The Evolution of U.S. Gulf Coast Fuel Oil Imports: Market Transformations and Strategic Shifts
The U.S. Gulf Coast, home to over 55% of America's refining capacity, has experienced significant shifts in fuel oil import patterns in recent years. These changes reflect broader transformations in global trade dynamics that are reshaping the energy landscape across the region.
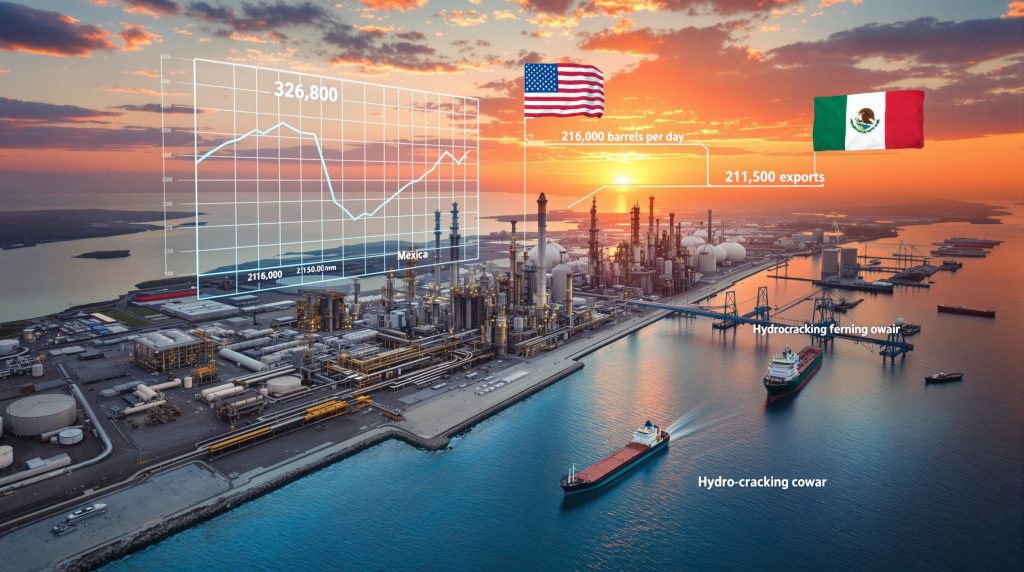
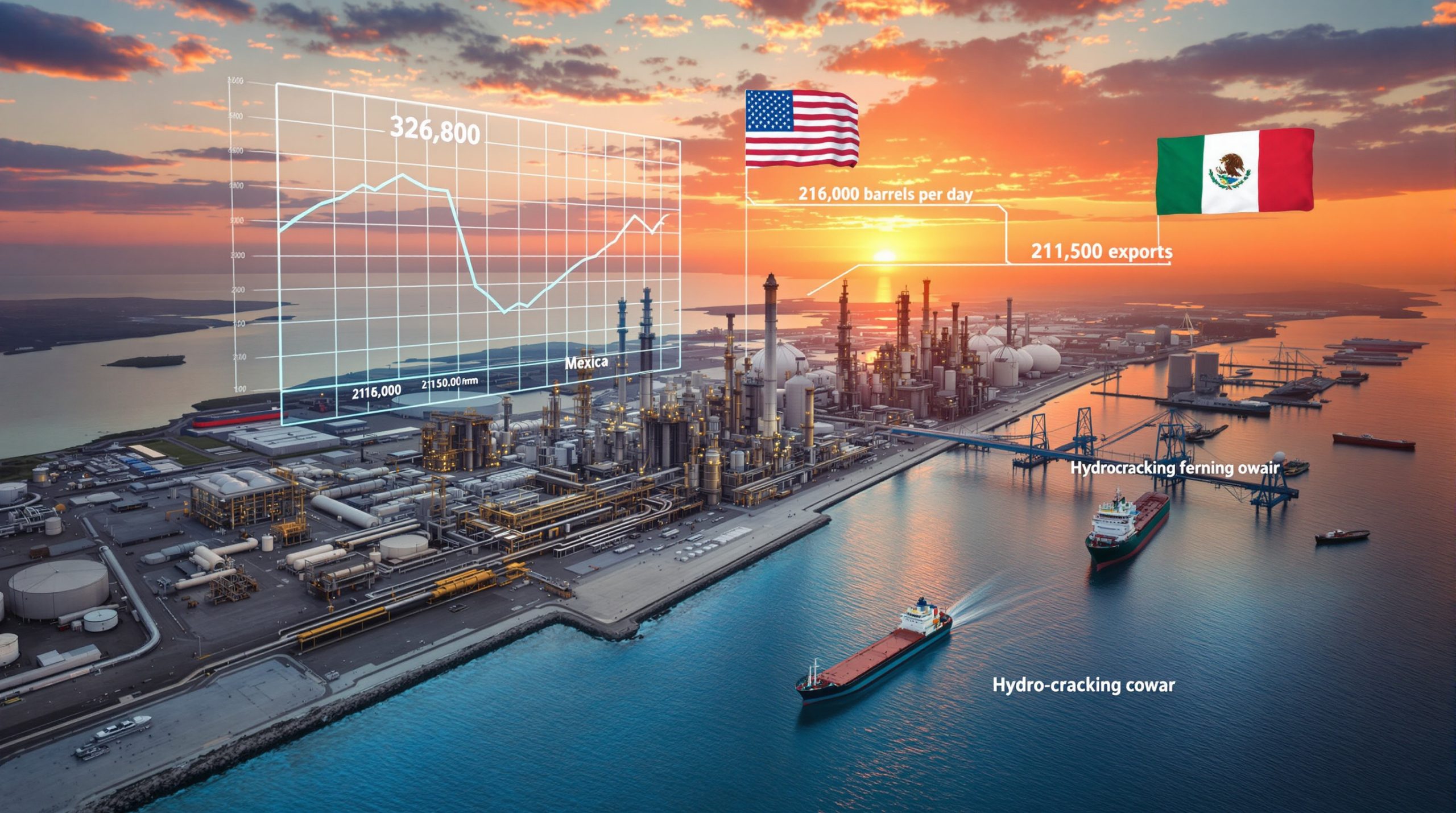
Recent data reveals a notable decline in Gulf Coast fuel oil imports, dropping from approximately 326,800 barrels per day (b/d) in 2024 to roughly 238,200 b/d during the first seven months of 2025. June 2025 marked a particularly significant low point, with imports plummeting to approximately 213,000 b/d – a dramatic decrease from over 430,000 b/d recorded in June 2024.
Behind these numbers lies a complex story of industry adaptation, technological advancement, and strategic realignment that carries important implications for energy markets nationwide.
Key Drivers Behind Declining Gulf Coast Fuel Oil Imports
Strategic Shifts in Domestic Refining Approaches
Gulf Coast refiners have strategically pivoted toward processing heavier, sour crude varieties domestically, creating a fundamental change in their operational approach. This strategy offers several distinct advantages:
- Processing heavy, sour crude produces more residual material that can be upgraded within existing facilities
- In-house upgrading capabilities allow refiners to create higher-value products from lower-cost inputs
- The shift reduces dependence on direct fuel oil imports, enhancing energy security
- Enhanced operational flexibility helps refineries adapt to market volatility
This strategic evolution represents a broader industry trend toward maximizing refinery efficiency and adaptability in response to changing market conditions and technological capabilities.
Mexican Export Reductions Transform Traditional Supply Channels
Mexico, traditionally the largest supplier of residual fuel oil to the Gulf Coast, has significantly reduced its shipments, creating ripple effects throughout the market:
| Period | Mexican Fuel Oil Exports to Gulf Coast (b/d) | Percentage Change |
