Resource Nationalism and Market Control in Critical Mineral Markets
Congo cobalt export control policies represent a sophisticated attempt by the Democratic Republic of Congo to leverage its dominant market position in this critical battery metal. This comprehensive framework demonstrates how resource-rich nations are increasingly using strategic export management to capture greater value from their mineral endowments while navigating complex international market dynamics.
The Democratic Republic of Congo's approach to cobalt market management represents a sophisticated attempt to balance domestic development objectives with global supply chain stability. As the source of approximately 70% of worldwide cobalt production, the DRC possesses unprecedented leverage over a metal essential for battery technology and electric vehicle manufacturing.
Understanding Congo's Cobalt Export Control Framework
The Strategic Quota System Architecture
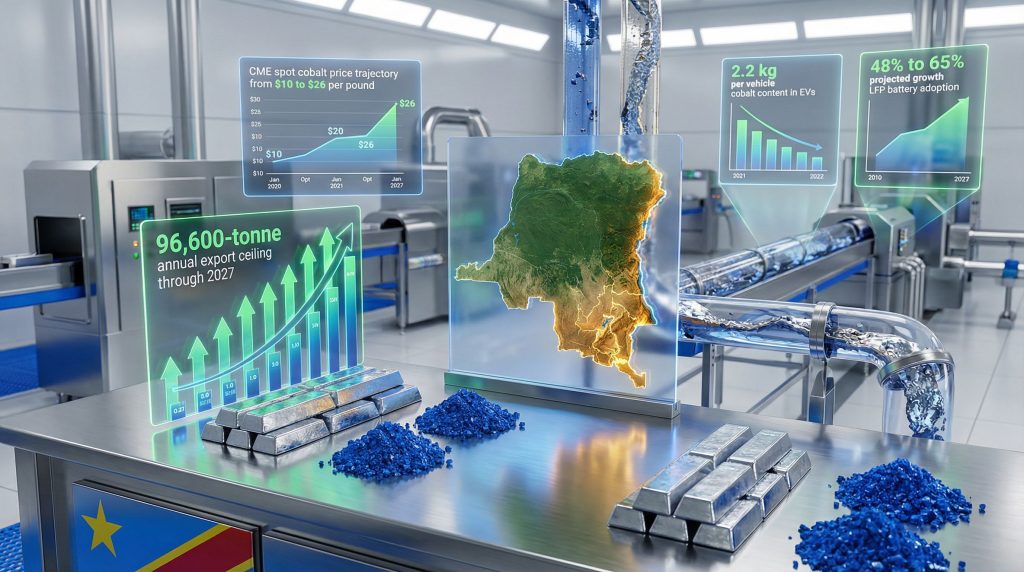
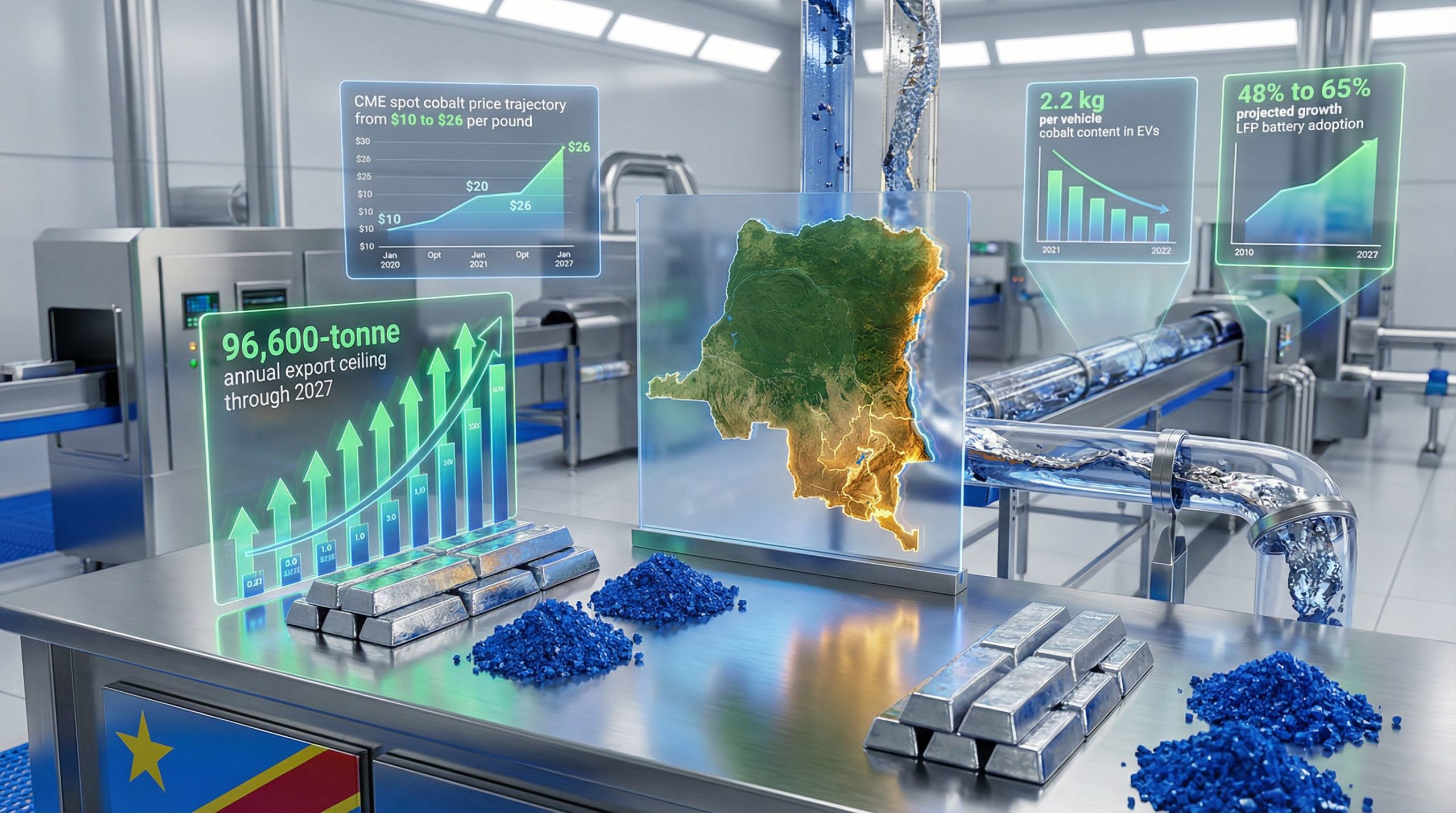
Congo's export control regime centres on a carefully structured quota system designed to manage approximately 96,600 tonnes of annual cobalt exports through 2027. This framework represents a fundamental departure from the country's previous approach to mineral exports, replacing market-driven production with government-managed supply allocation.
The system operates through monthly approval processes administered by ARECOMS, Congo's minerals regulatory authority. Producers must secure explicit authorisation before shipping materials, creating administrative checkpoints that allow for precise supply management. This use-it-or-lose-it enforcement mechanism ensures that allocated quotas translate into actual market supply rather than speculative hoarding.
A critical component involves the 9,600-tonne strategic reserve allocation, representing roughly 10% of total export capacity. This reserved portion enables the government to prioritise national development projects while maintaining flexibility to adjust market supply based on domestic policy objectives. Furthermore, this strategic allocation demonstrates how congo cobalt export control mechanisms can balance international market obligations with domestic development needs.
