Understanding the Foundation of Modern US-China Trade Relations
The complex landscape of US-China trade negotiations in 2025 reflects decades of economic interdependence overshadowed by recent strategic competition. Current diplomatic efforts represent the fifth round of formal trade discussions, with meetings held in Kuala Lumpur throughout late October 2025. These negotiations involve senior leadership from both nations, including Chinese Vice-Premier He Lifeng and US Secretary of the Treasury Scott Bessent, signaling the high-stakes nature of contemporary bilateral commerce.
Modern trade discussions build upon previous frameworks while addressing emerging challenges in supply chain resilience, technology transfer protocols, and critical minerals security. The negotiation process demonstrates how economic diplomacy operates within broader geopolitical constraints, where domestic political considerations intersect with international commercial interests.
Current negotiations differ significantly from earlier trade agreements by focusing on restoration rather than innovation. According to recent reports from Fortune, the primary objective involves returning to pre-tariff economic conditions rather than establishing entirely new commercial frameworks. This approach suggests both nations recognise the economic costs of prolonged trade disputes while maintaining their respective strategic priorities.
How Do Tariff Mechanisms Shape Bilateral Commerce?
Strategic Pause Extensions and Temporary Relief Measures
The implementation of 90-day tariff pause mechanisms has become a central feature of US-China trade negotiations. These temporary suspension periods serve multiple diplomatic functions, providing breathing space for substantive policy discussions while preventing immediate escalation of trade tensions. Industry representatives express confidence that these pause periods will continue beyond their initial timeframes, creating predictable windows for business planning and investment decisions.
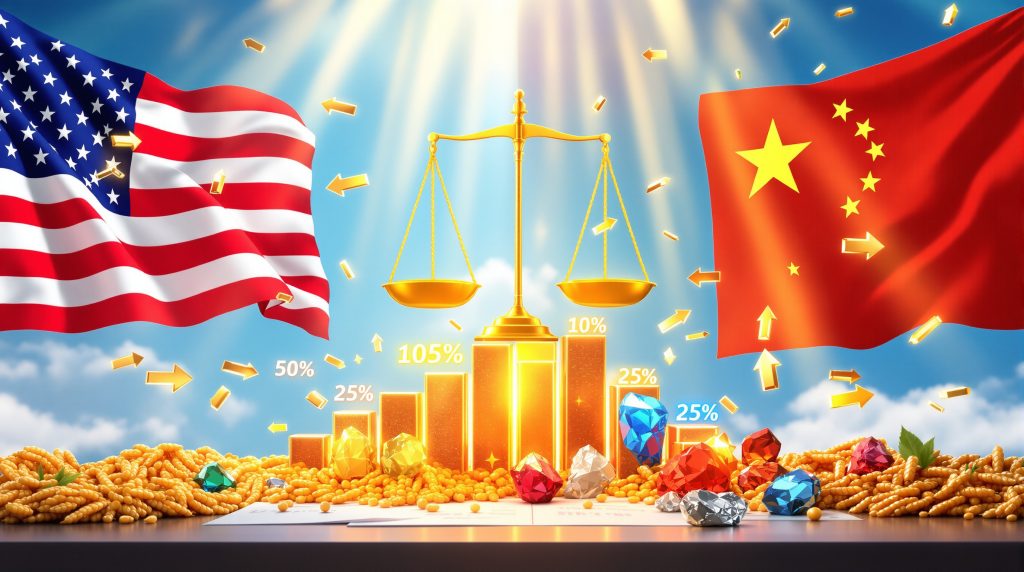
Current tariff structures demonstrate the complexity of modern trade policy implementation. Furthermore, the tariff impact insights reveal that key sectors face varying rates of protection, with general merchandise experiencing reductions from previous levels of 25-60% to approximately 10%, while specialised products like copper face continued elevated rates of 50%. Agricultural products remain under negotiable frameworks, reflecting their dual role as commercial commodities and diplomatic tools.
| Product Category | Current Rate | Previous Range | Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| General Merchandise | 10% | 25-60% | Temporary reduction |
| Industrial Metals | 50% | Variable | Ongoing adjustment |
| Agricultural Products | Negotiable | 15-25% | Under review |
| Technology Components | Variable | 20-40% | Sector-specific |
Implementation Challenges and Compliance Monitoring
Tariff mechanisms operate within sophisticated compliance frameworks that track implementation progress and measure economic outcomes. These systems incorporate dispute resolution pathways and performance benchmarks, enabling both nations to assess whether temporary measures achieve their intended economic and diplomatic objectives.
The strategic value of tariff pauses extends beyond immediate commercial relief. In addition, these mechanisms allow negotiators to address underlying structural issues while maintaining existing trade flows. For businesses operating across US-China supply chains, tariff predictability becomes crucial for inventory management, production planning, and long-term investment strategies.