|---|---|---|
| Early 2024 | 136,400 | Baseline |
| 2025 Average | 67,100 | ~51% Decline |
This dramatic reduction stems from Mexico's ambitious domestic refinery modernization program, particularly at the 340,000 b/d Olmeca refinery. These upgrades aim to convert residual fuel oil into more valuable middle distillates, reducing export volumes while enhancing Mexico's domestic fuel production capabilities and energy independence.
Global Supply-Demand Imbalances Reshape Trade Patterns
Complex global market dynamics have created regional imbalances that significantly impact Gulf Coast import patterns:
- Asian Market Surplus: Increased fuel oil production from India, Iraq, and Bahrain has created oversupply conditions in Asian markets, depressing regional prices
- Middle East Consumption Growth: Rising domestic fuel consumption in Middle Eastern countries has tightened regional supplies for export
- Geopolitical Disruptions: Ongoing shipping route challenges and political tensions have disrupted traditional trade flows and created new risk premiums
- Price Arbitrage Fluctuations: Evolving price differentials between regions have altered economically viable trade routes and import strategies
These factors collectively recalibrate the economic calculations for Gulf Coast importers, influencing strategic sourcing decisions and reshaping long-established trade relationships.
The Transformation of Gulf Coast Refining Capabilities
Historical Import Dependence and Infrastructure Development
The Gulf Coast refining sector developed with substantial reliance on imported feedstocks, establishing patterns that influenced decades of energy trade:
- Approximately 60% of crude oil refined in the region came from imports in previous decades
- OPEC nations and Mexico traditionally served as major suppliers
- Fuel oil imports complemented crude oil imports in the overall feedstock mix
- Infrastructure development prioritized receiving and processing imported materials
This historical pattern established trade relationships, port facilities, and processing infrastructure that continue to influence current market dynamics even as strategies evolve.