Revenue Optimisation Through Prepaid Royalty Requirements
The export control system incorporates financial mechanisms that guarantee government revenue regardless of market fluctuations. Companies seeking export licenses must satisfy prepaid royalty obligations, ensuring the state captures value from mineral extraction before materials leave national territory.
This approach addresses historical challenges where volatile commodity pricing created uncertainty in government revenues from mining operations. By requiring advance payments, Congo secures fiscal benefits while maintaining the ability to adjust export volumes based on market conditions.
Export quota increases remain tied to local processing facility investments, creating incentives for foreign companies to develop downstream manufacturing capacity within Congo. This linkage reflects a broader strategy to move beyond raw material exports toward value-added production that generates higher-skilled employment and technology transfer. In addition, these requirements align with broader energy transition strategy objectives that prioritise domestic value creation.
Implementation Challenges and Bureaucratic Complexities
The transition from export ban to quota system has revealed significant administrative challenges. Following the February 2025 export suspension, Congo announced its quota framework in October but experienced a seven-week implementation delay before approvals resumed. This extended pause highlighted the complexity of establishing entirely new regulatory processes for managing strategic mineral exports.
ARECOMS faces the challenge of balancing multiple objectives: ensuring adequate global supply to prevent market disruption, maximising government revenue through controlled scarcity, and promoting domestic value-addition through processing requirements. These competing priorities require sophisticated coordination between regulatory oversight, industry relations, and international diplomacy.
