Strategic Intelligence from Canada's Mining Social Acceptability Framework
Complex stakeholder dynamics now determine project viability across global jurisdictions, with Canadians back critical minerals push emerging as a significant factor in resource development. Furthermore, public sentiment serves as a critical risk factor for capital allocation and operational sustainability. The emergence of systematic social acceptability measurement represents a fundamental shift in how resource development projects approach community engagement and permitting frameworks.
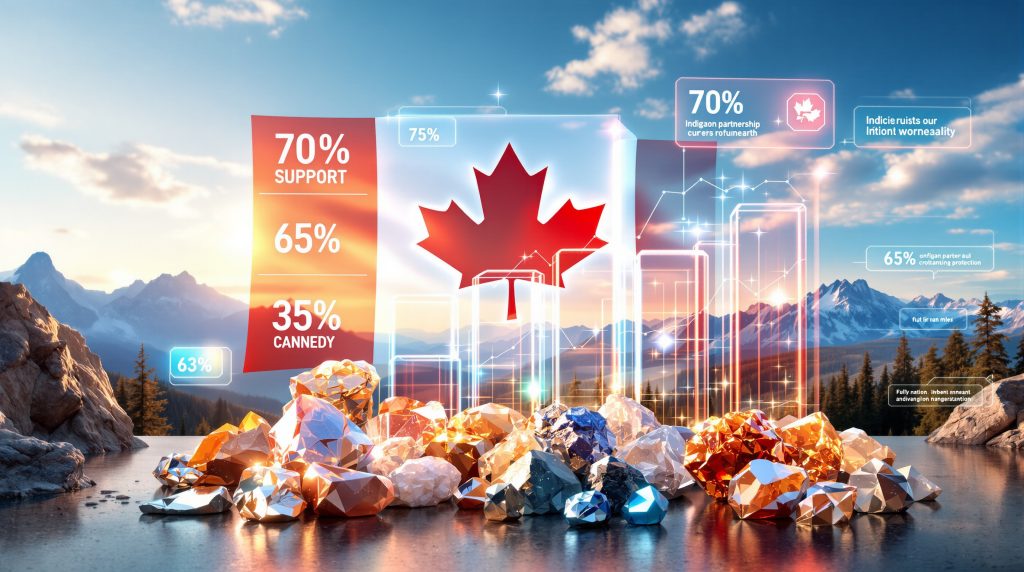
Comprehensive analysis of public attitudes toward critical minerals development across Canada reveals sophisticated stakeholder perspectives that challenge conventional mining industry assumptions. The inaugural Social Acceptability Barometer, encompassing responses from 4,800 participants across all provincial and territorial jurisdictions, establishes baseline metrics for understanding how Canadians navigate the intersection between economic development imperatives and environmental protection demands.
Research methodology incorporated geographic distribution analysis, demographic stratification, and sector-specific questioning to generate statistically robust insights. The survey framework addressed multiple dimensions of public perception, including regulatory confidence, consultation adequacy, environmental protection expectations, and Indigenous participation effectiveness. This multifaceted approach enables identification of specific factors driving social licence maintenance versus erosion across different regional contexts.
National Support Metrics for Critical Minerals Development
National Support Metrics for Critical Minerals Development
| Support Category | Percentage | Regional Variations |
|---|---|---|
| Critical minerals essential for energy transition | 70% | Consistent across provinces |
| Domestic production preference over imports | 70% | Higher in resource-dependent regions |
| Gold mining support (national level) | 65% | Variable by proximity to operations |
| Mining company confidence (5-point scale) | 2.76 | Below-average trust levels |
| Overall sector acceptability score | 3.48 | Moderate acceptance with conditions |
The data reveals that public support operates within conditional frameworks rather than representing unconditional endorsement of mining expansion. Canadians back critical minerals push whilst demonstrating nuanced understanding of critical minerals' role in clean energy infrastructure whilst maintaining scepticism about industry motivations and environmental commitments. This sophisticated public stance creates both opportunities for responsible developers and significant risks for companies failing to meet evolving social expectations.
Environmental concern prevalence shows 70% of respondents believing mining contributes to climate change, whilst approximately 50% express specific concerns about water quality and site restoration. The simultaneous support for critical minerals development and acknowledgement of environmental impacts indicates public acceptance of mining only within frameworks demonstrating net environmental benefit through clean energy transition facilitation.
What drives domestic production preferences?
Canadian preference for domestic critical minerals production reflects strategic understanding of global supply chain vulnerabilities rather than simple economic nationalism. The 70% domestic production preference correlates directly with public recognition that international supply concentration, particularly China's dominance in rare earth element processing at approximately 70% of global capacity, creates national security and economic stability risks.
