like tungsten often create significant market opportunities when alternative producers emerge to challenge dominant suppliers. Discovery Alert's proprietary Discovery IQ model identifies breakthrough mineral discoveries across Australia's ASX, including critical metals that could reshape global supply security. Explore how major mineral discoveries have historically delivered exceptional returns, then begin your 30-day free trial to position yourself ahead of emerging strategic mineral opportunities.