Technological Advancements Drive Processing Innovation
Modern refining technologies have fundamentally transformed how Gulf Coast facilities process crude oil, enabling greater flexibility and efficiency:
- Advanced coking and hydrocracking units can now convert significantly more residual oil into valuable products
- Catalyst innovations have dramatically improved conversion efficiency and product yields
- Sophisticated automation and control systems optimize processing parameters in real-time
- Emissions reduction technologies address environmental concerns while maintaining operational efficiency
These technological advances enable refiners to extract more value from each barrel processed, reducing the need for supplementary fuel oil imports while improving profit margins and environmental performance.
Economic Implications of Changing Import Patterns
Market Price Effects and Differential Shifts
The decline in Gulf Coast fuel oil imports has created ripple effects throughout regional and global markets:
- Reduced import demand has widened price differentials between regions, creating new trading opportunities
- Changing trade flows have altered shipping patterns and freight rates, impacting transportation economics
- Market participants have developed innovative trading strategies to capitalize on emerging price dislocations
- Price signals have influenced investment decisions in refining and logistics infrastructure
According to recent EIA data, these economic effects highlight the interconnected nature of global energy markets and demonstrate how regional shifts can trigger cascading impacts throughout the industry.
Supply Chain Reconfiguration and Adaptation
As import patterns evolve, supply chains throughout the industry are undergoing significant reconfiguration:
- Terminal operators are adjusting storage and handling capabilities to accommodate changing product flows
- Shipping companies are realigning vessel deployments to match new trade patterns
- Trading houses are developing alternative sourcing strategies to ensure reliable supply
- Refiners are modifying operational plans to accommodate changing feedstock availability
This reconfiguration creates both challenges and opportunities for market participants throughout the value chain, rewarding adaptability and strategic foresight.
Geopolitical Factors Influencing Gulf Coast Import Dynamics
Sanctions Regimes and Trade Policy Impacts
International sanctions and evolving trade policies significantly impact fuel oil import patterns across the Gulf Coast:
- Restrictions on certain suppliers limit available import sources and create compliance challenges
- Tariff structures influence the economic viability of various trade routes and sourcing strategies
- Trade agreements create preferential access for specific partners, shaping competitive dynamics
- Compliance requirements add complexity and cost to international transactions
The comprehensive tariff impact analysis reveals these policy factors add another layer of complexity to Gulf Coast import decisions, requiring market participants to navigate an increasingly intricate regulatory landscape while maintaining operational efficiency.
Regional Stability Considerations and Supply Security
Political stability in key producing regions directly affects the reliability and cost of imports:
- Production disruptions in politically volatile regions create supply uncertainties and price volatility
- Security concerns along critical shipping routes add risk premiums to transportation costs
- Diplomatic relationships influence bilateral trade arrangements and investment decisions
- Regional conflicts can rapidly alter established trade patterns, requiring contingency planning
These stability factors contribute to the risk assessment calculations that inform import strategies and supply security planning throughout the Gulf Coast refining sector.
Environmental Regulations Transforming Fuel Oil Markets
IMO 2020 Impact on Global Fuel Oil Demand
The International Maritime Organization's sulfur regulations (IMO 2020) have fundamentally altered global fuel oil markets:
- Regulations dramatically reduced demand for high-sulfur fuel oil in the shipping sector
- Implementation created significant price spreads between compliant and non-compliant fuels
- The regulations accelerated installation of scrubber technology on vessels to enable continued HSFO use
- Refinery production shifted toward lower-sulfur products, transforming global supply patterns
These regulatory changes have fundamentally transformed the composition of fuel oil trade flows, affecting both volumes and specifications throughout the Gulf Coast market.
Emerging Carbon Policies Influence Investment Decisions
Evolving carbon reduction initiatives are increasingly influencing fuel oil import and refining decisions:
- Carbon pricing mechanisms affect the economics of high-carbon feedstocks and processing methods
- Clean fuel standards create incentives for lower-carbon alternatives and production processes
- Emissions reporting requirements add compliance considerations to operational planning
- Investor pressure for decarbonization influences corporate strategies and capital allocation
These environmental factors increasingly shape the decision-making framework for Gulf Coast importers and refiners, driving long-term strategic planning and investment priorities.
Future Trends Shaping Gulf Coast Fuel Oil Imports
Projected Import Scenarios and Market Outlook
Based on current oil price movements and market dynamics, several scenarios could unfold for Gulf Coast fuel oil imports in coming years:
| Scenario | Key Drivers | Projected Import Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Continued Decline | Further domestic refining optimization, sustained Mexican export reductions | 15-20% additional decrease by 2027 |
| Stabilization | Balanced global market, steady regional demand | Leveling at 200,000-225,000 b/d |
| Partial Recovery | New supplier emergence, refinery outages | Modest increase to 250,000-275,000 b/d |
These scenarios highlight the range of possible outcomes depending on how key variables evolve in the coming years, emphasizing the need for strategic flexibility among market participants.