What Role Do Agricultural Commodities Play in Trade Balance?
Soybean Trade as Economic and Diplomatic Barometer
Agricultural trade represents one of three primary areas identified in current US-China trade negotiations, alongside fentanyl cooperation and rare earth minerals. Soybean purchases specifically serve as both significant commercial transactions and indicators of broader relationship stability. The resumption of substantial US soybean imports by China signals diplomatic progress while addressing practical food security and livestock feed requirements.
Beijing confirmed preliminary consensus on agricultural trade issues during October 2025 negotiations, suggesting both nations recognise the mutual benefits of restored agricultural commerce. For American farmers, particularly in midwest agricultural regions, Chinese market access provides critical revenue streams that support rural economic stability.
Key Agricultural Trade Dynamics:
- Market Access Restoration: Chinese commitment to resume significant US soybean purchases
- Supply Chain Diversification: Evaluation of alternative sourcing from Brazil, Argentina, and other suppliers
- Seasonal Production Cycles: Alignment of purchase commitments with American harvest schedules
- Food Security Considerations: Chinese domestic demand for livestock feed and protein sources
Supply Chain Resilience and Alternative Sourcing
Current agricultural negotiations consider broader supply chain resilience beyond bilateral trade volumes. Chinese importers developed alternative sourcing relationships during periods of reduced US imports, creating lasting changes in global agricultural trade patterns. These shifts affect pricing dynamics, shipping routes, and long-term market relationships across multiple continents.
The restoration of US agricultural exports requires addressing logistical infrastructure, financing arrangements, and quality assurance protocols that may have changed during trade disruption periods. However, success in agricultural trade resumption often serves as a confidence-building measure for broader economic cooperation.
How Do Critical Minerals Factor into Trade Discussions?
Rare Earth Elements and Strategic Resource Security
Critical mineral negotiations represent one of the most strategically significant aspects of current US-China trade discussions. Rare earth elements occupy a central position in these talks due to their essential role in defence technologies, renewable energy systems, and advanced manufacturing applications. China's dominant position in rare earth processing and refining creates both commercial opportunities and strategic vulnerabilities that both nations must address.
The preliminary consensus on export controls reached during October 2025 negotiations encompasses critical mineral policies, indicating both sides recognise the need for predictable access to these essential materials. Furthermore, analysis from CNBC suggests that for the United States, securing reliable rare earth supplies supports domestic manufacturing capabilities and reduces dependencies that could affect national security interests.
Critical Mineral Categories Under Discussion:
- Processing and Refining Capacity: Value-added manufacturing capabilities beyond raw material extraction
- Technology Sharing Agreements: Joint venture opportunities in mineral processing operations
- Supply Security Protocols: Long-term availability commitments for strategic industries
- Quality Standards: Technical specifications for defence and aerospace applications
Processing Capabilities and Downstream Manufacturing
Beyond raw material access, negotiations increasingly focus on processing and refining capabilities that add value to extracted minerals. China's current dominance in rare earth processing stems from decades of investment in specialised facilities and technical expertise. American negotiators seek to address both immediate supply needs and longer-term domestic processing capacity development.
The strategic importance of rare earth elements extends across multiple technology sectors, from wind turbine generators and electric vehicle motors to precision-guided military systems. Negotiated agreements must balance commercial efficiency with strategic autonomy, ensuring both nations can access necessary materials while maintaining competitive positions in advanced manufacturing.
Disclaimer: Rare earth market dynamics involve complex geological, technological, and geopolitical factors that create inherent uncertainty in supply chain planning and investment strategies.
What Are the Key Enforcement Mechanisms in Trade Agreements?
Compliance Monitoring and Implementation Tracking
Modern trade agreements incorporate sophisticated monitoring frameworks that track compliance across multiple dimensions of bilateral commercial relations. The preliminary consensus reached in October 2025 addresses intellectual property protection protocols, technology transfer regulatory frameworks, and financial services market access provisions, each requiring distinct enforcement approaches.
Implementation tracking systems measure progress against specific benchmarks while providing dispute resolution pathways when compliance issues arise. These mechanisms evolved from earlier Phase One Agreement experiences, incorporating lessons learned about effective monitoring and enforcement in complex bilateral trade relationships.
Primary Enforcement Areas:
- Intellectual Property Protection: Patent filing procedures, trademark enforcement, and trade secret protections
- Technology Transfer Regulations: Voluntary versus mandatory transfer requirements in joint ventures
- Financial Services Access: Market entry requirements and operational restrictions for foreign institutions
- Agricultural Purchase Commitments: Volume tracking and timeline compliance for commodity imports
Investigation and Review Processes
Section 301 investigations provide formal mechanisms for assessing compliance with existing agreements and identifying areas requiring additional attention or modification. These procedures operate parallel to high-level negotiations, offering technical expertise and detailed analysis of specific trade practices and their economic impacts.