The implementation of congo cobalt export control systems requires careful consideration of international legal frameworks and trade obligations. Moreover, the administrative burden of monthly quota allocations creates potential bottlenecks that could disrupt supply chains even when quotas remain available.
Historical Context: Resource Cartel Effectiveness and Market Outcomes
OPEC's Production Management Legacy
The Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries provides the most established model for coordinated supply management among resource-rich nations. Since implementing production quotas in the 1980s, OPEC has demonstrated both the potential and limitations of cartel-style market control.
OPEC production management experience reveals that successful supply management requires consistent member compliance, market share discipline, and the ability to respond quickly to demand fluctuations. Saudi Arabia's role as swing producer has been crucial, with the kingdom adjusting output to maintain target price ranges while other members focus on maximising individual revenues.
Key lessons from OPEC's evolution include the importance of maintaining spare capacity for market flexibility, the challenge of preventing free-rider behaviour among members, and the risk of encouraging consumer substitution through sustained high pricing.
China's Rare Earth Export Restrictions: A Cautionary Tale
Between 2010 and 2015, China implemented export quotas on rare earth elements, controlling over 95% of global supply. This period offers direct parallels to Congo's cobalt strategy, including the use of export licences, processing requirements, and strategic reserve allocations.
China's rare earth controls initially achieved significant price increases, with some elements rising 500-1000% during peak restriction periods. However, these gains proved temporary as consumers accelerated substitution research, alternative suppliers ramped production, and recycling technologies improved dramatically.
The World Trade Organization's 2014 ruling against China's export restrictions ultimately forced policy changes, demonstrating the international legal constraints on resource nationalism strategies. This precedent suggests that Congo's cobalt controls may face similar challenges if they create significant consumer market disruptions.
Indonesia's Nickel Processing Requirements: A Successful Model
Indonesia's 2020 ban on unprocessed nickel ore exports provides perhaps the most relevant comparison for Congo's approach. By requiring domestic processing before export, Indonesia successfully developed downstream manufacturing capacity while maintaining control over raw material supply.
The Indonesian model achieved remarkable results within four years:
- Raw nickel ore exports fell from 50 million tonnes (2018) to near-zero by 2022
- Refined nickel production capacity increased 300%
- Indonesia became the world's largest nickel processing hub
- Major international investment flowed into domestic smelting facilities
This success demonstrates that supply-side market interventions can achieve long-term structural changes when combined with clear processing requirements and consistent policy implementation.
Supply Chain Disruption Analysis and Timeline Implications
Chinese Processing Bottlenecks and Inventory Depletion
Congo's export controls have created immediate pressure on Chinese cobalt processing facilities, which handle the majority of global hydroxide-to-sulfate conversion. The 3-4 month shipping timeline from DRC to Chinese ports means that supply disruptions compound over time, creating increasingly severe inventory constraints.
Chinese imports of cobalt intermediaries declined sharply following the February 2025 export suspension. Volumes totalling 50,000 metric tonnes across June through September represent a significant reduction from historical monthly throughput levels that previously exceeded this four-month aggregate.
Current projections suggest that even immediate export resumption would not restore normal supply flows until late Q1 2026, given the extended shipping and customs clearance timelines. This delay creates a critical vulnerability window for battery manufacturers dependent on steady cobalt sulfate availability.
| Supply Chain Phase | Pre-Control Period | Current Status | Projected Recovery |
|---|---|---|---|
| Monthly DRC Exports | 15,000+ tonnes | 0 tonnes (since Feb 2025) | 8,050 tonnes (quota system) |
| Chinese Processing Utilisation | 85% capacity | 45% capacity | 65% capacity |
| Inventory Buffer Period | 4-6 months | 2-3 months | 1-2 months |
Alternative Supply Source Development Potential
The Congo supply constraints have accelerated development timelines for alternative cobalt sources, though most projects require 3-5 years to reach meaningful production levels. Australian cobalt operations offer the most immediate expansion potential, with existing facilities capable of increasing output by 20-30% within 12-18 months.
Canadian cobalt projects, primarily located in Ontario and Quebec, could contribute additional supply by 2027-2028 if development accelerates. However, these sources face environmental permitting challenges and higher production costs compared to Congolese operations. Consequently, mining investment strategies increasingly focus on diversification away from single-source dependencies.