Supply chain analysis reveals that global lithium production concentrates in the "lithium triangle" comprising Argentina, Bolivia, and Chile, plus Australia, with these jurisdictions accounting for approximately 98% of global production. However, the critical minerals energy security discussion has highlighted the need for greater supply chain resilience.
The proliferation of North American battery manufacturing facilities creates demand for domestically-proximate critical minerals processing capabilities. Federal government commitment of C$2 billion over five years to the Critical Minerals Sovereign Fund, announced in the November 4, 2025 Budget, represents policy alignment with public preference for supply chain localisation and strategic autonomy in critical materials sourcing.
Economic security drivers underlying domestic production support include:
• Supply chain resilience enhancement through reduced dependence on geographically concentrated suppliers
• Strategic autonomy development in critical materials sourcing for national security considerations
• Value-added processing opportunities prioritising domestic beneficiation over raw material exports
• Employment creation in regional development contexts, particularly in resource-dependent communities
• Clean energy transition reliability through domestic control of essential input materials
Environmental Protection Conditions and Regulatory Expectations
Public environmental demands constitute binding conditions for social licence maintenance rather than aspirational preferences. In addition, survey results indicate 67% dissatisfaction with current consultation opportunities, suggesting that perceived environmental inadequacy stems from procedural exclusion from decision-making processes rather than solely technical environmental concerns.
Water quality concerns represent primary environmental risks associated with mining operations, including acid mine drainage from sulfide mineral oxidation, heavy metal leaching involving copper, nickel, and zinc, tailings pond seepage and groundwater contamination, and groundwater depletion from extraction operations. The 50% of respondents expressing water quality concerns likely reference these established technical risks requiring comprehensive monitoring and protection protocols.
Regulatory confidence exhibits significant regional variation, with higher trust levels recorded in Saskatchewan and Newfoundland and Labrador compared to lower confidence in Quebec and Yukon territories. These disparities reflect differences in provincial permitting frameworks, enforcement consistency, and historical mining industry performance across jurisdictions.
Public Environmental Safeguard Priorities
• Biodiversity protection commitments requiring clear frameworks for ecosystem preservation and species habitat maintenance
• Water quality assurance protocols incorporating comprehensive monitoring systems and contamination prevention measures
• Site rehabilitation guarantees providing binding commitments for post-mining restoration and long-term environmental liability
• Climate impact mitigation strategies integrating mining operations with national emission reduction targets and clean energy transition objectives
The gap between environmental concern prevalence and mining company confidence suggests that industry credibility depends on demonstrated environmental performance rather than regulatory compliance minimums. Consequently, companies achieving social licence must exhibit transparency in environmental monitoring, proactive community engagement, and binding commitments to ecosystem restoration, including mining reclamation innovations.
How do Indigenous partnerships influence mining acceptance?
Indigenous respondents, particularly First Nations participants, demonstrate comparatively higher levels of trust and project acceptability compared to general population responses. This differential reflects the effectiveness of formal institutional arrangements, specifically Impact Benefit Agreements (IBAs), in translating abstract consultation principles into tangible decision-making authority and economic participation mechanisms.
The finding that 44% of the general population believes Indigenous peoples lack sufficient influence in mining decisions indicates widespread recognition that current consultation frameworks require enhancement to achieve meaningful Indigenous leadership in resource governance. Furthermore, this perspective suggests that non-Indigenous Canadians understand Indigenous rights as extending beyond consultation requirements to encompass substantive decision-making power.
Impact Benefit Agreements typically incorporate multiple governance and economic components:
• Revenue-sharing mechanisms providing percentage-based profit distributions or production-volume payments
• Employment and training provisions ensuring Indigenous workforce participation and capacity development
• Environmental protection commitments with Indigenous enforcement rights and monitoring authority
• Project governance participation through board representation or project veto authority
• Cultural heritage protection provisions integrating traditional knowledge and sacred site preservation
Canada's legal framework recognises Indigenous peoples' rights through Constitution Act, 1982, Section 35 protecting Aboriginal and treaty rights, and the United Nations Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples (UNDRIP), adopted into Canadian law through Bill C-15 in 2021. However, implementation gaps remain significant regarding how mining project approval processes integrate Indigenous governance authority versus consultation obligations.
Industry Transformation Requirements and Investment Implications
Mining company confidence averaging 2.76 out of 5.0 represents a critical challenge requiring comprehensive industry transformation toward greater transparency, environmental excellence, and genuine community partnership. The gap between sector acceptability (3.48) and company-specific confidence indicates that public support exists for mining development whilst trust in implementation institutions remains compromised.