Effective enforcement requires balancing flexibility for changing economic conditions with accountability for agreed commitments. Consequently, both nations maintain review processes that evaluate whether negotiated agreements achieve their intended economic outcomes while addressing legitimate concerns about market access, fair competition, and regulatory transparency.
How Do Negotiation Venues Influence Outcomes?
Third-Country Meeting Advantages and Neutral Territory Benefits
The selection of Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, for the fifth round of US-China trade negotiations demonstrates the strategic importance of neutral meeting venues in high-stakes diplomatic discussions. Third-country locations provide several diplomatic advantages, including reduced domestic political pressure, enhanced privacy for sensitive discussions, and symbolic equality between negotiating parties.
US Trade Representative Jamieson Greer noted that Malaysia negotiations brought both sides to positions where leaders could conduct productive meetings, suggesting neutral venues facilitate meaningful progress on technical issues. The success of these preparatory discussions enabled planning for subsequent leadership meetings between President Trump and President Xi Jinping.
Benefits of Neutral Venue Selection:
- Reduced Political Pressure: Distance from domestic media coverage and political constituencies
- Enhanced Privacy: Controlled environment for sensitive commercial and strategic discussions
- Symbolic Equality: Neither party appears to be negotiating from a position of seeking favour
- Technical Focus: Professional diplomatic facilities supporting detailed policy discussions
Multi-Track Diplomatic Engagement
Current negotiations demonstrate multi-level engagement strategies, with technical working groups addressing specific sector issues while senior leadership focuses on strategic framework agreements. This approach allows detailed policy development to proceed parallel to high-level diplomatic relationship management.
The planned Trump-Xi meeting in South Korea represents the culmination of technical negotiations conducted in Malaysia, illustrating how venue selection supports different phases of complex diplomatic processes. In addition, each location serves specific functions in building consensus and finalising agreements between the world's two largest economies.
What Are the Economic Implications of Current Negotiations?
Market Stability and Business Confidence Indicators
Current trade negotiations directly impact global commodity markets, supply chain planning decisions, and investment strategies across multiple industries and geographic regions. The preliminary consensus reached on five key issue areas provides market participants with improved visibility regarding trade policy direction and tariff stability.
Industry confidence in negotiation outcomes varies by sector, with agricultural exporters expressing optimism about resumed market access while technology companies remain cautious about ongoing restrictions. However, the extension of 90-day tariff pauses creates predictable planning windows for businesses managing international supply chains and production schedules.
Economic Impact Areas:
- Supply Chain Planning: Inventory management and production scheduling decisions
- Investment Strategy: Long-term capital allocation for manufacturing and distribution
- Commodity Markets: Price discovery and forward contract development
- Currency Exchange: Trade balance impacts on USD-CNY exchange rates
Business Community Perspectives and Industry Responses
The US-China Business Council and similar organisations provide valuable input on practical implementation challenges, regulatory compliance costs, and market access priorities. Business community engagement helps negotiators understand real-world consequences of policy decisions and identify solutions that serve both commercial and diplomatic objectives.
Different industry sectors experience varying impacts from trade negotiations, with technology companies facing ongoing restrictions while agricultural and traditional manufacturing sectors anticipate benefits from reduced tariffs and improved market access. For instance, the global tariff impact shows these diverse perspectives require negotiators to balance competing interests while maintaining overall relationship stability.
Disclaimer: Economic projections and market impact assessments involve inherent uncertainty and depend on multiple variables beyond bilateral trade agreements.
How Do Geopolitical Factors Influence Trade Policy?
Regional Alliance Considerations and Strategic Partnerships
US-China trade negotiations occur within broader geopolitical contexts that include alliance relationships, regional economic partnerships, and multilateral organisation commitments. The selection of South Korea for planned Trump-Xi leadership meetings reflects consideration of regional diplomatic dynamics and alliance partnership sensitivities.
Trade policy decisions must account for how bilateral agreements affect relationships with third-party nations, particularly in the Indo-Pacific region where multiple countries maintain significant economic relationships with both the United States and China. Furthermore, the trade war developments show these considerations influence negotiation strategies and acceptable agreement terms.
Regional Geopolitical Factors:
- Alliance Relationships: US partnerships with Japan, South Korea, and Australia
- Regional Economic Frameworks: ASEAN, CPTPP, and other multilateral arrangements
- Security Considerations: Defence cooperation impacts on commercial relationships
- Technology Competition: Strategic rivalry in semiconductors, artificial intelligence, and telecommunications
Timeline Pressures and Political Calendar Constraints
Negotiation timelines reflect domestic political considerations, economic calendar constraints, and international summit scheduling requirements. The timing of current negotiations considers electoral cycles, budget planning periods, and coordination with other international diplomatic initiatives.