Emerging Supplier Relationships Reshape Trade Networks
As traditional supply sources change, new supplier relationships are likely to emerge and reshape the Gulf Coast import landscape:
- South American producers seeking stable export markets may increase Gulf Coast shipments
- Middle Eastern suppliers looking to diversify customer bases could develop new trade channels
- African exporters may develop stronger Gulf Coast trade connections as production capacity grows
- Asian refiners with excess production during regional demand downturns could target opportunistic exports
These evolving relationships could significantly reshape the geography of Gulf Coast fuel oil imports in the years ahead, creating both challenges and opportunities for market participants.
Strategic Approaches for Market Participants
Diversification and Flexibility Enhancement
Industry stakeholders can employ several strategies to navigate changing import dynamics successfully:
- Diversifying supply sources reduces dependency on any single region or supplier
- Investing in flexibility-enhancing infrastructure accommodates varying feedstock qualities and availability
- Developing robust market intelligence capabilities helps anticipate shifts and identify opportunities
- Building strategic inventory positions buffers against supply disruptions
- Forming strategic partnerships across the value chain enhances resilience and market access
These approaches can help market participants maintain competitiveness amid evolving market conditions while managing risks effectively.
Technology and Innovation Focus
Technological innovation offers powerful pathways to adapt to changing import patterns:
- Advanced analytics can optimize feedstock selection and processing parameters
- Alternative feedstock processing capabilities enhance operational flexibility
- Digitalization of supply chain management improves visibility and responsiveness
- Process innovations extract more value from available feedstocks
- Integration of renewable feedstocks diversifies supply options and addresses environmental concerns
According to a recent Reuters report, these technological approaches can create significant competitive advantages in a dynamic market environment, positioning forward-thinking companies for long-term success.
Frequently Asked Questions: U.S. Gulf Coast Fuel Oil Imports
What is the primary use of imported fuel oil in Gulf Coast refineries?
Imported fuel oil primarily serves as feedstock for specialized processing units like cokers and hydrocracking facilities, which convert heavy residual materials into higher-value products including gasoline, diesel, and jet fuel. Some refineries also strategically use imported fuel oil to blend with other feedstocks to achieve optimal processing characteristics based on their specific configuration and target product slate.
How do seasonal factors affect Gulf Coast fuel oil import patterns?
Seasonal variations significantly impact import volumes, with winter typically seeing higher imports to support heating oil demand in the Northeast. Summer driving season indirectly affects patterns as refineries adjust their overall crude slate and processing priorities to maximize gasoline production, which can influence fuel oil import requirements and timing throughout the year.
Which ports handle the majority of Gulf Coast fuel oil imports?
The primary import terminals include Houston, Port Arthur, and Corpus Christi in Texas, along with Louisiana facilities in Lake Charles and New Orleans. These ports have developed specialized infrastructure for handling heavy fuel oil, including heated storage tanks, dedicated pipeline connections to nearby refineries, and specialized marine facilities designed for efficient unloading.
How do fuel oil imports compare to crude oil imports in the Gulf Coast?
Fuel oil imports represent a smaller but strategically important component of overall petroleum imports. While crude oil imports to the Gulf Coast average several million barrels per day, fuel oil imports are measured in hundreds of thousands of barrels daily, serving as complementary feedstocks that provide specific processing advantages for certain refinery configurations and product slates.
What quality specifications are most important for Gulf Oil imports?
Key specifications include sulfur content (with lower sulfur commanding premium prices), API gravity (density), metals content (particularly nickel and vanadium), and carbon residue. These characteristics determine how the fuel oil will perform in various refinery processes and what final products can be economically produced, making quality assessment critical for importers and processors.
Looking Ahead: The Dynamic Future of Gulf Coast Fuel Oil Markets
The U.S. Gulf Coast fuel oil import market continues to demonstrate remarkable adaptability in the face of changing global dynamics. As refineries enhance their processing capabilities, environmental regulations evolve, and global trade patterns shift, market participants who embrace technological innovation and strategic flexibility will be best positioned to thrive in this transforming landscape.
Understanding these complex interactions between technology, regulation, geopolitics, and economics provides valuable perspective for industry stakeholders navigating the future of Gulf Coast energy markets. Analysts continue to monitor oil price rally insights and potential oil price crash factors to anticipate how these variables might impact the broader transition occurring throughout the global petroleum industry.
Want to Identify the Next Major Mineral Discovery?
Discovery Alert's proprietary Discovery IQ model delivers instant notifications on significant ASX mineral discoveries, empowering investors to capitalise on opportunities before the broader market. Explore why historic discoveries can generate substantial returns by visiting Discovery Alert's dedicated discoveries page and begin your 30-day free trial today.