Strategic development frameworks emerging from social acceptability analysis require integration of environmental performance, stakeholder engagement quality, and transparent governance mechanisms. For instance, success factors extend beyond geological and economic considerations to encompass social licence maintenance and stakeholder relationship management across project lifecycles, reflecting broader industry transformation trends.
Industry Transformation Priority Areas
• Transparency enhancement through public reporting on environmental performance metrics and community benefit distribution
• Stakeholder engagement reform moving beyond regulatory consultation minimums to genuine partnership arrangements
• Technology demonstration showcasing advanced environmental protection systems and real-time monitoring capabilities
• Community investment commitments providing long-term development support and capacity building beyond project duration
Investment strategy implications require evaluation of companies and projects based on social licence maintenance capabilities rather than solely geological endowments and market conditions. The only 33% of respondents feeling meaningful participation opportunities exist indicates that standard community consultation processes fail to generate social licence, requiring enhanced engagement frameworks for project viability.
Policy framework optimisation scenarios present three potential pathways: status quo maintenance with incremental regulatory improvements, accelerated reform involving comprehensive consultation process overhaul, or partnership innovation developing collaborative governance models based on Indigenous success stories. However, the survey results suggest public preference for accelerated reform or partnership innovation rather than incremental change, particularly given Canada's energy transition challenges.
What are the global context considerations?
Canada's social acceptability profile reflects international patterns where public support for mining increasingly depends on environmental performance demonstration, community engagement quality, and transparent governance mechanisms. The 70% support for critical minerals development positions Canada favourably compared to jurisdictions experiencing stronger opposition to resource development projects.
International benchmarking reveals varying acceptance levels based on economic dependency, environmental protection standards, and governance frameworks. Australia demonstrates similar critical minerals support levels with stronger emphasis on export revenue generation. Chile exhibits higher mining acceptance due to economic dependency whilst facing growing environmental concerns. European Union jurisdictions show lower mining acceptance with greater focus on recycling and material substitution strategies.
United States mining acceptance exhibits regional variation with stronger support in traditional mining states compared to jurisdictions without established mining economies. These international comparisons suggest that Canadian acceptance levels reflect favourable positioning for critical minerals development, conditional on environmental stewardship and community engagement excellence.
Strategic Development Framework and Future Pathways
Success in Canada's critical minerals sector requires comprehensive integration of geological, economic, environmental, and social factors rather than traditional focus on resource endowments and market conditions. Moreover, the survey results provide strategic guidance for companies and investors evaluating Canadian opportunities within evolving social licence requirements.
Comprehensive Development Strategy Components
• Pre-development phase incorporating extensive community engagement and environmental baseline establishment before formal project announcement
• Permitting strategy integrating Indigenous partnership models and enhanced consultation processes exceeding regulatory minimums
• Operational excellence featuring continuous environmental monitoring and transparent performance reporting to stakeholder communities
• Legacy planning including binding site restoration commitments and long-term community benefit provision beyond mine closure
The path forward requires industry transformation toward unprecedented transparency levels, environmental protection standards, and genuine community partnership arrangements. Companies failing to meet evolving social expectations face significant project viability risks regardless of geological quality or market conditions.
Social licence maintenance demands ongoing stakeholder relationship management rather than front-end consultation completion. Consequently, the survey findings suggest that public support remains conditional and requires continuous demonstration of environmental stewardship, community benefit delivery, and transparent governance practices throughout project lifecycles.
Canadians back critical minerals push implementation will depend not only on federal financial commitments but on industry capacity to earn and maintain social licence through demonstrated commitment to sustainable and inclusive development practices. The Social Acceptability Barometer provides baseline metrics for measuring progress toward enhanced stakeholder trust and community acceptance, as Canada continues to secure international partnerships for critical minerals development.
Disclaimer: This analysis is based on publicly available survey data and should not be considered as investment advice. Critical minerals development involves significant technical, environmental, regulatory, and market risks. Investors should conduct independent due diligence and consult qualified professionals before making investment decisions related to Canadian mining opportunities.
Ready to Capitalise on Critical Minerals Investment Opportunities?
Discovery Alert's proprietary Discovery IQ model delivers instant notifications on significant ASX mineral discoveries, empowering investors to identify actionable opportunities in the rapidly expanding critical minerals sector. With social acceptability frameworks now driving project viability across global jurisdictions, securing immediate alerts on breakthrough discoveries becomes essential for maintaining your competitive edge—begin your 30-day free trial today to position yourself ahead of the market.