Recycling capacity expansion presents another pathway for reducing dependence on primary cobalt supply. Current recycling operations handle approximately 15% of total cobalt consumption, but technological improvements and higher scrap prices could increase this proportion to 25-30% over the next five years.
Processing Technology and Reverse-Smelting Constraints
Limited reverse-smelting capacity represents a critical bottleneck in the cobalt supply chain. Converting cobalt metal to sulfate requires specialised equipment and environmental permits that restrict processing flexibility.
According to industry analysis, fewer than five Chinese facilities possess the necessary environmental authorisation for reverse-smelting operations. This constraint prevents easy substitution between different cobalt forms and amplifies the impact of hydroxide supply disruptions.
The economic viability of reverse-smelting depends on price differentials between metal and sulfate forms, with processing costs requiring spreads of $3-5 per pound to justify the conversion. Current market conditions support this economics, but environmental regulations limit operational expansion.
Battery Chemistry Evolution and Cobalt Demand Resilience
Lithium Iron Phosphate Market Share Expansion
The electric vehicle battery market continues shifting toward lithium iron phosphate (LFP) chemistry, which eliminates cobalt requirements entirely. Macquarie Bank projects LFP market share will increase from 48% in 2024 to 65% in 2029, accelerating the timeline for cobalt-free battery adoption.
This transition reflects multiple factors beyond supply chain concerns:
- LFP batteries cost 20-25% less than nickel-cobalt-manganese alternatives
- Safety performance advantages reduce thermal runaway risks
- Energy density improvements have narrowed the performance gap
- Manufacturing scaling has improved production consistency
Chinese EV manufacturers like CATL have led LFP adoption, demonstrating that cobalt-free chemistry can meet consumer performance expectations while reducing battery costs. This trend creates structural demand headwinds for cobalt beyond short-term supply constraints. Furthermore, this evolution demonstrates how mining industry evolution responds to technological advances and supply chain risks.
Cobalt Intensity Reduction in Next-Generation Technologies
Even batteries that retain cobalt content continue reducing metal intensity through chemistry optimisation. The average cobalt deployment in new passenger vehicles declined 6% year-over-year, reaching 2.2 kilograms per vehicle in September 2025.
Nickel-rich cathode development enables cobalt ratios to fall below 5% in many applications while maintaining energy density and cycle life performance. This optimisation reflects both supply chain risk management and cost reduction objectives across the automotive industry.
"Battery manufacturers have successfully reduced cobalt content per kilowatt-hour by 40% since 2020 while improving overall performance metrics through advanced chemistry and manufacturing optimisation."
Solid-state battery technology development could further reduce cobalt dependence over the next decade. Leading automotive companies and battery manufacturers have committed significant research investments to solid-state systems that promise higher energy density with simplified chemistry requirements.
Demand Growth Versus Intensity Reduction Dynamics
Despite declining cobalt intensity per vehicle, absolute demand growth continues due to expanding electric vehicle adoption globally. EV battery cobalt consumption increased 2,300 tonnes in 2024, with portable electronics adding another 2,700 tonnes to total demand.
Projections suggest EV battery demand will grow 6,800 tonnes in 2025, driven primarily by Western market adoption of electric and hybrid vehicles. This growth offsets intensity reductions in the near term, though the trajectory favours declining unit consumption over time.
The timing of Congo's cobalt export controls may prove problematic for sustaining long-term cobalt demand. Accelerated chemistry substitution, combined with alternative supply development, could reduce the DRC's market leverage faster than anticipated when the quota system was designed. However, congo cobalt export control implementation continues despite these technological headwinds.
Geopolitical Implications and Strategic Mineral Security
China-Africa Resource Partnership Dynamics
Congo's cobalt export controls operate within the broader context of deepening China-Africa resource partnerships. Chinese companies have invested heavily in Congolese mining infrastructure over the past decade, creating economic ties that influence policy implementation and enforcement decisions.
The Belt and Road Initiative framework provides institutional support for Chinese resource investments across Africa, including financing for processing facilities that align with Congo's value-addition objectives. This relationship creates mutual incentives for managing export controls in ways that benefit both Chinese industry and Congolese development goals.
However, export quotas also create tension with Chinese manufacturers accustomed to reliable supply access. Balancing these competing interests requires careful diplomatic coordination alongside the technical implementation of quota systems.
Western Supply Chain Diversification Imperatives
European Union and United States critical mineral security strategies explicitly prioritise supply chain diversification away from single-source dependencies. Congo's export controls validate these concerns and accelerate alternative sourcing initiatives.