Political calendar pressures create both opportunities and constraints for negotiators seeking to finalise agreements. Consequently, successful negotiations must balance the urgency of economic relief with the complexity of addressing underlying structural issues in the bilateral relationship.
What Are the Prospects for Comprehensive Agreement Framework?
Building Blocks Approach and Incremental Progress
Current negotiations favour incremental progress on specific issues rather than comprehensive framework overhauls, allowing for confidence-building while addressing complex technical challenges. The preliminary consensus on five distinct areas including export controls, tariff extensions, port fees, agricultural trade, and fentanyl cooperation demonstrates this sector-specific approach.
This building blocks methodology enables negotiators to achieve concrete progress on manageable issues while developing trust and momentum for addressing more complex structural questions. Success in initial areas creates foundation for expanding cooperation into additional sectors and policy domains.
Preliminary Consensus Areas (October 2025):
- Export Controls: Critical mineral and technology transfer regulations
- Tariff Extension: 90-day pause renewal and potential longer-term reductions
- Port Fees: Administrative cost adjustments for trade facilitation
- Agricultural Trade: Market access restoration and purchase commitments
- Fentanyl Cooperation: Law enforcement collaboration and related tariff adjustments
Success Metrics and Performance Benchmarks
Measuring negotiation success requires considering multiple factors including trade volume changes, dispute resolution effectiveness, and broader relationship stability indicators. Both nations seek agreements that demonstrate tangible benefits to domestic constituencies while maintaining face-saving elements for international audiences.
The focus on returning to pre-tariff conditions rather than establishing new comprehensive frameworks suggests both sides recognise the economic costs of prolonged trade disputes. This pragmatic approach prioritises economic recovery over structural reform, potentially creating more sustainable agreement foundations.
Key Success Indicators:
- Trade Volume Recovery: Return to pre-dispute import/export levels
- Market Access Expansion: Reduction of non-tariff barriers and regulatory restrictions
- Dispute Resolution: Effective mechanisms for addressing future commercial disagreements
- Relationship Stability: Reduced frequency of trade-related diplomatic tensions
Disclaimer: Future negotiation outcomes depend on multiple variables including domestic political developments, global economic conditions, and international security considerations that may affect agreement implementation and sustainability.
Future Outlook and Strategic Considerations
The trajectory of US-China trade negotiations will likely depend on successful implementation of interim agreements, continued diplomatic engagement, and broader geopolitical stability. Both nations demonstrate commitment to finding workable solutions that address core economic interests while managing political sensitivities and domestic constituency expectations.
The building blocks approach adopted in current negotiations suggests future agreements may continue focusing on specific sector solutions rather than comprehensive trade architecture reforms. This methodology allows both countries to demonstrate progress to domestic audiences while avoiding complex structural issues that could derail broader diplomatic relationship management.
Factors Influencing Future Negotiations:
- Global Economic Conditions: GDP growth rates, inflation pressures, and employment levels affecting trade policy priorities
- Technology Competition: Semiconductor, artificial intelligence, and telecommunications sector developments
- Climate Cooperation: Clean energy technology collaboration opportunities and challenges
- Regional Security: South China Sea, Taiwan, and North Korea considerations affecting bilateral relations
- Multilateral Frameworks: WTO reform, G20 coordination, and other international trade organisation roles
The emphasis on restoring pre-tariff economic relationships suggests both nations recognise the mutual benefits of expanded commercial engagement while maintaining strategic competition in other domains. However, success in current negotiations may establish precedents for managing future trade disputes through diplomatic engagement rather than unilateral economic measures.
Long-term stability requires addressing underlying structural issues that contributed to trade tensions, including intellectual property protection, technology transfer requirements, market access reciprocity, and state-enterprise competition policies. Nevertheless, current negotiations prioritise immediate economic relief over comprehensive structural reform, potentially creating challenges for sustainable long-term agreements.
Important Note: This analysis reflects conditions and negotiations as reported through October 2025. Trade negotiations remain dynamic processes subject to rapid changes based on political developments, economic conditions, and international events that may affect final outcomes and implementation timelines.
Ready to Capitalise on US-China Trade Developments?
Major trade negotiations like these often create significant opportunities for savvy investors tracking ASX-listed companies with exposure to critical minerals and agricultural commodities. Discovery Alert's proprietary Discovery IQ model delivers real-time alerts on significant mineral discoveries, helping subscribers identify actionable opportunities before broader market awareness drives price movements. Begin your 30-day free trial today to position yourself ahead of the market as global trade dynamics continue to evolve.