Porphyry and Epithermal Mineral Deposits: A Geological Perspective
Porphyry and epithermal mineral deposits represent complex geological formations critical to global metal supplies. These unique mineral concentrations form through intricate processes deep within the Earth’s crust, providing significant sources of copper, gold, silver, and molybdenum.
Understanding these deposit types requires an in-depth examination of their geological origins, formation mechanisms, and economic significance. Geologists have extensively studied these mineral systems to comprehend their complex development over millions of years.
How Do Porphyry Deposits Originate?
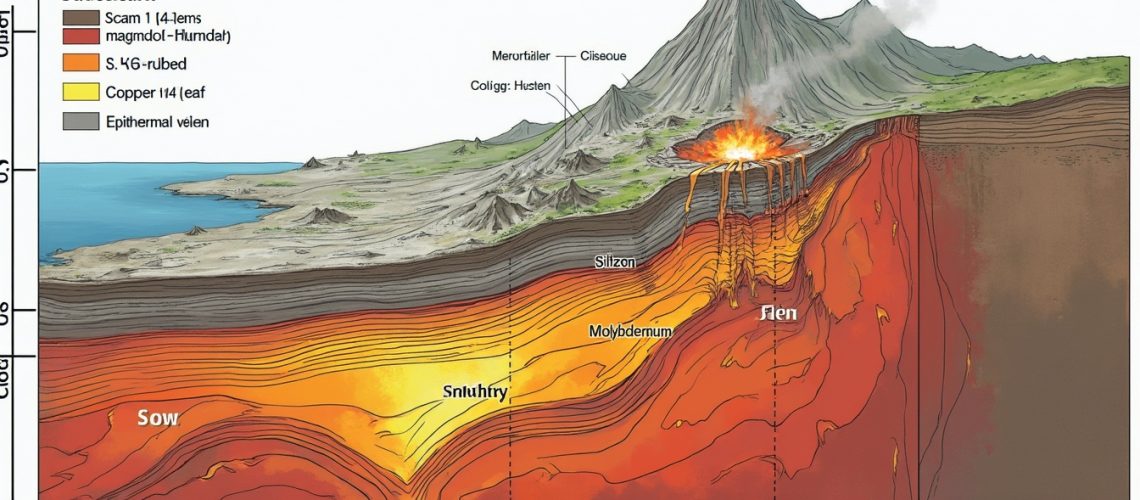
Most porphyry deposits formed during a specific geological period between 200 to 150 million years ago. These deposits develop at depths ranging from 1 to 6 kilometres below the Earth’s surface, created by complex Geological processes contributing to deposit formation involving plate tectonics and magma intrusion.
The formation begins with the melting of upper mantle and lower crustal rocks along continental margins. As oceanic plates are subducted deep into the mantle, volatile substances like water and sulfur are released, triggering magma generation. This magma creates chambers by exploiting weak zones in the surrounding rock structure.
What Geological Mechanisms Drive Metal Transportation?
Hydrothermal fluid circulation plays a pivotal role in metal transportation within these geological systems. Under immense pressure and heat, these fluids scavenge metals from magma and surrounding rocks, creating metal-rich brines.
The cooling magma generates a sophisticated metal precipitation process. Copper typically precipitates first, closest to the heat source, followed by molybdenum, gold, silver, lead, and zinc. This systematic metal zonation occurs through the continuous circulation of hydrothermal fluids.
How Do Epithermal Deposits Form?
Epithermal deposits develop above cooling magma chambers through unique crystallisation processes. As the magma chamber’s top crystallises, it releases water and other volatiles that carry metals into surrounding rock formations.
These metal-rich brines ascend through cracks and voids, precipitating metals as pressure decreases. The process creates mineral veins and deposits along sedimentary planes, offering different mineralisation patterns compared to deeper porphyry formations.
Where Are These Mineral Deposits Located?
Geological preservation of these deposits varies significantly due to erosion. The Quesnel Terrane in central British Columbia represents a notable example of a prolific region for porphyry and epithermal deposits.
Erosion continuously redistributes sediments and metals, potentially initiating new metal concentration cycles. Understanding these geographical distributions helps geologists and miners identify potential resource-rich areas.
What Are the Economic Implications?
Porphyry deposits create large, low-grade mineral concentrations that support Stable, long-life mines for major mining companies. These deposits require substantial resources for development and extraction.
Epithermal deposits, conversely, often feature higher-grade mineral concentrations that have traditionally attracted smaller-scale prospecting operations. The Economic implications of mining operations depend on multiple geological and technical factors.
How Can Mineral Deposit Exploration Be Enhanced?
Modern exploration relies on Advanced geological survey methods to identify potential mineral-rich regions. Technological innovations continue to improve our capacity to locate and assess these complex geological formations.
Geophysical surveys, remote sensing techniques, and sophisticated data analysis have dramatically improved exploration efficiency. Researchers constantly develop new methodologies to enhance our understanding of mineral deposit formation.
Conclusion: The Ongoing Significance of Mineral Deposits
Porphyry and epithermal deposits remain crucial to global metal supplies, supporting numerous industrial and technological applications. Continuous research and technological advancement will further our understanding of these remarkable geological systems.
The mining industry’s future depends on comprehending these complex mineral formations, their origins, and potential economic opportunities. Ongoing exploration and innovative research will continue to reveal new insights into these fascinating geological processes.
Ready to Discover the Next Big Mineral Find?
Unlock the secrets of complex geological formations with Discovery Alert. Offering real-time notifications on significant ASX mineral discoveries, our service simplifies the intricacies of porphyry and epithermal deposits for investors like you. Enhance your investment potential with AI-driven alerts and expert geological analysis. Start your journey with a 30-day free trial today by visiting Discovery Alert.