The U.S. Defense Production Act and EU Critical Raw Materials Act provide policy frameworks for supporting non-Chinese, non-Congolese cobalt development through loan guarantees, tax incentives, and strategic stockpile purchases. These programmes could reduce Congo's long-term market leverage by underwriting higher-cost alternative supplies.
Bilateral agreements between Western nations and alternative suppliers (Australia, Canada, Chile) aim to create secure supply chains that bypass potential disruption sources. While these arrangements cannot immediately replace Congolese supply volumes, they establish frameworks for gradual substitution over 5-10 year horizons.
Artisanal Mining Formalisation and Compliance Standards
General Cobalt Company's exclusive rights to export artisanal cobalt create additional complexity in Congo's supply management system. Integrating small-scale miners into formal export channels requires extensive coordination between cooperative structures, compliance monitoring, and international certification systems.
Child labour concerns and human rights compliance standards add regulatory layers that affect export licensing decisions. International buyers increasingly require detailed traceability documentation that proves ethical sourcing standards, creating administrative burdens that can delay shipment approvals.
The intersection of export quotas with artisanal mining formalisation means that supply management must balance volume targets with social compliance objectives. This dual mandate complicates implementation timelines and creates additional points of potential disruption.
Investment Scenarios and Market Psychology
Cobalt Price Volatility and Trading Opportunities
Congo's export controls have generated significant price volatility that creates both opportunities and risks for commodity investors. CME spot cobalt prices increased from $10 to $26 per pound between February and December 2025, while cobalt hydroxide surged from $6 to $23 per pound over the same period.
This 160-280% price appreciation reflects both physical supply constraints and speculative positioning by hedge funds and commodity trading firms. The combination of genuine supply shortages with financial market speculation amplifies price movements beyond levels justified by fundamental supply-demand imbalances.
Volatility creates opportunities for sophisticated investors with proper risk management systems, but it also reinforces automotive industry concerns about cobalt price stability. This paradox means that short-term trading profits may undermine long-term demand growth by accelerating substitution efforts.
Downstream Processing Investment Acceleration
Local value-addition requirements drive foreign direct investment into Congolese processing facilities, though implementation timelines remain extended. Major international mining companies have announced plans for hydroxide processing plants, precursor manufacturing, and battery component assembly operations.
These investments face significant infrastructure challenges:
- Limited electrical grid capacity for energy-intensive processing
- Transportation constraints for importing specialised equipment
- Skilled workforce development requirements for technical operations
- Political risk considerations for long-term capital commitments
Technology transfer agreements accompanying FDI commitments create opportunities for domestic capability development, though realising these benefits requires sustained implementation over multiple years. In particular, the cobalt expansion project developments demonstrate how alternative supply sources respond to market disruptions.
Strategic Inventory Management and Hedging Approaches
Battery manufacturers and automotive companies have responded to supply uncertainty by increasing strategic inventory levels and implementing sophisticated hedging strategies. Physical stockpiling provides supply security but ties up working capital and creates storage cost burdens.
Financial hedging through futures contracts and supply agreements helps manage price risk but requires careful coordination with production planning cycles. The limited liquidity in cobalt derivatives markets constrains hedging effectiveness for larger consumers.
Vertical integration strategies, including direct investment in mining operations and processing facilities, offer long-term supply security but require substantial capital commitments and operational expertise outside core automotive competencies.
Long-Term Sustainability and Market Adaptation Scenarios
Enforcement Challenges and Governance Vulnerabilities
Congo's quota system faces inherent enforcement challenges that could undermine long-term effectiveness. Monthly allocation decisions create opportunities for preferential treatment, rent-seeking behaviour, and corruption that could distort intended market management objectives.
Transparency concerns around quota distribution criteria and approval processes may generate international criticism and legal challenges similar to those faced by China's rare earth export restrictions. Establishing clear, predictable allocation mechanisms becomes crucial for maintaining system legitimacy.
Border control effectiveness and smuggling prevention require substantial investment in customs infrastructure and monitoring systems. Without robust enforcement, quota systems can create incentives for unofficial export channels that undermine government revenue objectives. Moreover, reports suggest that quota implementation may exacerbate existing governance challenges.
Market Adaptation Timeline and Substitution Acceleration
Consumer market adaptation to sustained cobalt supply constraints will likely accelerate substitution timelines beyond current projections. Automotive manufacturers face strong incentives to reduce cobalt dependence through chemistry optimisation and alternative battery technologies.
The critical timeframe for Congo's market leverage appears to be 2025-2027, coinciding with the announced quota system duration. Beyond this period, alternative supply sources and substitution technologies may reduce the DRC's ability to maintain premium pricing through supply restrictions.
Investment flows into alternative cobalt sources have already accelerated in response to supply uncertainty. Australian, Canadian, and recycling capacity expansion projects could collectively add 40,000-50,000 tonnes of annual production capacity by 2028-2029.
| Scenario | Probability | Price Impact (2026-2028) | Congo Market Share | Alternative Supply Response |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sustained Quota System | 60% | +40-60% vs 2024 levels | 55-60% | Moderate acceleration |
| Gradual Quota Relaxation | 25% | +15-25% vs 2024 levels | 60-65% | Limited acceleration |
| System Abandonment | 15% | -20-30% vs current levels | 70%+ | Delayed investment |
Strategic Response Options for Market Participants
Automaker Supply Chain Diversification Strategies
Automotive manufacturers face immediate pressure to develop cobalt supply chain alternatives while managing current production requirements. Long-term offtake agreements with non-DRC producers provide supply security but often require price premiums and minimum volume commitments.
Vertical integration approaches, including direct investment in mining operations and processing facilities, offer greater supply control but require substantial capital allocation and operational expertise development. Companies like Tesla and Ford have announced strategic partnerships with mining companies to secure dedicated supply streams.
Accelerated battery chemistry transition investments focus on reducing cobalt intensity through nickel-rich cathodes and LFP adoption. These technological approaches address supply risk while potentially reducing battery costs and improving performance characteristics.
Mining Company Positioning and Expansion Opportunities
Non-DRC cobalt producers benefit from sustained premium pricing but face pressure to accelerate expansion timelines to capture market share. Australian companies like Jervois Global and Canadian developers like First Cobalt have expedited development schedules in response to market opportunities.
Technology partnerships for cobalt-free battery development create opportunities for mining companies to participate in substitution trends rather than resist them. Strategic investments in nickel, lithium, and manganese projects position companies for chemistry transitions while maintaining exposure to battery metal demand growth.
Strategic inventory management and price hedging approaches help mining companies optimise revenue capture during volatile pricing periods while managing operational cash flow requirements and capital allocation decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions About Congo's Cobalt Export Controls
When Will Normal Cobalt Exports Resume?
ARECOMS approval processes remain under development as of December 2025, with the regulatory authority working to establish consistent monthly allocation mechanisms. Current expectations suggest partial export resumption during Q1 2026, though volumes will remain significantly below historical levels.
The quota system design envisions exports at approximately half of previous shipping volumes, meaning normal export levels may not resume until after the current system expires in 2027. Monthly allocation criteria focus on compliance with local processing requirements and strategic reserve contributions.
How Will This Affect Electric Vehicle Prices?
Battery cost impacts will likely transmit to vehicle pricing with a 6-12 month lag, depending on existing inventory levels and supply contract terms. Automaker margin compression may initially absorb some cost increases, particularly for high-volume models where price sensitivity is greatest.
Regional market variations in pricing effects reflect different supply chain structures and competitive dynamics. European and North American markets may experience greater price pressure due to limited alternative sourcing options compared to Asian markets with established recycling infrastructure.
What Are the Long-Term Implications for Cobalt Markets?
Structural demand changes appear more significant than temporary supply constraints, with battery chemistry evolution creating permanent reductions in cobalt intensity per vehicle. Technology substitution acceleration may reduce total cobalt demand growth below current projections within 3-5 years.
Alternative supply source development timelines suggest meaningful capacity additions by 2027-2029, coinciding with the end of Congo's announced quota period. This timing may limit the DRC's ability to extend export controls without risking significant market share losses.
Disclaimer: This analysis contains forward-looking statements based on current market conditions and publicly available information. Commodity markets involve significant risks, and past performance does not guarantee future results. Readers should consult qualified financial advisors before making investment decisions.
Looking to Capitalise on Critical Mineral Supply Disruptions?
Discovery Alert's proprietary Discovery IQ model delivers real-time alerts on significant ASX mineral discoveries, helping investors identify actionable opportunities in cobalt, lithium, and other critical minerals ahead of broader market recognition. Begin your 30-day free trial today to gain an immediate trading advantage during these volatile commodity markets.